[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
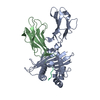
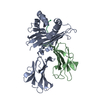
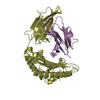
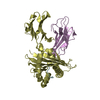
Yorodumi- PDB-1ed3: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RAT MINOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN COMPLEX... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 1ed3 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF RAT MINOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY ANTIGEN COMPLEX RT1-AA/MTF-E. | ||||||
 Components Components |
| ||||||
 Keywords Keywords | IMMUNE SYSTEM / major histocompatibility complex / rat minor histocompatibility complex / MHC / immunology / peptide antigen presentation / cellular immunity / cell surface receptor / T cell receptor ligand | ||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationFormation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / DAP12 interactions / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / ER-Phagosome pathway / Mitochondrial protein degradation / DAP12 signaling / proton channel activity ...Formation of ATP by chemiosmotic coupling / Cristae formation / Endosomal/Vacuolar pathway / DAP12 interactions / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / Antigen Presentation: Folding, assembly and peptide loading of class I MHC / ER-Phagosome pathway / Mitochondrial protein degradation / DAP12 signaling / proton channel activity / Neutrophil degranulation / proton motive force-driven ATP synthesis / proton motive force-driven mitochondrial ATP synthesis / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class Ib / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I via ER pathway, TAP-independent / response to hyperoxia / response to cadmium ion / proton-transporting ATP synthase complex / proton-transporting ATP synthase activity, rotational mechanism / proton transmembrane transport / lumenal side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / T cell mediated cytotoxicity / cellular response to iron(III) ion / iron ion transport / negative regulation of forebrain neuron differentiation / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous protein antigen via MHC class Ib, TAP-dependent / peptide antigen assembly with MHC class I protein complex / regulation of iron ion transport / regulation of erythrocyte differentiation / HFE-transferrin receptor complex / response to molecule of bacterial origin / MHC class I peptide loading complex / cellular response to iron ion / positive regulation of T cell cytokine production / antigen processing and presentation of endogenous peptide antigen via MHC class I / MHC class I protein complex / peptide antigen assembly with MHC class II protein complex / negative regulation of neurogenesis / positive regulation of receptor-mediated endocytosis / cellular response to nicotine / MHC class II protein complex / positive regulation of T cell mediated cytotoxicity / multicellular organismal-level iron ion homeostasis / peptide antigen binding / antigen processing and presentation of exogenous peptide antigen via MHC class II / phagocytic vesicle membrane / positive regulation of immune response / positive regulation of T cell activation / negative regulation of epithelial cell proliferation / sensory perception of smell / positive regulation of cellular senescence / MHC class II protein complex binding / T cell differentiation in thymus / late endosome membrane / negative regulation of neuron projection development / protein refolding / amyloid fibril formation / protein homotetramerization / intracellular iron ion homeostasis / learning or memory / mitochondrial inner membrane / immune response / response to xenobiotic stimulus / signaling receptor binding / external side of plasma membrane / lysosomal membrane / structural molecule activity / protein homodimerization activity / extracellular space / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||
| Biological species |  | ||||||
| Method |  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / X-RAY DIFFRACTION /  SYNCHROTRON / SYNCHROTRON /  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.55 Å MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT / Resolution: 2.55 Å | ||||||
 Authors Authors | Speir, J.A. / Stevens, J. / Joly, E. / Butcher, G.W. / Wilson, I.A. | ||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Immunity / Year: 2001 Journal: Immunity / Year: 2001Title: Two different, highly exposed, bulged structures for an unusually long peptide bound to rat MHC class I RT1-Aa. Authors: Speir, J.A. / Stevens, J. / Joly, E. / Butcher, G.W. / Wilson, I.A. #1:  Journal: J.Immunol. / Year: 1997 Journal: J.Immunol. / Year: 1997Title: Identification of the rat maternally transmitted minor histocompatibility antigen Authors: Bhuyan, P.K. / Young, L.L. / Lindahl, K.F. / Butcher, G.W. #2:  Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1998 Journal: J.Biol.Chem. / Year: 1998Title: Efficient generation of major histocompatibility complex class I-peptide complexes using synthetic peptide libraries Authors: Stevens, J. / Wiesmuller, K.-H. / Barker, P.J. / Walden, P. / Bucher, G.W. / Joly, E. #3:  Journal: Eur.J.Biochem. / Year: 1998 Journal: Eur.J.Biochem. / Year: 1998Title: Peptide length preferences for rat and mouse MHC class I molecules using random peptide libraries Authors: Stevens, J. / Wiesmuller, K.-H. / Walden, P. / Joly, E. #4:  Journal: Immunity / Year: 1996 Journal: Immunity / Year: 1996Title: The rat cim effect: TAP allele-dependent changes in a class I MHC anchor motif and evidence against C-terminal trimming of peptides in the ER Authors: Powis, S.J. / Young, L.L. / Joly, E. / Barker, P.J. / Richardson, L. / Brandt, R.P. / Melief, C.J. / Howard, J.C. / Butcher, G.W. #5:  Journal: Immunogenetics / Year: 1995 Journal: Immunogenetics / Year: 1995Title: An analysis of the antigen binding site of RT1-Aa suggests an allele-specific motif Authors: Thorpe, C.J. / Moss, D.S. / Powis, S.J. / Howard, J.C. / Butcher, G.W. / Travers, P.J. | ||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  1ed3.cif.gz 1ed3.cif.gz | 168.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb1ed3.ent.gz pdb1ed3.ent.gz | 134.9 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  1ed3.json.gz 1ed3.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/1ed3 https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/1ed3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/1ed3 ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/ed/1ed3 | HTTPS FTP |
|---|
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  2clrS S: Starting model for refinement |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 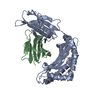
| ||||||||||||
| 2 | 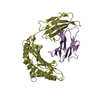
| ||||||||||||
| Unit cell |
| ||||||||||||
| Noncrystallographic symmetry (NCS) | NCS domain:
| ||||||||||||
| Details | There are two heterotrimeric biological assemblies in the asymmetric unit constructed from chains A, B, and C, or chains D, E, and F. |
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 32045.551 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: EXTRACELLULAR DOMAINS Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #2: Protein | Mass: 11652.282 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)   #3: Protein/peptide | Mass: 1533.773 Da / Num. of mol.: 2 / Fragment: RESIDUES 29-41 OF RAT ATPASE 6 / Source method: obtained synthetically / Details: This sequence occurs naturally in rats / References: UniProt: P05504 #4: Water | ChemComp-HOH / | Has protein modification | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method:  X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 X-RAY DIFFRACTION / Number of used crystals: 1 |
|---|
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Crystal | Density Matthews: 2.46 Å3/Da / Density % sol: 48.8 % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crystal grow | Temperature: 290 K / Method: vapor diffusion, sitting drop / pH: 6.5 Details: 0.1M morpholine ethansulfonic acid (MES), 0.2M ammonium sulfate, 15-20% MPEG 5000, 0.025M beta-octyl-glucoside, 0.5% glycerol, pH 6.5, VAPOR DIFFUSION, SITTING DROP, temperature 290K | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crystal grow | *PLUS Temperature: 17 ℃ / pH: 7.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Components of the solutions | *PLUS
|
-Data collection
| Diffraction | Mean temperature: 93 K |
|---|---|
| Diffraction source | Source:  SYNCHROTRON / Site: SYNCHROTRON / Site:  SSRL SSRL  / Beamline: BL9-1 / Wavelength: 0.98 / Beamline: BL9-1 / Wavelength: 0.98 |
| Detector | Type: MARRESEARCH / Detector: IMAGE PLATE / Date: Jul 9, 1997 |
| Radiation | Protocol: SINGLE WAVELENGTH / Monochromatic (M) / Laue (L): M / Scattering type: x-ray |
| Radiation wavelength | Wavelength: 0.98 Å / Relative weight: 1 |
| Reflection | Resolution: 2.55→20 Å / Num. all: 28978 / Num. obs: 28978 / % possible obs: 94.3 % / Observed criterion σ(F): 0 / Observed criterion σ(I): 0 / Redundancy: 3.2 % / Biso Wilson estimate: 38.7 Å2 / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.095 / Net I/σ(I): 11.4 |
| Reflection shell | Resolution: 2.55→2.64 Å / Redundancy: 2.7 % / Rmerge(I) obs: 0.318 / Mean I/σ(I) obs: 2.6 / Num. unique all: 2757 / % possible all: 91.2 |
| Reflection | *PLUS |
| Reflection shell | *PLUS % possible obs: 91.2 % / Num. unique obs: 2757 |
- Processing
Processing
| Software |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Method to determine structure:  MOLECULAR REPLACEMENT MOLECULAR REPLACEMENTStarting model: 2CLR Resolution: 2.55→19.89 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.006 / Data cutoff high rms absF: 10000 / Cross valid method: THROUGHOUT / σ(F): 0 Stereochemistry target values: Engh & Huber as implemented in X-PLOR and CNS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | Bsol: 33.8132 Å2 / ksol: 0.368077 e/Å3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | Biso mean: 27 Å2
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine analyze |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement step | Cycle: LAST / Resolution: 2.55→19.89 Å
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints NCS |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | Resolution: 2.55→2.64 Å / Rfactor Rfree error: 0.026 / Total num. of bins used: 10
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Xplor file |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Software | *PLUS Name: CNS / Classification: refinement | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refinement | *PLUS σ(F): 0 / % reflection Rfree: 7.5 % / Rfactor obs: 0.224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Solvent computation | *PLUS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Displacement parameters | *PLUS Biso mean: 27 Å2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Refine LS restraints | *PLUS
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| LS refinement shell | *PLUS Rfactor Rfree: 0.37 / % reflection Rfree: 7.5 % / Rfactor Rwork: 0.319 / Rfactor obs: 0.319 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 PDBj
PDBj










