[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-8769: Negative stain of influenza B virus recombinant neuraminidase bou... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8769 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Negative stain of influenza B virus recombinant neuraminidase bound to 4F11 Fab | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Influenza B virus bound to 4F11 Fab | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexo-alpha-sialidase / exo-alpha-sialidase activity / carbohydrate metabolic process / host cell plasma membrane / virion membrane / metal ion binding / membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Influenza B virus (B/Malaysia/2506/2004) Influenza B virus (B/Malaysia/2506/2004) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 25.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Podolsky K / Subramaniam S | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017 Journal: Nat Microbiol / Year: 2017Title: Broadly protective murine monoclonal antibodies against influenza B virus target highly conserved neuraminidase epitopes. Authors: Teddy John Wohlbold / Kira A Podolsky / Veronika Chromikova / Ericka Kirkpatrick / Veronica Falconieri / Philip Meade / Fatima Amanat / Jessica Tan / Benjamin R tenOever / Gene S Tan / ...Authors: Teddy John Wohlbold / Kira A Podolsky / Veronika Chromikova / Ericka Kirkpatrick / Veronica Falconieri / Philip Meade / Fatima Amanat / Jessica Tan / Benjamin R tenOever / Gene S Tan / Sriram Subramaniam / Peter Palese / Florian Krammer /  Abstract: A substantial proportion of influenza-related childhood deaths are due to infection with influenza B viruses, which co-circulate in the human population as two antigenically distinct lineages defined ...A substantial proportion of influenza-related childhood deaths are due to infection with influenza B viruses, which co-circulate in the human population as two antigenically distinct lineages defined by the immunodominant receptor binding protein, haemagglutinin. While broadly cross-reactive, protective monoclonal antibodies against the haemagglutinin of influenza B viruses have been described, none targeting the neuraminidase, the second most abundant viral glycoprotein, have been reported. Here, we analyse a panel of five murine anti-neuraminidase monoclonal antibodies that demonstrate broad binding, neuraminidase inhibition, in vitro antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity and in vivo protection against influenza B viruses belonging to both haemagglutinin lineages and spanning over 70 years of antigenic drift. Electron microscopic analysis of two neuraminidase-antibody complexes shows that the conserved neuraminidase epitopes are located on the head of the molecule and that they are distinct from the enzymatic active site. In the mouse model, one therapeutic dose of antibody 1F2 was more protective than the current standard of treatment, oseltamivir, given twice daily for six days. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8769.map.gz emd_8769.map.gz | 94.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8769-v30.xml emd-8769-v30.xml emd-8769.xml emd-8769.xml | 9.2 KB 9.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_8769.png emd_8769.png | 17.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8769 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8769 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_8769_validation.pdf.gz emd_8769_validation.pdf.gz | 78.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_8769_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_8769_full_validation.pdf.gz | 77.6 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_8769_validation.xml.gz emd_8769_validation.xml.gz | 495 B | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8769 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8769 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-8769 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8769.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8769.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Influenza B virus bound to 4F11 Fab | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.8 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
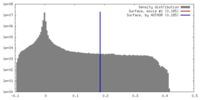
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Influenza B neuraminidase bound to 4F11 Fab
| Entire | Name: Influenza B neuraminidase bound to 4F11 Fab |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Influenza B neuraminidase bound to 4F11 Fab
| Supramolecule | Name: Influenza B neuraminidase bound to 4F11 Fab / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Influenza B virus (B/Malaysia/2506/2004) Influenza B virus (B/Malaysia/2506/2004) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) Trichoplusia ni (cabbage looper) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.3 |
|---|---|
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Material: Uranyl formate |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI 12 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN ULTRASCAN 4000 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 100.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 120 kV / Electron source: LAB6 |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 25.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: RELION (ver. 1.4) Details: The standard Fourier Shell Correlation-based measures for resolution are generally not very reliable for negative stain reconstructions because they tend to overestimate resolution and can ...Details: The standard Fourier Shell Correlation-based measures for resolution are generally not very reliable for negative stain reconstructions because they tend to overestimate resolution and can result in spurious values that depend on data size rather than quality, a feature that is also true for cryo-EM reconstructions (some of these issues are discussed in Subramaniam et al, Curr Opin Str. Biol 41: 194-202 (2016)). In negative stain reconstructions, we therefore use a comparison of the experimentally obtained maps with maps computed from the fitted coordinates over a range of resolutions and use this to estimate resolution conservatively. The computed maps at 20 A and 25 A are easily comparable to an experimentally obtained map, which is why we used 25 A as an estimate for resolution. Number images used: 13665 |
|---|---|
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


 UCSF Chimera
UCSF Chimera








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)