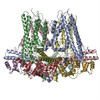
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-70275タイトル Cryo-EM structure of KCa3.1/calmodulin channel in complex with NS309 Cryo-EM map of KCa3.1/calmodulin channel in complex with NS309 複合体 : Human Ca3.1/calmodulin channel in complex with NS309タンパク質・ペプチド : Intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel protein 4タンパク質・ペプチド : Calmodulin-1リガンド : POTASSIUM IONリガンド : (3E)-6,7-dichloro-3-(hydroxyimino)-1,3-dihydro-2H-indol-2-oneリガンド : CALCIUM ION / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト) / Rattus norvegicus (ドブネズミ)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.59 Å Nam YW / Zhang M 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 American Heart Association 23AIREA1039423 American Heart Association 24CDA1260237 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NIH/NINDS) 4R33 NS101182-03 National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NIH/NINDS) R15 NS130420-01A1
ジャーナル : Res Sq / 年 : 2025タイトル : Structural basis for the subtype-selectivity of K2.2 channel activators.著者 : Miao Zhang / Young-Woo Nam / Alena Ramanishka / Yang Xu / Rose Marie Yasuda / Dohyun Im / Meng Cui / George Chandy / Heike Wulff / 要旨 : Small-conductance (K2.2) and intermediate-conductance (K3.1) Ca-activated K channels are gated by a Ca-calmodulin dependent mechanism. NS309 potentiates the activity of both K2.2 and K3.1, while ... Small-conductance (K2.2) and intermediate-conductance (K3.1) Ca-activated K channels are gated by a Ca-calmodulin dependent mechanism. NS309 potentiates the activity of both K2.2 and K3.1, while rimtuzalcap selectively activates K2.2. Rimtuzalcap has been used in clinical trials for the treatment of spinocerebellar ataxia and essential tremor. We report cryo-electron microscopy structures of K2.2 channels bound with NS309 and rimtuzalcap, in addition to K3.1 channels with NS309. The different conformations of calmodulin and the cytoplasmic HC helices in the two channels underlie the subtype-selectivity of rimtuzalcap for K2.2. Calmodulin's N-lobes in the K2.2 structure are far apart and undergo conformational changes to accommodate either NS309 or rimtuzalcap. Calmodulin's Nlobes in the K3.1 structure are closer to each other and are constrained by the HC helices of K3.1, which allows binding of NS309 but not of the bulkier rimtuzalcap. These structures provide a framework for structure-based drug design targeting K2.2 channels. 履歴 登録 2025年4月19日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2025年6月18日 - マップ公開 2025年6月18日 - 更新 2025年6月25日 - 現状 2025年6月25日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト) /
Homo sapiens (ヒト) / 
 データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 4件
米国, 4件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Res Sq / 年: 2025
ジャーナル: Res Sq / 年: 2025
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_70275.map.gz
emd_70275.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-70275-v30.xml
emd-70275-v30.xml emd-70275.xml
emd-70275.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_70275.png
emd_70275.png emd-70275.cif.gz
emd-70275.cif.gz emd_70275_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_70275_half_map_1.map.gz emd_70275_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_70275_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70275
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70275 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70275
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-70275 emd_70275_validation.pdf.gz
emd_70275_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_70275_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_70275_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_70275_validation.xml.gz
emd_70275_validation.xml.gz emd_70275_validation.cif.gz
emd_70275_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70275
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70275 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70275
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-70275 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_70275.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 476.8 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_70275.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 476.8 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー














 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)