+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-8708 | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
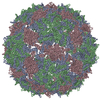
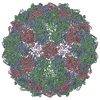
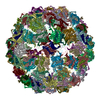
| Title | Phage Qbeta with icosahedral symmetry | |||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Phage Qbeta with icosahedral symmetry | |||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Qbeta / ssRNA / phage / virus | |||||||||||||||
| Function / homology | Levivirus coat protein / Levivirus coat protein / Bacteriophage RNA-type, capsid / T=3 icosahedral viral capsid / translation repressor activity / structural molecule activity / RNA binding / Capsid protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Escherichia phage Qbeta (virus) / Escherichia phage Qbeta (virus) /  Enterobacteria phage Qbeta (virus) Enterobacteria phage Qbeta (virus) | |||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | |||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cui Z / Zhang J | |||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 4 items United States, 4 items
| |||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2017Title: Structures of Qβ virions, virus-like particles, and the Qβ-MurA complex reveal internal coat proteins and the mechanism of host lysis. Authors: Zhicheng Cui / Karl V Gorzelnik / Jeng-Yih Chang / Carrie Langlais / Joanita Jakana / Ry Young / Junjie Zhang /  Abstract: In single-stranded RNA bacteriophages (ssRNA phages) a single copy of the maturation protein binds the genomic RNA (gRNA) and is required for attachment of the phage to the host pilus. For the ...In single-stranded RNA bacteriophages (ssRNA phages) a single copy of the maturation protein binds the genomic RNA (gRNA) and is required for attachment of the phage to the host pilus. For the canonical Qβ the maturation protein, A, has an additional role as the lysis protein, by its ability to bind and inhibit MurA, which is involved in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Here, we determined structures of Qβ virions, virus-like particles, and the Qβ-MurA complex using single-particle cryoelectron microscopy, at 4.7-Å, 3.3-Å, and 6.1-Å resolutions, respectively. We identified the outer surface of the β-region in A as the MurA-binding interface. Moreover, the pattern of MurA mutations that block Qβ lysis and the conformational changes of MurA that facilitate A binding were found to be due to the intimate fit between A and the region encompassing the closed catalytic cleft of substrate-liganded MurA. Additionally, by comparing the Qβ virion with Qβ virus-like particles that lack a maturation protein, we observed a structural rearrangement in the capsid coat proteins that is required to package the viral gRNA in its dominant conformation. Unexpectedly, we found a coat protein dimer sequestered in the interior of the virion. This coat protein dimer binds to the gRNA and interacts with the buried α-region of A, suggesting that it is sequestered during the early stage of capsid formation to promote the gRNA condensation required for genome packaging. These internalized coat proteins are the most asymmetrically arranged major capsid proteins yet observed in virus structures. | |||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_8708.map.gz emd_8708.map.gz | 21.4 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-8708-v30.xml emd-8708-v30.xml emd-8708.xml emd-8708.xml | 11.7 KB 11.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_8708_fsc.xml emd_8708_fsc.xml | 11 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_8708.png emd_8708.png | 312.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-8708.cif.gz emd-8708.cif.gz | 5.1 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8708 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8708 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8708 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-8708 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5vlyMC  8707C  8709C  8710C  8711C  5vlzC  5vm7C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_8708.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_8708.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
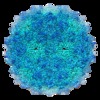
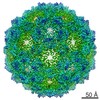
| Annotation | Phage Qbeta with icosahedral symmetry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.216 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
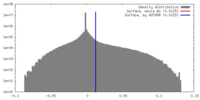
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Enterobacteria phage Qbeta
| Entire | Name:  Enterobacteria phage Qbeta (virus) Enterobacteria phage Qbeta (virus) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Enterobacteria phage Qbeta
| Supramolecule | Name: Enterobacteria phage Qbeta / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all / NCBI-ID: 39803 / Sci species name: Enterobacteria phage Qbeta / Virus type: VIRION / Virus isolate: SPECIES / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: No |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: Capsid protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Capsid protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Escherichia phage Qbeta (virus) Escherichia phage Qbeta (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.268071 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MAKLETVTLG NIGKDGKQTL VLNPRGVNPT NGVASLSQAG AVPALEKRVT VSVSQPSRNR KNYKVQVKIQ NPTACTANGS CDPSVTRQA YADVTFSFTQ YSTDEERAFV RTELAALLAS PLLIDAIDQL NPAY UniProtKB: Capsid protein |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 60 sec. |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III Details: Blotted for 6s, Plunged into liquid ethane (FEI VITROBOT MARK III). |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL 3200FSC |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Average exposure time: 0.2 sec. / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal magnification: 30000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)