+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3hbx | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Crystal structure of GAD1 from Arabidopsis thaliana | ||||||
 Components Components | Glutamate decarboxylase 1 | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LYASE / Calmodulin-binding / Decarboxylase / Pyridoxal phosphate | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglutamate decarboxylase / glutamate decarboxylase activity / glutamate metabolic process / pyridoxal phosphate binding / molecular adaptor activity / calmodulin binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.672 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.672 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Gut, H. / Dominici, P. / Pilati, S. / Gruetter, M.G. / Capitani, G. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2009 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2009Title: A common structural basis for pH- and calmodulin-mediated regulation in plant glutamate decarboxylase. Authors: Heinz Gut / Paola Dominici / Stefania Pilati / Alessandra Astegno / Maxim V Petoukhov / Dmitri I Svergun / Markus G Grütter / Guido Capitani /  Abstract: Glutamate decarboxylase (Gad) catalyzes glutamate to gamma-aminobutyrate conversion. Plant Gad is a approximately 340 kDa hexamer, involved in development and stress response, and regulated by pH and ...Glutamate decarboxylase (Gad) catalyzes glutamate to gamma-aminobutyrate conversion. Plant Gad is a approximately 340 kDa hexamer, involved in development and stress response, and regulated by pH and binding of Ca(2+)/calmodulin (CaM) to the C-terminal domain. We determined the crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana Gad1 in its CaM-free state, obtained a low-resolution structure of the calmodulin-activated Gad complex by small-angle X-ray scattering and identified the crucial residues, in the C-terminal domain, for regulation by pH and CaM binding. CaM activates Gad1 in a unique way by relieving two C-terminal autoinhibition domains of adjacent active sites, forming a 393 kDa Gad1-CaM complex with an unusual 1:3 stoichiometry. The complex is loosely packed: thanks to the flexible linkers connecting the enzyme core with the six C-terminal regulatory domains, the CaM molecules retain considerable positional and orientational freedom with respect to Gad1. The complex thus represents a prototype for a novel CaM-target interaction mode. Thanks to its two levels of regulation, both targeting the C-terminal domain, Gad can respond flexibly to different kinds of cellular stress occurring at different pH values. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
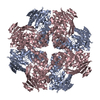
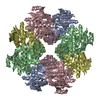
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3hbx.cif.gz 3hbx.cif.gz | 527.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3hbx.ent.gz pdb3hbx.ent.gz | 432.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3hbx.json.gz 3hbx.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/3hbx https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/3hbx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/3hbx ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/hb/3hbx | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1pmmS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
NCS domain segments:
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj