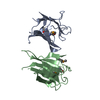
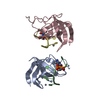
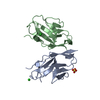
Entry Database : PDB / ID : 4u17Title Swapped dimer of the human Fyn-SH2 domain Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn Keywords / / Function / homology Function Domain/homology Component
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / Biological species Homo sapiens (human)Method / / / Resolution : 1.99 Å Authors Garcia-Pino, A. / Huculeci, R. / Lenaerts, T. / van Nuland, N.A.J. Journal : To Be Published Title : Swapped dimer of the human Fyn-SH2 domainAuthors : Garcia-Pino, A. / Huculeci, R. / Lenaerts, T. / van Nuland, N.A.J. History Deposition Jul 15, 2014 Deposition site / Processing site Revision 1.0 Jul 29, 2015 Provider / Type Revision 1.1 Dec 20, 2023 Group / Database references / Refinement descriptionCategory chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond ... chem_comp_atom / chem_comp_bond / database_2 / pdbx_initial_refinement_model Item / _database_2.pdbx_database_accession
Show all Show less
 Open data
Open data Basic information
Basic information Components
Components Keywords
Keywords Function and homology information
Function and homology information Homo sapiens (human)
Homo sapiens (human) X-RAY DIFFRACTION /
X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON /
SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.99 Å
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 1.99 Å  Authors
Authors Citation
Citation Journal: To Be Published
Journal: To Be Published Structure visualization
Structure visualization Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol Downloads & links
Downloads & links Download
Download 4u17.cif.gz
4u17.cif.gz PDBx/mmCIF format
PDBx/mmCIF format pdb4u17.ent.gz
pdb4u17.ent.gz PDB format
PDB format 4u17.json.gz
4u17.json.gz PDBx/mmJSON format
PDBx/mmJSON format Other downloads
Other downloads https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u1/4u17
https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u1/4u17 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u1/4u17
ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/u1/4u17
 Links
Links Assembly
Assembly

 Components
Components Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FYN / Production host:
Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: FYN / Production host: 
 X-RAY DIFFRACTION
X-RAY DIFFRACTION Sample preparation
Sample preparation SYNCHROTRON / Site:
SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SOLEIL
SOLEIL  / Beamline: PROXIMA 1 / Wavelength: 0.9801 Å
/ Beamline: PROXIMA 1 / Wavelength: 0.9801 Å Processing
Processing MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT
MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 PDBj
PDBj