+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
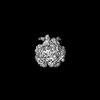
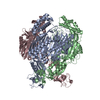
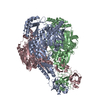
| Title | Cryo-EM map of human PNPase in closed form | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease / RNA degradation / RNA import / mitochondria / RNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.94 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Li YC / Yuan HS | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Taiwan, 1 items Taiwan, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2025 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2025Title: Structural insights into human PNPase in health and disease. Authors: Yi-Ching Li / Chun-Hsiung Wang / Malay Patra / Yi-Ping Chen / Wei-Zen Yang / Hanna S Yuan /  Abstract: Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase) is a 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease located in mitochondria, where it plays crucial roles in RNA degradation and RNA import. Mutations in hPNPase can impair ...Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase) is a 3'-to-5' exoribonuclease located in mitochondria, where it plays crucial roles in RNA degradation and RNA import. Mutations in hPNPase can impair these functions, leading to various mitochondrial dysfunctions and diseases. However, the mechanisms by which hPNPase switches between its roles as an RNA-degrading enzyme and an RNA carrier, as well as how disease-associated mutations may affect these distinct functions, remain unclear. In this study, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of hPNPase, highlighting the flexibility of its S1 domains, which cap the ring-like RNA-degradation chamber and shift between two distinctive open and closed conformations. We further demonstrate by small-angle X-ray scattering and biochemical analyses that the disease-associated mutations P467S and G499R impair hPNPase's stem-loop RNA-binding and degradation activities by limiting the S1 domain's ability to transition from an open to closed state. Conversely, the D713Y mutation, located within the S1 domain, does not affect the RNA-binding affinity of hPNPase, but diminishes its interaction with Suv3 helicase for cooperative degradation of structured RNA. Collectively, these findings underscore the critical role of S1 domain mobility in capturing structured RNA for degradation and import, as well as its involvement in mitochondrial degradosome assembly. Our study thereby reveals the molecular mechanism of hPNPase in RNA binding and degradation, and the multiple molecular defects that could be induced by disease-linked mutations in hPNPase. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_62373.map.gz emd_62373.map.gz | 106.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-62373-v30.xml emd-62373-v30.xml emd-62373.xml emd-62373.xml | 12.6 KB 12.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_62373_fsc.xml emd_62373_fsc.xml | 12.8 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_62373.png emd_62373.png | 76.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-62373.cif.gz emd-62373.cif.gz | 4.9 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_62373_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62373_half_map_1.map.gz emd_62373_half_map_2.map.gz emd_62373_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.7 MB 200.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62373 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62373 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62373 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-62373 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_62373.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_62373.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 216 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.83 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_62373_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_62373_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human PNPase in closed form
| Entire | Name: Human PNPase in closed form |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human PNPase in closed form
| Supramolecule | Name: Human PNPase in closed form / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase)
| Macromolecule | Name: Human polynucleotide phosphorylase (hPNPase) / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MGAVAVDLGN RKLEISSGKL ARFADGSAVV QSGDTAVMVT AVSKTKPSPS QFMPLVVDYR QKAAAAGRI PTNYLRREVG TSDKEILTSR IIDRSIRPLF PAGYFYDTQV LCNLLAVDGV N EPDVLAIN GASVALSLSD IPWNGPVGAV RIGIIDGEYV VNPTRKEMSS ...String: MGAVAVDLGN RKLEISSGKL ARFADGSAVV QSGDTAVMVT AVSKTKPSPS QFMPLVVDYR QKAAAAGRI PTNYLRREVG TSDKEILTSR IIDRSIRPLF PAGYFYDTQV LCNLLAVDGV N EPDVLAIN GASVALSLSD IPWNGPVGAV RIGIIDGEYV VNPTRKEMSS STLNLVVAGA PK SQIVMLE ASAENILQQD FCHAIKVGVK YTQQIIQGIQ QLVKETGVTK RTPQKLFTPS PEI VKYTHK LAMERLYAVF TDYEHDKVSR DEAVNKIRLD TEEQLKEKFP EADPYEIIES FNVV AKEVF RSIVLNEYKR CDGRDLTSLR NVSCEVDMFK TLHGSALFQR GQTQVLCTVT FDSLE SGIK SDQVITAING IKDKNFMLHY EFPPYATNEI GKVTGLNRRE LGHGALAEKA LYPVIP RDF PFTIRVTSEV LESNGSSSMA SACGGSLALM DSGVPISSAV AGVAIGLVTK TDPEKGE IE DYRLLTDILG IEDYNGDMDF KIAGTNKGIT ALQADIKLPG IPIKIVMEAI QQASVAKK E ILQIMNKTIS KPRASRKENG PVVETVQVPL SKRAKFVGPG GYNLKKLQAE TGVTISQVD EETFSVFAPT PSAMHEARDF ITEICKDDQE QQLEFGAVYT ATITEIRDTG VMVKLYPNMT AVLLHNTQL DQRKIKHPTA LGLEVGQEIQ VKYFGRDPAD GRMRLSRKVL QSPATTVVRT L NDRSSIVM GEPISQSSSN SQAAALEHHH HHH |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





































