[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- SASDAQ4: 6:3 complex of GAD:CaM (Calmodulin + Glutamate decarboxylase, GAD) -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: SASBDB / ID: SASDAQ4 |
|---|---|
 Sample Sample | 6:3 complex of GAD:CaM
|
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationglutamate decarboxylase / glutamate decarboxylase activity / : / : / : / : / : / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / L-glutamate catabolic process / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation ...glutamate decarboxylase / glutamate decarboxylase activity / : / : / : / : / : / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / L-glutamate catabolic process / negative regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / : / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / positive regulation of peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation / positive regulation of DNA binding / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / response to corticosterone / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / nitric-oxide synthase binding / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / adenylate cyclase binding / positive regulation of protein serine/threonine kinase activity / protein phosphatase activator activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / enzyme regulator activity / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / response to amphetamine / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of cytokinesis / spindle microtubule / response to calcium ion / mitochondrial membrane / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / disordered domain specific binding / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding / pyridoxal phosphate binding / myelin sheath / synaptic vesicle membrane / growth cone / vesicle / transmembrane transporter binding / calmodulin binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / protein domain specific binding / calcium ion binding / centrosome / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function |
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) Petunia x hybrida (garden petunia) Petunia x hybrida (garden petunia) |
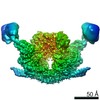
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2009 Journal: J Mol Biol / Year: 2009Title: A common structural basis for pH- and calmodulin-mediated regulation in plant glutamate decarboxylase. Authors: Heinz Gut / Paola Dominici / Stefania Pilati / Alessandra Astegno / Maxim V Petoukhov / Dmitri I Svergun / Markus G Grütter / Guido Capitani /  Abstract: Glutamate decarboxylase (Gad) catalyzes glutamate to gamma-aminobutyrate conversion. Plant Gad is a approximately 340 kDa hexamer, involved in development and stress response, and regulated by pH and ...Glutamate decarboxylase (Gad) catalyzes glutamate to gamma-aminobutyrate conversion. Plant Gad is a approximately 340 kDa hexamer, involved in development and stress response, and regulated by pH and binding of Ca(2+)/calmodulin (CaM) to the C-terminal domain. We determined the crystal structure of Arabidopsis thaliana Gad1 in its CaM-free state, obtained a low-resolution structure of the calmodulin-activated Gad complex by small-angle X-ray scattering and identified the crucial residues, in the C-terminal domain, for regulation by pH and CaM binding. CaM activates Gad1 in a unique way by relieving two C-terminal autoinhibition domains of adjacent active sites, forming a 393 kDa Gad1-CaM complex with an unusual 1:3 stoichiometry. The complex is loosely packed: thanks to the flexible linkers connecting the enzyme core with the six C-terminal regulatory domains, the CaM molecules retain considerable positional and orientational freedom with respect to Gad1. The complex thus represents a prototype for a novel CaM-target interaction mode. Thanks to its two levels of regulation, both targeting the C-terminal domain, Gad can respond flexibly to different kinds of cellular stress occurring at different pH values. |
 Contact author Contact author |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-Data source
| SASBDB page |  SASDAQ4 SASDAQ4 |
|---|
-Related structure data
- External links
External links
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
|---|
-Models
| Model #67 |  Type: mix / Software: Bunch / Radius of dummy atoms: 1.90 A / Symmetry: P6/P1  Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) Search similar-shape structures of this assembly by Omokage search (details) |
|---|
- Sample
Sample
 Sample Sample | Name: 6:3 complex of GAD:CaM / Sample MW: 357.22 kDa / Entity id: 58 / 61 |
|---|---|
| Buffer | Name: HEPES / Concentration: 50.00 mM / PK: 7 / pH: 7.5 / Comment: 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid / Composition: KCl 50.000 mM |
| Entity #58 | Type: protein / Description: Calmodulin / Formula weight: 16.84 / Num. of mol.: 1 / Source: Homo sapiens / References: UniProt: P62158 Sequence: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREAF RVFDKDGNGY ISAAELRHVM TNLGEKLTDE EVDEMIREAD IDGDGQVNYE EFVQMMTAK |
| Entity #61 | Name: GAD / Type: protein / Description: Glutamate decarboxylase / Formula weight: 56.73 / Num. of mol.: 6 / Source: Petunia x hybrida / References: UniProt: Q07346 Sequence: MVLSKTVSQS DVSIHSTFAS RYVRTSLPRF KMPDNSIPKE AAYQIINDEL MLDGNPRLNL ASFVTTWMEP ECDKLMMDSI NKNYVDMDEY PVTTELQNRC VNMIAHLFNA PLEDGETAVG VGTVGSSEAI MLAGLAFKRK WQNKMKAQGK PCDKPNIVTG ANVQVCWEKF ...Sequence: MVLSKTVSQS DVSIHSTFAS RYVRTSLPRF KMPDNSIPKE AAYQIINDEL MLDGNPRLNL ASFVTTWMEP ECDKLMMDSI NKNYVDMDEY PVTTELQNRC VNMIAHLFNA PLEDGETAVG VGTVGSSEAI MLAGLAFKRK WQNKMKAQGK PCDKPNIVTG ANVQVCWEKF ARYFEVELKE VKLSEGYYVM DPEKAVEMVD ENTICVAAIL GSTLNGEFED VKRLNDLLVE KNKETGWDTP IHVDAASGGF IAPFIYPELE WDFRLPLVKS INVSGHKYGL VYAGIGWVVW RNKDDLPDEL IFHINYLGAD QPTFTLNFSK GSSQVIAQYY QLIRLGYEGY KNVMENCQEN ASVLREGLEK TGRFNIISKE IGVPLVAFSL KDNRQHNEFE ISETLRRFGW IVPAYTMPPN AQHITVLRVV IREDFSRTLA ERLVRDIEKV LHELDTLPAR VNAKLAVAEE QAAANGSEVH KKTDSEVQLE MITAWKKFVE EKKKKTNRVC |
-Experimental information
| Beam | Instrument name:  DORIS III X33 DORIS III X33  / City: Hamburg / 国: Germany / City: Hamburg / 国: Germany  / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron / Type of source: X-ray synchrotron | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detector | Name: MAR 345 Image Plate | ||||||||||||||||||
| Scan |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Distance distribution function P(R) |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Result |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller