+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 2dfs | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
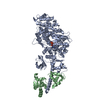
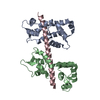
| Title | 3-D structure of Myosin-V inhibited state | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | CONTRACTILE PROTEIN/TRANSPORT PROTEIN / myosin-V / inhibited state / calmodulin / cryoelectron tomography / CONTRACTILE PROTEIN-TRANSPORT PROTEIN COMPLEX | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Cam-PDE 1 activation / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation ...negative regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transporter activity / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / Cam-PDE 1 activation / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / Calmodulin induced events / Inactivation, recovery and regulation of the phototransduction cascade / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / eNOS activation / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Protein methylation / RAF activation / minus-end directed microfilament motor activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / RAS processing / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / Ca2+ pathway / insulin-responsive compartment / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / Extra-nuclear estrogen signaling / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / PKA activation / regulation of response to tumor cell / positive regulation of autophagic cell death / DAPK1-calmodulin complex / RAF/MAP kinase cascade / Smooth Muscle Contraction / : / : / : / : / Platelet degranulation / : / High laminar flow shear stress activates signaling by PIEZO1 and PECAM1:CDH5:KDR in endothelial cells / Stimuli-sensing channels / : / Ion homeostasis / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / myosin complex / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / microfilament motor activity / response to corticosterone / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / nitric-oxide synthase binding / presynaptic endocytosis / filamentous actin / calcineurin-mediated signaling / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / adenylate cyclase binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / postsynaptic cytosol / catalytic complex / enzyme regulator activity / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / activation of adenylate cyclase activity / positive regulation of nitric-oxide synthase activity / calcium channel inhibitor activity / presynaptic cytosol / cellular response to interferon-beta / vesicle-mediated transport / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / regulation of heart rate / actin filament organization / calyx of Held / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / sarcomere / response to amphetamine / regulation of cytokinesis / protein localization to plasma membrane / spindle microtubule / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / calcium-mediated signaling / response to calcium ion / cellular response to type II interferon / mitochondrial membrane / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |   | ||||||
| Method | ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY / electron tomography / Resolution: 24 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Liu, J. / Taylor, D.W. / Krementsova, E.B. / Trybus, K.M. / Taylor, K.A. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2006 Journal: Nature / Year: 2006Title: Three-dimensional structure of the myosin V inhibited state by cryoelectron tomography. Authors: Jun Liu / Dianne W Taylor / Elena B Krementsova / Kathleen M Trybus / Kenneth A Taylor /  Abstract: Unconventional myosin V (myoV) is an actin-based molecular motor that has a key function in organelle and mRNA transport, as well as in membrane trafficking. MyoV was the first member of the myosin ...Unconventional myosin V (myoV) is an actin-based molecular motor that has a key function in organelle and mRNA transport, as well as in membrane trafficking. MyoV was the first member of the myosin superfamily shown to be processive, meaning that a single motor protein can 'walk' hand-over-hand along an actin filament for many steps before detaching. Full-length myoV has a low actin-activated MgATPase activity at low [Ca2+], whereas expressed constructs lacking the cargo-binding domain have a high activity regardless of [Ca2+] (refs 5-7). Hydrodynamic data and electron micrographs indicate that the active state is extended, whereas the inactive state is compact. Here we show the first three-dimensional structure of the myoV inactive state. Each myoV molecule consists of two heads that contain an amino-terminal motor domain followed by a lever arm that binds six calmodulins. The heads are followed by a coiled-coil dimerization domain (S2) and a carboxy-terminal globular cargo-binding domain. In the inactive structure, bending of myoV at the head-S2 junction places the cargo-binding domain near the motor domain's ATP-binding pocket, indicating that ATPase inhibition might occur through decreased rates of nucleotide exchange. The actin-binding interfaces are unobstructed, and the lever arm is oriented in a position typical of strong actin-binding states. This structure indicates that motor recycling after cargo delivery might occur through transport on actively treadmilling actin filaments rather than by diffusion. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  2dfs.cif.gz 2dfs.cif.gz | 642.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb2dfs.ent.gz pdb2dfs.ent.gz | 504.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  2dfs.json.gz 2dfs.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/2dfs https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/2dfs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/2dfs ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/df/2dfs | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1201MC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 126415.695 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: residues 1-1080 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 16721.350 Da / Num. of mol.: 12 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON CRYSTALLOGRAPHY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: TISSUE / 3D reconstruction method: electron tomography |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: Myosin-V / Type: TISSUE / Details: myosin-V inhibited state |
|---|---|
| Buffer solution | Name: 20mM Na2HPO4, 80-100mM NaCl, 2mM MgCl2, 1mM ADP, 1mM EGTA, 8-9% PEG 8000 Details: 20mM Na2HPO4, 80-100mM NaCl, 2mM MgCl2, 1mM ADP, 1mM EGTA, 8-9% PEG 8000 |
| Specimen | Conc.: 0.2 mg/ml / Embedding applied: YES / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: NO |
| Specimen support | Details: 200 mesh copper grids covered with a reticulated carbon film |
| Vitrification | Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER / Cryogen name: ETHANE / Details: liquid ethane |
-Data collection
| Microscopy | Model: FEI/PHILIPS CM300FEG/ST / Date: Feb 1, 2004 |
|---|---|
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 24000 X / Calibrated magnification: 24000 X / Nominal defocus max: 4000 nm / Nominal defocus min: 12000 nm / Cs: 2 mm |
| Specimen holder | Temperature: 103 K / Tilt angle max: 70 ° / Tilt angle min: -70 ° |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 30 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F224 (2k x 2k) / Details: 2048x2048 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: electron |
| Radiation wavelength | Relative weight: 1 |
- Processing
Processing
| EM software |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: CTF gradient correction | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D reconstruction | Method: electron tomography and 3-D average / Resolution: 24 Å / Num. of particles: 4029 / Nominal pixel size: 5.56 Å / Actual pixel size: 5.56 Å Details: Tilt series images were aligned using marker-free alignment. Molecular volumes extracted from the cryotomograms, aligned in 3-D. Marker-free alignment is described in the reference: ...Details: Tilt series images were aligned using marker-free alignment. Molecular volumes extracted from the cryotomograms, aligned in 3-D. Marker-free alignment is described in the reference: Winkler,H. and Taylor,K.A. Accurate marker-free alignment with simultaneous geometry determination and reconstruction of tilt series in electron tomography. Ultramicroscopy, 106, 240-254 (2006) Symmetry type: 2D CRYSTAL | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building | Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Space: REAL / Target criteria: Cross correlation Details: METHOD--Rigid body docking first and then refined with normal mode flexible fitting. REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--Rigid body docking and normal mode flexible fitting. For the fitting the density ...Details: METHOD--Rigid body docking first and then refined with normal mode flexible fitting. REFINEMENT PROTOCOL--Rigid body docking and normal mode flexible fitting. For the fitting the density corresponding to the two myosin V heads within the asymmetric unit was segmented from the rest of the map using the watershed transform (Volkman 2002. J.STRUCT.BIOL. 138, 123-129). After fitting the atomic model against the head density, the coordinates were not refined further against the nearest neighbor myosin V heads to remove bad crystal contacts. The alpha-helical coiled-coil domain was manually fit to the and not refined further. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Atomic model building |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST
|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 PDBj
PDBj