[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
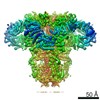
Yorodumi- EMDB-7983: Class 3 IP3-bound human type 3 1,4,5-inositol trisphosphate receptor -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7983 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
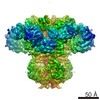
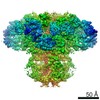
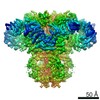
| Title | Class 3 IP3-bound human type 3 1,4,5-inositol trisphosphate receptor | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Class 3 IP3-bound human type 3 1,4,5-inositol trisphosphate receptor | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ion channel / Calcium channel / METAL TRANSPORT | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationDAG and IP3 signaling / inositol 1,3,4,5 tetrakisphosphate binding / sensory perception of bitter taste / inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated calcium channel activity / platelet dense tubular network membrane / sensory perception of umami taste / Effects of PIP2 hydrolysis / sensory perception of sweet taste / Elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ levels / PLC beta mediated events ...DAG and IP3 signaling / inositol 1,3,4,5 tetrakisphosphate binding / sensory perception of bitter taste / inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated calcium channel activity / platelet dense tubular network membrane / sensory perception of umami taste / Effects of PIP2 hydrolysis / sensory perception of sweet taste / Elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ levels / PLC beta mediated events / inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate binding / inositol hexakisphosphate binding / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / transport vesicle membrane / cytoplasmic side of endoplasmic reticulum membrane / intracellularly gated calcium channel activity / nuclear outer membrane / brush border / Role of phospholipids in phagocytosis / calcium ion homeostasis / Ion homeostasis / release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / phosphatidylinositol binding / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / secretory granule membrane / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / sarcoplasmic reticulum / Regulation of insulin secretion / response to calcium ion / platelet activation / memory / apical part of cell / Sensory perception of sweet, bitter, and umami (glutamate) taste / Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP1) regulates insulin secretion / long-term synaptic potentiation / sensory perception of taste / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / Ca2+ pathway / protein homotetramerization / receptor complex / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / neuronal cell body / calcium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum membrane / nucleolus / endoplasmic reticulum / zinc ion binding / nucleoplasm / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.12 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hite RK / Paknejad N | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2018Title: Structural basis for the regulation of inositol trisphosphate receptors by Ca and IP. Authors: Navid Paknejad / Richard K Hite /  Abstract: Inositol trisphosphate receptors (IPRs) are ubiquitous Ca-permeable channels that mediate release of Ca from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby regulating numerous processes including cell division, ...Inositol trisphosphate receptors (IPRs) are ubiquitous Ca-permeable channels that mediate release of Ca from the endoplasmic reticulum, thereby regulating numerous processes including cell division, cell death, differentiation and fertilization. IPRs are jointly activated by inositol trisphosphate (IP) and their permeant ion, Ca. At high concentrations, however, Ca inhibits activity, ensuring precise spatiotemporal control over intracellular Ca. Despite extensive characterization of IPR, the mechanisms through which these molecules control channel gating have remained elusive. Here, we present structures of full-length human type 3 IPRs in ligand-bound and ligand-free states. Multiple IP-bound structures demonstrate that the large cytoplasmic domain provides a platform for propagation of long-range conformational changes to the ion-conduction gate. Structures in the presence of Ca reveal two Ca-binding sites that induce the disruption of numerous interactions between subunits, thereby inhibiting IPR. These structures thus provide a mechanistic basis for beginning to understand the regulation of IPR. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7983.map.gz emd_7983.map.gz | 200.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7983-v30.xml emd-7983-v30.xml emd-7983.xml emd-7983.xml | 17.7 KB 17.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7983.png emd_7983.png | 122.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7983.cif.gz emd-7983.cif.gz | 7.6 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7983 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7983 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7983 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7983 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6dqsMC 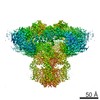 7978C  7979C  7980C  7981C  7982C  7984C  7985C  7986C  7987C  7988C  7989C  7990C  7991C  7992C  7993C  7994C  7995C  7996C  6dqjC  6dqnC  6dqvC  6dqzC  6dr0C  6dr2C  6draC  6drcC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7983.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7983.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Class 3 IP3-bound human type 3 1,4,5-inositol trisphosphate receptor | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
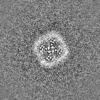
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.088 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor
| Entire | Name: human type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: human type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: human type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3
| Macromolecule | Name: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 304.488688 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MSEMSSFLHI GDIVSLYAEG SVNGFISTLG LVDDRCVVEP AAGDLDNPPK KFRDCLFKVC PMNRYSAQKQ YWKAKQTKQD KEKIADVVL LQKLQHAAQM EQKQNDTENK KVHGDVVKYG SVIQLLHMKS NKYLTVNKRL PALLEKNAMR VTLDATGNEG S WLFIQPFW ...String: MSEMSSFLHI GDIVSLYAEG SVNGFISTLG LVDDRCVVEP AAGDLDNPPK KFRDCLFKVC PMNRYSAQKQ YWKAKQTKQD KEKIADVVL LQKLQHAAQM EQKQNDTENK KVHGDVVKYG SVIQLLHMKS NKYLTVNKRL PALLEKNAMR VTLDATGNEG S WLFIQPFW KLRSNGDNVV VGDKVILNPV NAGQPLHASN YELSDNAGCK EVNSVNCNTS WKINLFMQFR DHLEEVLKGG DV VRLFHAE QEKFLTCDEY KGKLQVFLRT TLRQSATSAT SSNALWEVEV VHHDPCRGGA GHWNGLYRFK HLATGNYLAA EEN PSYKGD ASDPKAAGMG AQGRTGRRNA GEKIKYCLVA VPHGNDIASL FELDPTTLQK TDSFVPRNSY VRLRHLCTNT WIQS TNVPI DIEEERPIRL MLGTCPTKED KEAFAIVSVP VSEIRDLDFA NDASSMLASA VEKLNEGFIS QNDRRFVIQL LEDLV FFVS DVPNNGQNVL DIMVTKPNRE RQKLMREQNI LKQVFGILKA PFREKGGEGP LVRLEELSDQ KNAPYQHMFR LCYRVL RHS QEDYRKNQEH IAKQFGMMQS QIGYDILAED TITALLHNNR KLLEKHITKT EVETFVSLVR KNREPRFLDY LSDLCVS NH IAIPVTQELI CKCVLDPKNS DILIRTELRP VKEMAQSHEY LSIEYSEEEV WLTWTDKNNE HHEKSVRQLA QEARAGNA H DENVLSYYRY QLKLFARMCL DRQYLAIDEI SQQLGVDLIF LCMADEMLPF DLRASFCHLM LHVHVDRDPQ ELVTPVKFA RLWTEIPTAI TIKDYDSNLN ASRDDKKNKF ANTMEFVEDY LNNVVSEAVP FANEEKNKLT FEVVSLAHNL IYFGFYSFSE LLRLTRTLL GIIDCVQGPP AMLQAYEDPG GKNVRRSIQG VGHMMSTMVL SRKQSVFSAP SLSAGASAAE PLDRSKFEEN E DIVVMETK LKILEILQFI LNVRLDYRIS YLLSVFKKEF VEVFPMQDSG ADGTAPAFDS TTANMNLDRI GEQAEAMFGV GK TSSMLEV DDEGGRMFLR VLIHLTMHDY APLVSGALQL LFKHFSQRQE AMHTFKQVQL LISAQDVENY KVIKSELDRL RTM VEKSEL WVDKKGSGKG EEVEAGAAKD KKERPTDEEG FLHPPGEKSS ENYQIVKGIL ERLNKMCGVG EQMRKKQQRL LKNM DAHKV MLDLLQIPYD KGDAKMMEIL RYTHQFLQKF CAGNPGNQAL LHKHLHLFLT PGLLEAETMQ HIFLNNYQLC SEISE PVLQ HFVHLLATHG RHVQYLDFLH TVIKAEGKYV KKCQDMIMTE LTNAGDDVVV FYNDKASLAH LLDMMKAARD GVEDHS PLM YHISLVDLLA ACAEGKNVYT EIKCTSLLPL EDVVSVVTHE DCITEVKMAY VNFVNHCYVD TEVEMKEIYT SNHIWTL FE NFTLDMARVC SKREKRVADP TLEKYVLSVV LDTINAFFSS PFSENSTSLQ THQTIVVQLL QSTTRLLECP WLQQQHKG S VEACIRTLAM VAKGRAILLP MDLDAHISSM LSSGASCAAA AQRNASSYKA TTRAFPRVTP TANQWDYKNI IEKLQDIIT ALEERLKPLV QAELSVLVDV LHWPELLFLE GSEAYQRCES GGFLSKLIQH TKDLMESEEK LCIKVLRTLQ QMLLKKTKYG DRGNQLRKM LLQNYLQNRK STSRGDLPDP IGTGLDPDWS AIAATQCRLD KEGATKLVCD LITSTKNEKI FQESIGLAIH L LDGGNTEI QKSFHNLMMS DKKSERFFKV LHDRMKRAQQ ETKSTVAVNM NDLGSQPHED REPVDPTTKG RVASFSIPGS SS RYSLGPS LRRGHEVSER VQSSEMGTSV LIMQPILRFL QLLCENHNRD LQNFLRCQNN KTNYNLVCET LQFLDIMCGS TTG GLGLLG LYINEDNVGL VIQTLETLTE YCQGPCHENQ TCIVTHESNG IDIITALILN DISPLCKYRM DLVLQLKDNA SKLL LALME SRHDSENAER ILISLRPQEL VDVIKKAYLQ EEERENSEVS PREVGHNIYI LALQLSRHNK QLQHLLKPVK RIQEE EAEG ISSMLSLNNK QLSQMLKSSA PAQEEEEDPL AYYENHTSQI EIVRQDRSME QIVFPVPGIC QFLTEETKHR LFTTTE QDE QGSKVSDFFD QSSFLHNEME WQRKLRSMPL IYWFSRRMTL WGSISFNLAV FINIIIAFFY PYMEGASTGV LDSPLIS LL FWILICFSIA ALFTKRYSIR PLIVALILRS IYYLGIGPTL NILGALNLTN KIVFVVSFVG NRGTFIRGYK AMVMDMEF L YHVGYILTSV LGLFAHELFY SILLFDLIYR EETLFNVIKS VTRNGRSILL TALLALILVY LFSIVGFLFL KDDFILEVD RLPNNHSTAS PLGMPHGAAA FVDTCSGDKM DCVSGLSVPE VLEEDRELDS TERACDTLLM CIVTVMNHGL RNGGGVGDIL RKPSKDESL FPARVVYDLL FFFIVIIIVL NLIFGVIIDT FADLRSEKQK KEEILKTTCF ICGLERDKFD NKTVSFEEHI K LEHNMWNY LYFIVLVRVK NKTDYTGPES YVAQMIKNKN LDWFPRMRAM SLVSNEGEGE QNEIRILQDK LNSTMKLVSH LT AQLNELK EQMTEQRKRR QRLGFVDVQN CISR UniProtKB: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated calcium channel ITPR3 |
-Macromolecule #2: ZINC ION
| Macromolecule | Name: ZINC ION / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: ZN |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 65.409 Da |
-Macromolecule #3: D-MYO-INOSITOL-1,4,5-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: D-MYO-INOSITOL-1,4,5-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: I3P |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 420.096 Da |
| Chemical component information | 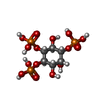 ChemComp-I3P: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 8 mg/mL | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Component:
Details: 150mM Nacl 50mM Tris-HCl, pH 8.0 2mM DTT 0.06% Digitonin 5mM EGTA 50 micromolar IP3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 293 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: Blot for 2 seconds prior to freezing. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | human type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in detergent micelles |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: SUPER-RESOLUTION / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 7420 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 7676 pixel / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-40 / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 1801 / Average exposure time: 8.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 61.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 22500 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL / Overall B value: 193.5 / Target criteria: map-to-model FSC |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6dqs: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)