[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- PDB-3err: Microtubule binding domain from mouse cytoplasmic dynein as a fus... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 3err | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
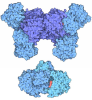
| Title | Microtubule binding domain from mouse cytoplasmic dynein as a fusion with seryl-tRNA synthetase | ||||||
 Components Components | fusion protein of microtubule binding domain from mouse cytoplasmic dynein and seryl-tRNA synthetase from Thermus thermophilus | ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | LIGASE / dynein / microtubule binding domain / coiled coil / fusion protein | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationCOPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / L-selenocysteine biosynthetic process / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / serine binding / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity / seryl-tRNA aminoacylation ...COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / L-selenocysteine biosynthetic process / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / serine binding / Amplification of signal from unattached kinetochores via a MAD2 inhibitory signal / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Aggrephagy / serine-tRNA ligase / serine-tRNA ligase activity / seryl-tRNA aminoacylation / Mitotic Prometaphase / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / cilium movement / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / positive regulation of intracellular transport / regulation of metaphase plate congression / MHC class II antigen presentation / positive regulation of spindle assembly / establishment of spindle localization / dynein complex / P-body assembly / minus-end-directed microtubule motor activity / dynein light intermediate chain binding / cytoplasmic dynein complex / dynein intermediate chain binding / Neutrophil degranulation / stress granule assembly / regulation of mitotic spindle organization / filopodium / positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis / microtubule / tRNA binding / cell division / centrosome / protein homodimerization activity / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.27 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.27 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Carter, A.P. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2008 Journal: Science / Year: 2008Title: Structure and functional role of dynein's microtubule-binding domain. Authors: Andrew P Carter / Joan E Garbarino / Elizabeth M Wilson-Kubalek / Wesley E Shipley / Carol Cho / Ronald A Milligan / Ronald D Vale / I R Gibbons /  Abstract: Dynein motors move various cargos along microtubules within the cytoplasm and power the beating of cilia and flagella. An unusual feature of dynein is that its microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) is ...Dynein motors move various cargos along microtubules within the cytoplasm and power the beating of cilia and flagella. An unusual feature of dynein is that its microtubule-binding domain (MTBD) is separated from its ring-shaped AAA+ adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) domain by a 15-nanometer coiled-coil stalk. We report the crystal structure of the mouse cytoplasmic dynein MTBD and a portion of the coiled coil, which supports a mechanism by which the ATPase domain and MTBD may communicate through a shift in the heptad registry of the coiled coil. Surprisingly, functional data suggest that the MTBD, and not the ATPase domain, is the main determinant of the direction of dynein motility. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  3err.cif.gz 3err.cif.gz | 436.4 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb3err.ent.gz pdb3err.ent.gz | 358.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  3err.json.gz 3err.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/er/3err https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/er/3err ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/er/3err ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/er/3err | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1581C  1sryS S: Starting model for refinement C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 60957.734 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Mutation: C3323A, C3387A Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Details: The coiled coil stalk of cytoplasmic dynein was fused onto the base coiled coil from seryl tRNA synthetase Source: (gene. exp.)    Thermus thermophilus (bacteria) Thermus thermophilus (bacteria)Production host:  #2: Chemical | #3: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.63 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 53.21 % |
|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 300 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop Details: Protein was changed into crystallization buffer (20mM K-HEPES, pH7.5, 10% w/v glycerol, 0.2mM PMSF, 1mM DTT, 4mM Mg-ATP, 0.01% Na-Azide) and concentrated to 18 mg/ml. Crystallization was ...Details: Protein was changed into crystallization buffer (20mM K-HEPES, pH7.5, 10% w/v glycerol, 0.2mM PMSF, 1mM DTT, 4mM Mg-ATP, 0.01% Na-Azide) and concentrated to 18 mg/ml. Crystallization was carried out by setting hanging drops containing 2 ul of protein, (diluted to 13.5mg/ml with 20mM K-Hepes, pH 7.5, 10% glycerol), 0.3 ul 70% glycerol and 1.8 ul of precipitant (20% PEG 4000, 200mM Ammonium sulfate, 100mM Bis-Tris, pH 5.5) over 500ml of the same precipitant solution. Crystals appeared within one day and were of dimensions up to 200 um., VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 300K |
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 77 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  ALS ALS  / Beamline: 8.3.1 / Wavelength: 1.5 Å / Beamline: 8.3.1 / Wavelength: 1.5 Å |
| Detector | Type: ADSC QUANTUM 315 / Detector: CCD / Date: Apr 12, 2008 |
| Radiation | Monochromator: Double flat crystal, Si(111) / Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.5 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.27→49.27 Å / Num. all: 57296 / Num. obs: 57296 / % possible obs: 99.4 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 2 / Observed criterion σ(I): 2 / Redundancy: 5.6 % / Net I/σ(I): 18.6 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.27→2.35 Å / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2 / Rsym value: 62 / % possible all: 94.5 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: pdb entry 1SRY Resolution: 2.27→49.27 Å / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc: 0.959 / Cor.coef. Fo:Fc free: 0.938 / SU B: 15.276 / SU ML: 0.184 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 2 / ESU R: 0.299 / ESU R Free: 0.227 / Stereochemistry target values: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD / Details: HYDROGENS HAVE BEEN ADDED IN THE RIDING POSITIONS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Ion probe radii: 0.8 Å / Shrinkage radii: 0.8 Å / VDW probe radii: 1.2 Å / Solvent model: MASK | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 55.202 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.27→49.27 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.27→2.326 Å / Total num. of bins used: 20
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS params. | Method: refined / Refine-ID: X-RAY DIFFRACTION
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement TLS group |
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 PDBj
PDBj