[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-63543: Cryo-EM structure of neurotensin receptor 1 in complex with beta-... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 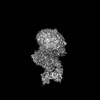 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of neurotensin receptor 1 in complex with beta-arrestin 1 | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | GPCR / Neurotensin receptore 1 / Complex / beta-arrestin 1 / Phosphorylation / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationG protein-coupled neurotensin receptor activity / inositol phosphate catabolic process / symmetric synapse / angiotensin receptor binding / D-aspartate import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / positive regulation of arachidonate secretion / L-glutamate import across plasma membrane ...G protein-coupled neurotensin receptor activity / inositol phosphate catabolic process / symmetric synapse / angiotensin receptor binding / D-aspartate import across plasma membrane / positive regulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid secretion / TGFBR3 regulates TGF-beta signaling / Activation of SMO / positive regulation of arachidonate secretion / L-glutamate import across plasma membrane / negative regulation of interleukin-8 production / regulation of respiratory gaseous exchange / positive regulation of inhibitory postsynaptic potential / negative regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure / arrestin family protein binding / G protein-coupled receptor internalization / negative regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / positive regulation of glutamate secretion / regulation of membrane depolarization / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / : / response to lipid / stress fiber assembly / positive regulation of cardiac muscle hypertrophy / positive regulation of inositol phosphate biosynthetic process / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / temperature homeostasis / positive regulation of Rho protein signal transduction / detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain / pseudopodium / negative regulation of interleukin-6 production / positive regulation of receptor internalization / negative regulation of Notch signaling pathway / neuropeptide signaling pathway / insulin-like growth factor receptor binding / clathrin-coated pit / negative regulation of protein ubiquitination / enzyme inhibitor activity / GTPase activator activity / Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol / dendritic shaft / learning / adult locomotory behavior / electron transport chain / Signaling by high-kinase activity BRAF mutants / MAP2K and MAPK activation / G protein-coupled receptor binding / G protein-coupled receptor activity / cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane / positive regulation of protein phosphorylation / terminal bouton / Signaling by RAF1 mutants / Signaling by moderate kinase activity BRAF mutants / Paradoxical activation of RAF signaling by kinase inactive BRAF / Signaling downstream of RAS mutants / endocytic vesicle membrane / Signaling by BRAF and RAF1 fusions / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / protein transport / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / Thrombin signalling through proteinase activated receptors (PARs) / cytoplasmic vesicle / G alpha (s) signalling events / G alpha (q) signalling events / dendritic spine / ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / chemical synaptic transmission / molecular adaptor activity / proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process / perikaryon / transcription coactivator activity / electron transfer activity / periplasmic space / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / Ub-specific processing proteases / nuclear body / positive regulation of apoptotic process / protein ubiquitination / iron ion binding / membrane raft / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / Golgi membrane / lysosomal membrane / heme binding / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / positive regulation of gene expression / regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / negative regulation of apoptotic process / chromatin / protein-containing complex binding / cell surface / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / signal transduction / positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II / nucleoplasm / identical protein binding Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.41 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Sun DM / Li X / Yuan QN / Tian CL | |||||||||
| Funding support | 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2025 Journal: Cell Res / Year: 2025Title: Molecular mechanism of the arrestin-biased agonism of neurotensin receptor 1 by an intracellular allosteric modulator. Authors: Demeng Sun / Xiang Li / Qingning Yuan / Yuanxia Wang / Pan Shi / Huanhuan Zhang / Tao Wang / Wenjing Sun / Shenglong Ling / Yuanchun Liu / Jinglin Lai / Wenqin Xie / Wanchao Yin / Lei Liu / ...Authors: Demeng Sun / Xiang Li / Qingning Yuan / Yuanxia Wang / Pan Shi / Huanhuan Zhang / Tao Wang / Wenjing Sun / Shenglong Ling / Yuanchun Liu / Jinglin Lai / Wenqin Xie / Wanchao Yin / Lei Liu / H Eric Xu / Changlin Tian /  Abstract: Biased allosteric modulators (BAMs) of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been at the forefront of drug discovery owing to their potential to selectively stimulate therapeutically relevant ...Biased allosteric modulators (BAMs) of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) have been at the forefront of drug discovery owing to their potential to selectively stimulate therapeutically relevant signaling and avoid on-target side effects. Although structures of GPCRs in complex with G protein or GRK in a BAM-bound state have recently been resolved, revealing that BAM can induce biased signaling by directly modulating interactions between GPCRs and these two transducers, no BAM-bound GPCR-arrestin complex structure has yet been determined, limiting our understanding of the full pharmacological profile of BAMs. Herein, we developed a chemical protein synthesis strategy to generate neurotensin receptor 1 (NTSR1) with defined hexa-phosphorylation at its C-terminus and resolved high-resolution cryo-EM structures (2.65-2.88 Å) of NTSR1 in complex with both β-arrestin1 and the BAM SBI-553. These structures revealed a unique "loop engagement" configuration of β-arrestin1 coupling to NTSR1 in the presence of SBI-553, markedly different from the typical "core engagement" configuration observed in the absence of BAMs. This configuration is characterized by the engagement of the intracellular loop 3 of NTSR1 with a cavity in the central crest of β-arrestin1, representing a previously unobserved, arrestin-selective conformation of GPCR. Our findings fill the critical knowledge gap regarding the regulation of GPCR-arrestin interactions and biased signaling by BAMs, which would advance the development of safer and more efficacious GPCR-targeted therapeutics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_63543.map.gz emd_63543.map.gz | 146.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-63543-v30.xml emd-63543-v30.xml emd-63543.xml emd-63543.xml | 19.3 KB 19.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_63543.png emd_63543.png | 88.5 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-63543.cif.gz emd-63543.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_63543_half_map_1.map.gz emd_63543_half_map_1.map.gz emd_63543_half_map_2.map.gz emd_63543_half_map_2.map.gz | 144.2 MB 144.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63543 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63543 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63543 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-63543 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9m0dMC  8zytC  8zyuC  8zyyC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_63543.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 155.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_63543.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 155.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.82 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_63543_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_63543_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of neurotensin receptor 1 with beta-arrestin 1 an...
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of neurotensin receptor 1 with beta-arrestin 1 and Fab30 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of neurotensin receptor 1 with beta-arrestin 1 an...
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of neurotensin receptor 1 with beta-arrestin 1 and Fab30 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Soluble cytochrome b562,Neurotensin receptor type 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Soluble cytochrome b562,Neurotensin receptor type 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 62.097848 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism: Mammalian expression vector Flag-MCS-pcDNA3.1 (others) |
| Sequence | String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFAGSAD LEDNWETLND NLKVIEKADN AAQVKDALTK MRAAALDAQK ATPPKLEDKS PDSPEMKDFR HGFDILVGQ IDDALKLANE GKVKEAQAAA EQLKTTRNAY IQKYLASGSL EVLFQGPMRL NSSAPGTPGT PAADPFQRAQ A GLEEALLA ...String: MKTIIALSYI FCLVFAGSAD LEDNWETLND NLKVIEKADN AAQVKDALTK MRAAALDAQK ATPPKLEDKS PDSPEMKDFR HGFDILVGQ IDDALKLANE GKVKEAQAAA EQLKTTRNAY IQKYLASGSL EVLFQGPMRL NSSAPGTPGT PAADPFQRAQ A GLEEALLA PGFGNASGNA SERVLAAPSS ELDVNTDIYS KVLVTAVYLA LFVVGTVGNT VTAFTLARKK SLQSLQSTVH YH LGSLALS DLLTLLLAMP VELYNFIWVH HPWAFGDAGC RGYYFLRDAC TYATALNVAS LSVERYLALC HPFKAKTLMS RSR TKKFIS AIWLASALLA VPMLFTMGEQ NRSADGQHAG GLVCTPTIHT ATVKVVIQVN TFMSFIFPMV VISVLNTIIA NKLT VMVRQ AAEQGQVCTV GGEHSTFSMA IEPGRVQALR HGVRVLRAVV IAFVVCWLPY HVRRLMFCYI SDEQWTPFLY DFYHY FYMV TNALFYVSST INPILYNLVS ANFRHIFLAT LACLCPVWRR RRKRPCFNAF SRKCD(SEP)V(SEP)(SEP)N H (TPO)L(SEP)(SEP)NATR ETLY UniProtKB: Soluble cytochrome b562, Neurotensin receptor type 1 |
-Macromolecule #2: Beta-arrestin-1
| Macromolecule | Name: Beta-arrestin-1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.224598 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGSHHHHHHH HGSLEVLFQG PGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLD VLGLTFRKDL FVANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA C GVDYEVKA ...String: MGSHHHHHHH HGSLEVLFQG PGDKGTRVFK KASPNGKLTV YLGKRDFVDH IDLVDPVDGV VLVDPEYLKE RRVYVTLTCA FRYGREDLD VLGLTFRKDL FVANVQSFPP APEDKKPLTR LQERLIKKLG EHAYPFTFEI PPNLPCSVTL QPGPEDTGKA C GVDYEVKA FCAENLEEKI HKRNSVRLVI RKVQYAPERP GPQPTAETTR QFLMSDKPLH LEASLDKEIY YHGEPISVNV HV TNNTNKT VKKIKISVRQ YADICLFNTA QYKCPVAMEE ADDTVAPSST FCKVYTLTPF LANNREKRGL ALDGKLKHED TNL ASSTLL REGANREILG IIVSYKVKVK LVVSRGGLLG DLASSDVAVE LPFTLMHPKP KEEPPHREVP ENETPVDTNL IELD TN UniProtKB: Beta-arrestin-1 |
-Macromolecule #3: Fab30 heavy chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 heavy chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 27.72701 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVSAIVLYVL LAAAAHSAFA EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NVYSSSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VASISSYYGY TYYADSVKG RFTISADTSK NTAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARSRQFWYSG LDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK S TSGGTAAL ...String: MVSAIVLYVL LAAAAHSAFA EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NVYSSSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VASISSYYGY TYYADSVKG RFTISADTSK NTAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARSRQFWYSG LDYWGQGTLV TVSSASTKGP SVFPLAPSSK S TSGGTAAL GCLVKDYFPE PVTVSWNSGA LTSGVHTFPA VLQSSGLYSL SSVVTVPSSS LGTQTYICNV NHKPSNTKVD KK VEPKSCD KTAAAHHHHH HHH |
-Macromolecule #4: Fab30 light chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Fab30 light chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.422467 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MVSAIVLYVL LAAAAHSAFA SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSG TDFTLTISSL NPEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN F YPREAKVQ ...String: MVSAIVLYVL LAAAAHSAFA SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSG TDFTLTISSL NPEDFATYYC QQYKYVPVTF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN F YPREAKVQ WKVDNALQSG NSQESVTEQD SKDSTYSLSS TLTLSKADYE KHKVYACEVT HQGLSSPVTK SFNRGEC |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.41 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 6359592 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
| Final angle assignment | Type: ANGULAR RECONSTITUTION |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































