[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7538: Cryo-EM structure of the human SK4/calmodulin channel complex in ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7538 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
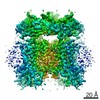
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the human SK4/calmodulin channel complex in the Ca2+ bound state I | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | human SK4/calmodulin channel complex in the Ca2+ bound state I: sharpened, filtered map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ion channel / neuroscience / calmodulin / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationintermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / saliva secretion / small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / Ca2+ activated K+ channels / stabilization of membrane potential / macropinocytosis / calcium-activated potassium channel activity / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cell volume homeostasis ...intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / saliva secretion / small conductance calcium-activated potassium channel activity / Ca2+ activated K+ channels / stabilization of membrane potential / macropinocytosis / calcium-activated potassium channel activity / regulation of calcium ion import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / cell volume homeostasis / CaM pathway / Cam-PDE 1 activation / Sodium/Calcium exchangers / Calmodulin induced events / Reduction of cytosolic Ca++ levels / Activation of Ca-permeable Kainate Receptor / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of CaMKII/CaMKK/CaMKIV cascasde / phospholipid translocation / Loss of phosphorylation of MECP2 at T308 / CREB1 phosphorylation through the activation of Adenylate Cyclase / CaMK IV-mediated phosphorylation of CREB / PKA activation / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / Glycogen breakdown (glycogenolysis) / CLEC7A (Dectin-1) induces NFAT activation / Activation of RAC1 downstream of NMDARs / negative regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / organelle localization by membrane tethering / mitochondrion-endoplasmic reticulum membrane tethering / autophagosome membrane docking / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / Synthesis of IP3 and IP4 in the cytosol / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / positive regulation of T cell receptor signaling pathway / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / calcineurin-mediated signaling / Negative regulation of NMDA receptor-mediated neuronal transmission / Unblocking of NMDA receptors, glutamate binding and activation / RHO GTPases activate PAKs / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / Uptake and function of anthrax toxins / regulation of ryanodine-sensitive calcium-release channel activity / Long-term potentiation / protein phosphatase activator activity / Calcineurin activates NFAT / Regulation of MECP2 expression and activity / DARPP-32 events / catalytic complex / Smooth Muscle Contraction / detection of calcium ion / potassium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / cellular response to interferon-beta / Protein methylation / calcium channel inhibitor activity / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / presynaptic cytosol / Ion homeostasis / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / eNOS activation / titin binding / Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) synthesis, recycling, salvage and regulation / immune system process / sperm midpiece / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / FCERI mediated Ca+2 mobilization / Ras activation upon Ca2+ influx through NMDA receptor / regulation of heart rate / FCGR3A-mediated IL10 synthesis / calyx of Held / Antigen activates B Cell Receptor (BCR) leading to generation of second messengers / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / regulation of cytokinesis / VEGFR2 mediated cell proliferation / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / VEGFR2 mediated vascular permeability / positive regulation of protein secretion / spindle microtubule / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / positive regulation of receptor signaling pathway via JAK-STAT / establishment of localization in cell / Stimuli-sensing channels / RAF activation / Transcriptional activation of mitochondrial biogenesis / defense response / response to calcium ion / potassium ion transport / RAS processing / cellular response to type II interferon / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.5 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lee CH / MacKinnon R | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Science / Year: 2018 Journal: Science / Year: 2018Title: Activation mechanism of a human SK-calmodulin channel complex elucidated by cryo-EM structures. Authors: Chia-Hsueh Lee / Roderick MacKinnon /  Abstract: Small-conductance Ca-activated K (SK) channels mediate neuron excitability and are associated with synaptic transmission and plasticity. They also regulate immune responses and the size of blood ...Small-conductance Ca-activated K (SK) channels mediate neuron excitability and are associated with synaptic transmission and plasticity. They also regulate immune responses and the size of blood cells. Activation of SK channels requires calmodulin (CaM), but how CaM binds and opens SK channels has been unclear. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of a human SK4-CaM channel complex in closed and activated states at 3.4- and 3.5-angstrom resolution, respectively. Four CaM molecules bind to one channel tetramer. Each lobe of CaM serves a distinct function: The C-lobe binds to the channel constitutively, whereas the N-lobe interacts with the S4-S5 linker in a Ca-dependent manner. The S4-S5 linker, which contains two distinct helices, undergoes conformational changes upon CaM binding to open the channel pore. These structures reveal the gating mechanism of SK channels and provide a basis for understanding SK channel pharmacology. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7538.map.gz emd_7538.map.gz | 96.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7538-v30.xml emd-7538-v30.xml emd-7538.xml emd-7538.xml | 19.6 KB 19.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_7538.png emd_7538.png | 187.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7538.cif.gz emd-7538.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_7538_additional.map.gz emd_7538_additional.map.gz | 76.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7538 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7538 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7538 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7538 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_7538_validation.pdf.gz emd_7538_validation.pdf.gz | 570.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_7538_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_7538_full_validation.pdf.gz | 570.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_7538_validation.xml.gz emd_7538_validation.xml.gz | 6.2 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_7538_validation.cif.gz emd_7538_validation.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7538 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7538 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7538 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-7538 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6cnnMC  7537C  7539C  6cnmC  6cnoC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7538.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7538.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | human SK4/calmodulin channel complex in the Ca2+ bound state I: sharpened, filtered map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
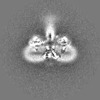
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.03 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
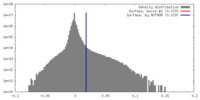
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: human SK4/calmodulin channel complex in the Ca2+ bound...
| File | emd_7538_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
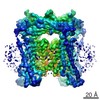
| Annotation | human SK4/calmodulin channel complex in the Ca2+ bound state I: unsharpened, unfiltered map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
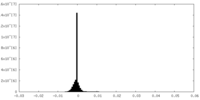
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human SK4/calmodulin channel complex
| Entire | Name: human SK4/calmodulin channel complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: human SK4/calmodulin channel complex
| Supramolecule | Name: human SK4/calmodulin channel complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 4
| Macromolecule | Name: Intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 4 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.758496 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGGDLVLGLG ALRRRKRLLE QEKSLAGWAL VLAGTGIGLM VLHAEMLWFG GCSWALYLFL VKCTISISTF LLLCLIVAFH AKEVQLFMT DNGLRDWRVA LTGRQAAQIV LELVVCGLHP APVRGPPCVQ DLGAPLTSPQ PWPGFLGQGE ALLSLAMLLR L YLVPRAVL ...String: MGGDLVLGLG ALRRRKRLLE QEKSLAGWAL VLAGTGIGLM VLHAEMLWFG GCSWALYLFL VKCTISISTF LLLCLIVAFH AKEVQLFMT DNGLRDWRVA LTGRQAAQIV LELVVCGLHP APVRGPPCVQ DLGAPLTSPQ PWPGFLGQGE ALLSLAMLLR L YLVPRAVL LRSGVLLNAS YRSIGALNQV RFRHWFVAKL YMNTHPGRLL LGLTLGLWLT TAWVLSVAER QAVNATGHLS DT LWLIPIT FLTIGYGDVV PGTMWGKIVC LCTGVMGVCC TALLVAVVAR KLEFNKAEKH VHNFMMDIQY TKEMKESAAR VLQ EAWMFY KHTRRKESHA ARRHQRKLLA AINAFRQVRL KHRKLREQVN SMVDISKMHM ILYDLQQNLS SSHRALEKQI DTLA GKLDA LTELLSTALG PRQLPEPSQQ SK UniProtKB: Intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 4 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(tri...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2S)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyloxy]propyl 2-(trimethylammonio)ethyl phosphate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: POV |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 760.076 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-POV: |
-Macromolecule #5: DODECYL-BETA-D-MALTOSIDE
| Macromolecule | Name: DODECYL-BETA-D-MALTOSIDE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 8 / Formula: LMT |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 510.615 Da |
| Chemical component information | 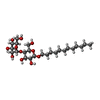 ChemComp-LMT: |
-Macromolecule #6: CALCIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: CALCIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: CA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 40.078 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 75.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


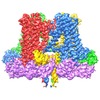


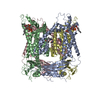
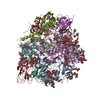























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)