[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
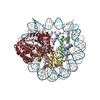
Yorodumi- EMDB-72473: Human nucleosome structure on Nickel-NTA lipid affinity grid (C1 ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human nucleosome structure on Nickel-NTA lipid affinity grid (C1 refinement) | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | deepEMhancer sharpened map | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Nucleosome / chromatin / DNA / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationnegative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere ...negative regulation of megakaryocyte differentiation / protein localization to CENP-A containing chromatin / Chromatin modifying enzymes / Replacement of protamines by nucleosomes in the male pronucleus / CENP-A containing nucleosome / Packaging Of Telomere Ends / Negative Regulation of CDH1 Gene Transcription / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected purine / Cleavage of the damaged purine / Deposition of new CENPA-containing nucleosomes at the centromere / telomere organization / Interleukin-7 signaling / Recognition and association of DNA glycosylase with site containing an affected pyrimidine / Cleavage of the damaged pyrimidine / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Opening / Inhibition of DNA recombination at telomere / Assembly of the ORC complex at the origin of replication / Meiotic synapsis / SUMOylation of chromatin organization proteins / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by the Human Silencing Hub (HUSH) complex / DNA methylation / Condensation of Prophase Chromosomes / Chromatin modifications during the maternal to zygotic transition (MZT) / SIRT1 negatively regulates rRNA expression / HCMV Late Events / ERCC6 (CSB) and EHMT2 (G9a) positively regulate rRNA expression / PRC2 methylates histones and DNA / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by KRAB-ZFP proteins / innate immune response in mucosa / Defective pyroptosis / HDACs deacetylate histones / Regulation of endogenous retroelements by Piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) / RNA Polymerase I Promoter Escape / Nonhomologous End-Joining (NHEJ) / Transcriptional regulation by small RNAs / Formation of the beta-catenin:TCF transactivating complex / Activated PKN1 stimulates transcription of AR (androgen receptor) regulated genes KLK2 and KLK3 / RUNX1 regulates genes involved in megakaryocyte differentiation and platelet function / HDMs demethylate histones / G2/M DNA damage checkpoint / NoRC negatively regulates rRNA expression / B-WICH complex positively regulates rRNA expression / PKMTs methylate histone lysines / DNA Damage/Telomere Stress Induced Senescence / Pre-NOTCH Transcription and Translation / Meiotic recombination / Activation of anterior HOX genes in hindbrain development during early embryogenesis / Metalloprotease DUBs / Transcriptional regulation of granulopoiesis / RMTs methylate histone arginines / HCMV Early Events / antimicrobial humoral immune response mediated by antimicrobial peptide / structural constituent of chromatin / UCH proteinases / antibacterial humoral response / heterochromatin formation / nucleosome / nucleosome assembly / E3 ubiquitin ligases ubiquitinate target proteins / Recruitment and ATM-mediated phosphorylation of repair and signaling proteins at DNA double strand breaks / HATs acetylate histones / RUNX1 regulates transcription of genes involved in differentiation of HSCs / Factors involved in megakaryocyte development and platelet production / gene expression / MLL4 and MLL3 complexes regulate expression of PPARG target genes in adipogenesis and hepatic steatosis / chromatin organization / Processing of DNA double-strand break ends / Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) / Oxidative Stress Induced Senescence / Estrogen-dependent gene expression / chromosome, telomeric region / defense response to Gram-positive bacterium / Ub-specific processing proteases / Amyloid fiber formation / protein heterodimerization activity / chromatin binding / enzyme binding / negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / protein-containing complex / extracellular space / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding / nucleus / membrane / cytosol Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.74 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Baker RW / Strauss JD / McGinty RK / Skrajna A | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2025Title: Nickel-NTA lipid-monolayer affinity grids allow for high-resolution structure determination by cryo-EM. Authors: Aleksandra Skrajna / Clara Lenger / Emily Robinson / Kevin Cannon / Reta Sarsam / Richard G Ouellette / Alberta M Abotsi / Patrick Brennwald / Robert K McGinty / Joshua D Strauss / Richard W Baker /  Abstract: Grid preparation is a rate-limiting step in determining high-resolution structures by single particle cryo-EM. Particle interaction with the air-water interface often leads to denaturation, ...Grid preparation is a rate-limiting step in determining high-resolution structures by single particle cryo-EM. Particle interaction with the air-water interface often leads to denaturation, aggregation, or a preferred orientation within the ice. Some samples yield insufficient quantities of particles when using traditional grid making techniques and require the use of solid supports that concentrate samples onto the grid. Recent advances in grid-preparation show that affinity grids are promising tools to selectively concentrate proteins while simultaneously protecting samples from the air-water interface. One such technique utilizes lipid monolayers containing a lipid species with an affinity handle. Some of the first affinity grids used a holey carbon layer coated with nickel nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) lipid, which allowed for the binding of proteins bearing the commonly used poly-histidine affinity tag. These studies however used complicated protocols and were conducted before the "resolution revolution" of cryo-EM. Here, we provide a straightforward preparation method and systematic analysis of Ni-NTA lipid monolayers as a tool for high-resolution single particle cryo-EM. We found the lipid affinity grids concentrate particles away from the AWI in thin ice (∼30 nm). We determined three structures ranging from 2.4 to 3.0 Å resolution, showing this method is amenable to high-resolution. Furthermore, we determined a 3.1 Å structure of a sub-100 kDa protein without symmetry, demonstrating the utility for a range of biological macromolecules. Lipid monolayers are therefore an easily extendable tool for most systems and help alleviate common problems such as low yield, disruption by the air-water interface, and thicker ice. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_72473.map.gz emd_72473.map.gz | 54.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-72473-v30.xml emd-72473-v30.xml emd-72473.xml emd-72473.xml | 27.4 KB 27.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_72473.png emd_72473.png | 144.7 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_72473_msk_1.map emd_72473_msk_1.map | 64 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-72473.cif.gz emd-72473.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_72473_additional_1.map.gz emd_72473_additional_1.map.gz emd_72473_half_map_1.map.gz emd_72473_half_map_1.map.gz emd_72473_half_map_2.map.gz emd_72473_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.6 MB 49.7 MB 49.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-72473 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-72473 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-72473 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-72473 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9y47MC  9y45C  9y46C  9y48C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_72473.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_72473.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | deepEMhancer sharpened map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.91 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_72473_msk_1.map emd_72473_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: unsharpened full map
| File | emd_72473_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | unsharpened full map | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map 1
| File | emd_72473_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 1 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: half map 2
| File | emd_72473_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | half map 2 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human nucleosome
| Entire | Name: Human nucleosome |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human nucleosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Human nucleosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Human nucleosome core particle [Flag-His-tagged H2A (hH2A.D), H2B (hH2B.C), H3 (hH3.2), and H4 (hH4)] with a 185 bp 601 nucleosome positioning DNA sequence. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 220 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Histone H3.2
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H3.2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 Details: MSGRGKQGGKARAKAKTRSSRAGLQFPVGRVHRLLRKGNYAERVGAGAPVYLAAVLEYLTAEILELAGNAARDNKKTRIIPRHLQLAIRNDEELNKLLGKVTIAQGGVLPNIQAVLLPKKTESHHKAKGK Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 15.289904 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: ARTKQTARKS TGGKAPRKQL ATKAARKSAP ATGGVKKPHR YRPGTVALRE IRRYQKSTEL LIRKLPFQRL VREIAQDFKT DLRFQSSAV MALQEASEAY LVGLFEDTNL CAIHAKRVTI MPKDIQLARR IRGERA UniProtKB: Histone H3.2 |
-Macromolecule #2: Histone H4
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H4 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 Details: SGRGKGGKGLGKGGAKRHRKVLRDNIQGITKPAIRRLARRGGVKRISGLIYEETRGVLKVFLENVIRDAVTYTEHAKRKTVTAMDVVYALKRQGRTLYGFGG Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 11.263231 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SGRGKGGKGL GKGGAKRHRK VLRDNIQGIT KPAIRRLARR GGVKRISGLI YEETRGVLKV FLENVIRDAV TYTEHAKRKT VTAMDVVYA LKRQGRTLYG FGG UniProtKB: Histone H4 |
-Macromolecule #3: Histone H2A type 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2A type 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Details: human H2A.D with an N-terminal FLAG and HIS tag / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 17.55991 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GDYKDDDDKG SSHHHHHHSS GSGGGGGENL YFQGSGRGKQ GGKARAKAKT RSSRAGLQFP VGRVHRLLRK GNYAERVGAG APVYLAAVL EYLTAEILEL AGNAARDNKK TRIIPRHLQL AIRNDEELNK LLGKVTIAQG GVLPNIQAVL LPKKTESHHK A KGK UniProtKB: Histone H2A type 1 |
-Macromolecule #4: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I
| Macromolecule | Name: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 13.806018 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: PEPAKSAPAP KKGSKKAVTK AQKKDGKKRK RSRKESYSVY VYKVLKQVHP DTGISSKAMG IMNSFVNDIF ERIAGEASRL AHYNKRSTI TSREIQTAVR LLLPGELAKH AVSEGTKAVT KYTSSK UniProtKB: Histone H2B type 1-C/E/F/G/I |
-Macromolecule #5: Nucleosomal DNA - 185 bp
| Macromolecule | Name: Nucleosomal DNA - 185 bp / type: dna / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 57.118363 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DT) (DC)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DC) (DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DG) (DA)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DT)(DA) (DA)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG) (DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DA) (DG)(DC)(DT)(DG) (DT)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DG) (DC)(DG)(DG) (DC)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DG)(DG)(DA)(DT)(DT)(DC) (DT)(DC) (DG)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DG) (DG) (DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Macromolecule #6: Nucleosomal DNA - 185 bp
| Macromolecule | Name: Nucleosomal DNA - 185 bp / type: dna / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Classification: DNA |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 56.495992 KDa |
| Sequence | String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA) (DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT) ...String: (DA)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC) (DG)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DT)(DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DT)(DC) (DC)(DC)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DA) (DG) (DG)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DA) (DA)(DT)(DT)(DG)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DG)(DA) (DC)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DT) (DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DA)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DC)(DG) (DT)(DA)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DT)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DC)(DC)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DC)(DG)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DC)(DG)(DC)(DC) (DA)(DA)(DG)(DG)(DG) (DG)(DA)(DT)(DT) (DA)(DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DC)(DT)(DA)(DG)(DT) (DC)(DT)(DC)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DG)(DC)(DA) (DC)(DG)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DC)(DA)(DG)(DA)(DT) (DA)(DT)(DA)(DT)(DA)(DC)(DA) (DT)(DC) (DC)(DG)(DA)(DG)(DC)(DA)(DT)(DG)(DT)(DA) (DT)(DT)(DG)(DA)(DA)(DC)(DA)(DG) (DC) (DG)(DA)(DT) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.05 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil / Support film - Material: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS TALOS |
|---|---|
| Details | Beam tilt compensation enabled and calibrated using SerialEM |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 70.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 45000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)