[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
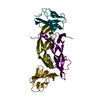
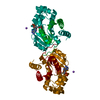
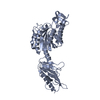
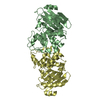
Yorodumi- PDB-1qty: VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR IN COMPLEX WITH DOMAIN 2 OF TH... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1qty | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR IN COMPLEX WITH DOMAIN 2 OF THE FLT-1 RECEPTOR | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | HORMONE/GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR / COMPLEX (GROWTH FACTOR-RECEPTOR) / FLT-1 / VEGF RECEPTOR / RECEPTOR TYROSINE KINASE / CYSTINE KNOT / GLYCOPROTEIN / IMMUNOGLOBULIN-LIKE DOMAIN / I-SET / HORMONE-GROWTH FACTOR RECEPTOR complex | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationvascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling pathway / placental growth factor receptor activity / basophil chemotaxis / positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway / VEGF-A complex / Signaling by VEGF / cellular stress response to acid chemical / positive regulation of lymphangiogenesis / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 binding / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding ...vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 signaling pathway / placental growth factor receptor activity / basophil chemotaxis / positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis by VEGF-activated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway / VEGF-A complex / Signaling by VEGF / cellular stress response to acid chemical / positive regulation of lymphangiogenesis / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 binding / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor binding / negative regulation of establishment of endothelial barrier / VEGF ligand-receptor interactions / positive regulation of mast cell chemotaxis / post-embryonic camera-type eye development / primitive erythrocyte differentiation / negative regulation of adherens junction organization / hyaloid vascular plexus regression / lymph vessel morphogenesis / positive regulation of cell proliferation by VEGF-activated platelet derived growth factor receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of blood-brain barrier permeability / regulation of nitric oxide mediated signal transduction / VEGF-activated neuropilin signaling pathway / bone trabecula formation / coronary vein morphogenesis / cardiac vascular smooth muscle cell development / lymphangiogenesis / Neurophilin interactions with VEGF and VEGFR / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 signaling pathway / positive regulation of epithelial tube formation / VEGF binds to VEGFR leading to receptor dimerization / motor neuron migration / positive regulation of trophoblast cell migration / positive regulation of axon extension involved in axon guidance / lung vasculature development / regulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell differentiation / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor activity / eye photoreceptor cell development / endothelial cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of protein localization to early endosome / positive regulation of protein autophosphorylation / vascular wound healing / camera-type eye morphogenesis / embryonic morphogenesis / neuropilin binding / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell proliferation involved in sprouting angiogenesis / positive regulation of branching involved in ureteric bud morphogenesis / induction of positive chemotaxis / commissural neuron axon guidance / transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activator activity / coronary artery morphogenesis / negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by cadherin / positive regulation of vascular permeability / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 binding / dopaminergic neuron differentiation / tube formation / positive regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway / positive regulation of blood vessel branching / surfactant homeostasis / platelet-derived growth factor receptor binding / cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis / sprouting angiogenesis / extracellular matrix binding / endothelial cell proliferation / epithelial cell maturation / retinal ganglion cell axon guidance / blood vessel morphogenesis / positive regulation of positive chemotaxis / positive regulation of leukocyte migration / cardiac muscle cell development / Regulation of gene expression by Hypoxia-inducible Factor / negative regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation / positive regulation of endothelial cell chemotaxis / positive regulation of cell migration involved in sprouting angiogenesis / artery morphogenesis / positive regulation of peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation / vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway / positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process / negative regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / growth factor binding / branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis / positive regulation of neuroblast proliferation / positive chemotaxis / negative regulation of fat cell differentiation / positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis / chemoattractant activity / positive regulation of MAP kinase activity / mesoderm development / outflow tract morphogenesis / fibronectin binding / monocyte chemotaxis / positive regulation of cell division / macrophage differentiation / positive regulation of receptor internalization / positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration / mammary gland alveolus development / cellular response to vascular endothelial growth factor stimulus / neuroblast proliferation / positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly / monocyte differentiation / vascular endothelial growth factor receptor signaling pathway Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT IN COMBINATION WITH MULTI-CRYSTAL AVERAGING / Resolution: 2.7 Å X-RAY DIFFRACTION / MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT IN COMBINATION WITH MULTI-CRYSTAL AVERAGING / Resolution: 2.7 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Wiesmann, C. / de Vos, A.M. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1999 Journal: J.Mol.Biol. / Year: 1999Title: Solution structure of the VEGF-binding domain of Flt-1: comparison of its free and bound states. Authors: Starovasnik, M.A. / Christinger, H.W. / Wiesmann, C. / Champe, M.A. / de Vos, A.M. / Skelton, N.J. #1:  Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 1997 Journal: Cell(Cambridge,Mass.) / Year: 1997Title: Crystal Structure at 1.7 A Resolution of Vegf in Complex with Domain 2 of the Flt-1 Receptor Authors: Wiesmann, C. / Fuh, G. / Christinger, H.W. / Eigenbrot, C. / Wells, J.A. / de Vos, A.M. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1qty.cif.gz 1qty.cif.gz | 159.3 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1qty.ent.gz pdb1qty.ent.gz | 128.4 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1qty.json.gz 1qty.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qt/1qty https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qt/1qty ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qt/1qty ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/qt/1qty | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  1qsvC  1qszC  1vpfS C: citing same article ( S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
| ||||||||
| 2 | 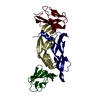
| ||||||||
| 3 | 
| ||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||
| Details | CHAINS V, W, X, and Y FORM A BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE COMPLEX. CHAINS R, S, T, and U FORM A BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE COMPLEX. |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 11948.680 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: RECEPTOR BINDING DOMAIN Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  #2: Protein | Mass: 11538.298 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 / Fragment: DOMAIN 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Production host:  Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.36 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 47.89 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 277 K / Method: vapor diffusion, hanging drop / pH: 8.5 Details: PEG 4000, AMMONIUMSULFATE, TRIS , pH 8.5, VAPOR DIFFUSION, HANGING DROP, temperature 277K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Details: Wiesmann, C., (1997) Cell, 91, 695. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 100 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU / Wavelength: 1.5418 ROTATING ANODE / Type: RIGAKU / Wavelength: 1.5418 |
| Detector | Type: MARRESEARCH / Detector: AREA DETECTOR / Date: Dec 24, 1996 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 1.5418 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.7→30 Å / Num. all: 24216 / Num. obs: 24098 / % possible obs: 99.5 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 0 / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 3.7 % / Rsym value: 0.049 / Net I/σ(I): 13.3 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.7→2.76 Å / Redundancy: 3 % / Num. unique all: 1544 / Rsym value: 0.311 / % possible all: 98 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure: MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT IN COMBINATION WITH MULTI-CRYSTAL AVERAGING Starting model: 1VPF Resolution: 2.7→20 Å / Data cutoff high absF: 1000000 / Data cutoff low absF: 0.001 / Cross valid method: FREE R / σ(F): 0.2 / σ(I): 0 / Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 63.5 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.7→20 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.7→2.82 Å / Total num. of bins used: 8
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name:  X-PLOR / Version: 3.851 / Classification: refinement X-PLOR / Version: 3.851 / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | *PLUS Rfactor Rfree: 0.4 / % reflection Rfree: 4.5 % / Rfactor Rwork: 0.383 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 PDBj
PDBj