[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3j41: Pseudo-atomic model of the Aquaporin-0/Calmodulin complex derived... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3j41 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Pseudo-atomic model of the Aquaporin-0/Calmodulin complex derived from electron microscopy | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | TRANSPORT PROTEIN/CALCIUM BINDING / calcium regulation / water channel / membrane protein complex / TRANSPORT PROTEIN-CALCIUM BINDING complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmaintenance of lens transparency / homotypic cell-cell adhesion / gap junction-mediated intercellular transport / cell adhesion mediator activity / water transport / water channel activity / : / : / : / : ...maintenance of lens transparency / homotypic cell-cell adhesion / gap junction-mediated intercellular transport / cell adhesion mediator activity / water transport / water channel activity / : / : / : / : / : / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / structural constituent of eye lens / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / : / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / lens development in camera-type eye / anchoring junction / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / positive regulation of DNA binding / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / response to corticosterone / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / PKA activation / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / nitric-oxide synthase binding / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / adenylate cyclase binding / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / Smooth Muscle Contraction / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / enzyme regulator activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / calcium channel inhibitor activity / presynaptic cytosol / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cellular response to interferon-beta / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / Protein methylation / Ion homeostasis / eNOS activation / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / titin binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / visual perception / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / sarcomere / response to amphetamine / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 25 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Reichow, S.L. / Clemens, D.M. / Freites, J.A. / Nemeth-Cahalan, K.L. / Heyden, M. / Tobias, D.J. / Hall, J.E. / Gonen, T. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2013 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2013Title: Allosteric mechanism of water-channel gating by Ca2+-calmodulin. Authors: Steve L Reichow / Daniel M Clemens / J Alfredo Freites / Karin L Németh-Cahalan / Matthias Heyden / Douglas J Tobias / James E Hall / Tamir Gonen /  Abstract: Calmodulin (CaM) is a universal regulatory protein that communicates the presence of calcium to its molecular targets and correspondingly modulates their function. This key signaling protein is ...Calmodulin (CaM) is a universal regulatory protein that communicates the presence of calcium to its molecular targets and correspondingly modulates their function. This key signaling protein is important for controlling the activity of hundreds of membrane channels and transporters. However, understanding of the structural mechanisms driving CaM regulation of full-length membrane proteins has remained elusive. In this study, we determined the pseudoatomic structure of full-length mammalian aquaporin-0 (AQP0, Bos taurus) in complex with CaM, using EM to elucidate how this signaling protein modulates water-channel function. Molecular dynamics and functional mutation studies reveal how CaM binding inhibits AQP0 water permeability by allosterically closing the cytoplasmic gate of AQP0. Our mechanistic model provides new insight, only possible in the context of the fully assembled channel, into how CaM regulates multimeric channels by facilitating cooperativity between adjacent subunits. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3j41.cif.gz 3j41.cif.gz | 231.7 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3j41.ent.gz pdb3j41.ent.gz | 182.8 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3j41.json.gz 3j41.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j41 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j41 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j41 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/j4/3j41 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5679MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
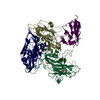
| Deposited unit | 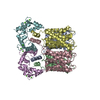
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 28244.865 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: SEE REMARK 999 / Source method: isolated from a natural source / Source: (natural)  #2: Protein | Mass: 16852.545 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human)Gene: CALM1, CALM, CAM, CAM1, CALM2, CAM2, CAMB, CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII Plasmid: pET / Production host:  #3: Chemical | ChemComp-CA / Sequence details | CHAINS A, B, C, AND D (AQUAPORIN) ARE FROM OVIS ARIES, BUT THE MODELED SEQUENCE IS FROM BOS TAURUS ...CHAINS A, B, C, AND D (AQUAPORIN) ARE FROM OVIS ARIES, BUT THE MODELED SEQUENCE IS FROM BOS TAURUS (UNP P06624). | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component |
| ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Value: 0.13 MDa / Experimental value: YES | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Buffer solution | Name: 25mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 5mM CaCl2, 0.3% decylmaltoside / pH: 7.4 / Details: 25mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 5mM CaCl2, 0.3% decylmaltoside | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.02 mg/ml / Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: YES / Vitrification applied: NO Details: 25mM HEPES, 5mM CaCl2, 0.3% decylmaltoside (Stain Details 0.75% Uranyl Formate) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| EM staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl Formate | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Specimen support | Details: 400 mesh carbon coated grid (Ted Pella) |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TECNAI 12 / Date: Feb 25, 2010 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source: LAB6 / Accelerating voltage: 120 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Electron beam tilt params: 0 |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 52000 X / Calibrated magnification: 52000 X / Nominal defocus max: 2000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 1000 nm / Cs: 2 mm Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 100,000 times magnification Camera length: 0 mm |
| Specimen holder | Specimen holder model: OTHER / Specimen holder type: FEI Single-Tilt / Tilt angle max: 50 ° / Tilt angle min: 0 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 15 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: KODAK SO-163 FILM |
| Image scans | Num. digital images: 200 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTF-TILT, each micrograph | |||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Point symmetry: C2 (2 fold cyclic) | |||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: Random Conical Tilt / Resolution: 25 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 11720 / Nominal pixel size: 3.98 Å / Actual pixel size: 3.98 Å / Magnification calibration: AQP0 cyrstal Details: Final Map with C2 Symmetry and Filtered to 25 Angstrom (Single particle details: Particles were selected from a tilted pair dataset at 0 and 50 degree tilt using SPIDER. An initial ...Details: Final Map with C2 Symmetry and Filtered to 25 Angstrom (Single particle details: Particles were selected from a tilted pair dataset at 0 and 50 degree tilt using SPIDER. An initial reconstruction was generated using random conical tilt methods in SPIDER and refined in FREALIGN.) (Single particle--Applied symmetry: C2) Symmetry type: POINT | |||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: cross-correlation Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--rigid body DETAILS--A complete model of AQP0-CaM was built by fitting 2B6P and 1NWD into the EM map in Chimera. Loops connecting the two structures were built using COOT ...Details: REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--rigid body DETAILS--A complete model of AQP0-CaM was built by fitting 2B6P and 1NWD into the EM map in Chimera. Loops connecting the two structures were built using COOT and the final model was energy minimized to remove steric clashes. The geometries of the modeled loops (AQP0 residues 222-227) were not refined due to lack of resolution in the experimental map. | |||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | 3D fitting-ID: 1 / Source name: PDB / Type: experimental model
| |||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera

 PDBj
PDBj























