[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-7100: The Structure of the Actin-Smooth Muscle Myosin Motor Domain Comp... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-7100 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | The Structure of the Actin-Smooth Muscle Myosin Motor Domain Complex in the Rigor State | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Muscle alpha-actin decorated with the motor domain of chicken gizzard smooth muscle myosin II | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ADP-F-actin / apo-myosin / helix muscle / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationelastic fiber assembly / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / myofibril assembly / myosin light chain binding / myosin II binding / muscle myosin complex / myosin filament / actomyosin structure organization / myosin II complex / cardiac muscle cell development ...elastic fiber assembly / skeletal muscle myosin thick filament assembly / myofibril assembly / myosin light chain binding / myosin II binding / muscle myosin complex / myosin filament / actomyosin structure organization / myosin II complex / cardiac muscle cell development / structural constituent of muscle / cytoskeletal motor activator activity / microfilament motor activity / myosin heavy chain binding / tropomyosin binding / myofibril / actin filament bundle / troponin I binding / filamentous actin / mesenchyme migration / skeletal muscle myofibril / actin filament bundle assembly / smooth muscle contraction / striated muscle thin filament / skeletal muscle thin filament assembly / actin monomer binding / skeletal muscle fiber development / stress fiber / titin binding / actin filament polymerization / actin filament / filopodium / ADP binding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on acid anhydrides to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / calcium-dependent protein binding / actin filament binding / lamellipodium / actin binding / cell body / calmodulin binding / protein domain specific binding / hydrolase activity / calcium ion binding / positive regulation of gene expression / magnesium ion binding / ATP binding / identical protein binding / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.0 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Taylor KA / Banerjee C | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 6 items United States, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2017 Journal: J Struct Biol / Year: 2017Title: The structure of the actin-smooth muscle myosin motor domain complex in the rigor state. Authors: Chaity Banerjee / Zhongjun Hu / Zhong Huang / J Anthony Warrington / Dianne W Taylor / Kathleen M Trybus / Susan Lowey / Kenneth A Taylor /  Abstract: Myosin-based motility utilizes catalysis of ATP to drive the relative sliding of F-actin and myosin. The earliest detailed model based on cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) and X-ray crystallography ...Myosin-based motility utilizes catalysis of ATP to drive the relative sliding of F-actin and myosin. The earliest detailed model based on cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) and X-ray crystallography postulated that higher actin affinity and lever arm movement were coupled to closure of a feature of the myosin head dubbed the actin-binding cleft. Several studies since then using crystallography of myosin-V and cryoEM structures of F-actin bound myosin-I, -II and -V have provided details of this model. The smooth muscle myosin II interaction with F-actin may differ from those for striated and non-muscle myosin II due in part to different lengths of important surface loops. Here we report a ∼6 Å resolution reconstruction of F-actin decorated with the nucleotide-free recombinant smooth muscle myosin-II motor domain (MD) from images recorded using a direct electron detector. Resolution is highest for F-actin and the actin-myosin interface (3.5-4 Å) and lowest (∼6-7 Å) for those parts of the MD at the highest radius. Atomic models built into the F-actin density are quite comparable to those previously reported for rabbit muscle actin and show density from the bound ADP. The atomic model of the MD, is quite similar to a recently published structure of vertebrate non-muscle myosin II bound to F-actin and a crystal structure of nucleotide free myosin-V. Larger differences are observed when compared to the cryoEM structure of F-actin decorated with rabbit skeletal muscle myosin subfragment 1. The differences suggest less closure of the 50 kDa domain in the actin bound skeletal muscle myosin structure. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_7100.map.gz emd_7100.map.gz | 34.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-7100-v30.xml emd-7100-v30.xml emd-7100.xml emd-7100.xml | 17.9 KB 17.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
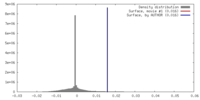
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_7100_fsc.xml emd_7100_fsc.xml | 14.4 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_7100.png emd_7100.png | 265.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-7100.cif.gz emd-7100.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7100 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7100 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7100 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-7100 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6bihMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_7100.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_7100.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
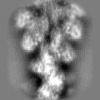
| Annotation | Muscle alpha-actin decorated with the motor domain of chicken gizzard smooth muscle myosin II | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
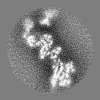
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.9861 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Filamentous muscle alpha-actin decorated with the motor domain of...
| Entire | Name: Filamentous muscle alpha-actin decorated with the motor domain of recombinant smooth muscle myosin II motor domain expressed in Sf9 cells |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Filamentous muscle alpha-actin decorated with the motor domain of...
| Supramolecule | Name: Filamentous muscle alpha-actin decorated with the motor domain of recombinant smooth muscle myosin II motor domain expressed in Sf9 cells type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: alpha-actin
| Supramolecule | Name: alpha-actin / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: myosin II
| Supramolecule | Name: myosin II / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Myosin-11
| Macromolecule | Name: Myosin-11 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 91.343227 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MSQKPLSDDE KFLFVDKNFV NNPLAQADWS AKKLVWVPSE KHGFEAASIK EEKGDEVTVE LQENGKKVTL SKDDIQKMNP PKFSKVEDM AELTCLNEAS VLHNLRERYF SGLIYTYSGL FCVVINPYKQ LPIYSEKIID MYKGKKRHEM PPHIYAIADT A YRSMLQDR ...String: MSQKPLSDDE KFLFVDKNFV NNPLAQADWS AKKLVWVPSE KHGFEAASIK EEKGDEVTVE LQENGKKVTL SKDDIQKMNP PKFSKVEDM AELTCLNEAS VLHNLRERYF SGLIYTYSGL FCVVINPYKQ LPIYSEKIID MYKGKKRHEM PPHIYAIADT A YRSMLQDR EDQSILCTGE SGAGKTENTK KVIQYLAVVA SSHKGKKDTS ITQGPSFSYG ELEKQLLQAN PILEAFGNAK TV KNDNSSR FGKFIRINFD VTGYIVGANI ETYLLEKSRA IRQAKDERTF HIFYYLIAGA SEQMRNDLLL EGFNNYTFLS NGH VPIPAQ QDDEMFQETL EAMTIMGFTE EEQTSILRVV SSVLQLGNIV FKKERNTDQA SMPDNTAAQK VCHLMGINVT DFTR SILTP RIKVGRDVVQ KAQTKEQADF AIEALAKAKF ERLFRWILTR VNKALDKTKR QGASFLGILD IAGFEIFEIN SFEQL CINY TNEKLQQLFN HTMFILEQEE YQREGIEWNF IDFGLDLQPC IELIERPTNP PGVLALLDEE CWFPKATDTS FVEKLI QEQ GNHAKFQKSK QLKDKTEFCI LHYAGKVTYN ASAWLTKNMD PLNDNVTSLL NQSSDKFVAD LWKDVDRIVG LDQMAKM TE SSLPSASKTK KGMFRTVGQL YKEQLTKLMT TLRNTNPNFV RCIIPNHEKR AGKLDAHLVL EQLRCNGVLE GIRICRQG F PNRIVFQEFR QRYEILAANA IPKGFMDGKQ ACILMIKALE LDPNLYRIGQ SKIFFRTGVL AHLEEERDLD YKDDDDK UniProtKB: Myosin-11 |
-Macromolecule #2: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle
| Macromolecule | Name: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 42.096953 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLDSGD G VTHNVPIY ...String: MCDEDETTAL VCDNGSGLVK AGFAGDDAPR AVFPSIVGRP RHQGVMVGMG QKDSYVGDEA QSKRGILTLK YPIEHGIITN WDDMEKIWH HTFYNELRVA PEEHPTLLTE APLNPKANRE KMTQIMFETF NVPAMYVAIQ AVLSLYASGR TTGIVLDSGD G VTHNVPIY EGYALPHAIM RLDLAGRDLT DYLMKILTER GYSFVTTAER EIVRDIKEKL CYVALDFENE MATAASSSSL EK SYELPDG QVITIGNERF RCPETLFQPS FIGMESAGIH ETTYNSIMKC DIDIRKDLYA NNVMSGGTTM YPGIADRMQK EIT ALAPST MKIKIIAPPE RKYSVWIGGS ILASLSTFQQ MWITKQEYDE AGPSIVHRKC F UniProtKB: Actin, alpha skeletal muscle |
-Macromolecule #3: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: ADENOSINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ADP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 427.201 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ADP: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 Details: actin buffer: 10 mM imidazole, 10 mM KCl, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM DTT, pH 7.4, myosin buffer: 10 mM imidazole, 10 mM KCl, 1.0 mM MgCl2, 1.0 mM EGTA, 0.5 mM DTT, pH 7.0 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 276 K / Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 Details: Some specimens were frozen manually using a homemade plunger.. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-20 (5k x 3k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-43 / Number real images: 4000 / Average exposure time: 1.34 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 / Details: Only 1417 of the 4000 recorded images were used. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 5.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 2.2 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Overall B value: 390.86 |
|---|---|
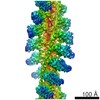
| Output model |  PDB-6bih: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)