[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-6206: Structure of 20S supercomplex determined by single particle cryoe... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-6206 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
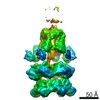
| Title | Structure of 20S supercomplex determined by single particle cryoelectron microscopy, state I | |||||||||
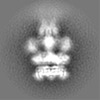
 Map data Map data | Map of 20S supercomplex, state I. This map is unsharpened and unfiltered. The map was normalized using the program MAPMAN. | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | vesicle trafficking | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationexocytic insertion of neurotransmitter receptor to postsynaptic membrane / trans-Golgi Network Vesicle Budding / regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / Intra-Golgi traffic / Retrograde transport at the Trans-Golgi-Network / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / soluble NSF attachment protein activity / BLOC-1 complex / myosin head/neck binding ...exocytic insertion of neurotransmitter receptor to postsynaptic membrane / trans-Golgi Network Vesicle Budding / regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / Intra-Golgi traffic / Retrograde transport at the Trans-Golgi-Network / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / soluble NSF attachment protein activity / BLOC-1 complex / myosin head/neck binding / Lysosome Vesicle Biogenesis / zymogen granule membrane / synaptic vesicle fusion to presynaptic active zone membrane / storage vacuole / Other interleukin signaling / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a-complexin II complex / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a complex / presynaptic dense core vesicle exocytosis / synaptobrevin 2-SNAP-25-syntaxin-1a-complexin I complex / extrinsic component of presynaptic membrane / calcium ion-regulated exocytosis of neurotransmitter / Glutamate Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / Norepinephrine Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / Acetylcholine Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / Serotonin Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / COPII-mediated vesicle transport / GABA synthesis, release, reuptake and degradation / positive regulation of catecholamine secretion / positive regulation of norepinephrine secretion / Dopamine Neurotransmitter Release Cycle / SNARE complex disassembly / synaptic vesicle docking / eosinophil degranulation / Golgi Associated Vesicle Biogenesis / regulation of synaptic vesicle priming / regulated exocytosis / Insertion of tail-anchored proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane / vesicle-mediated transport in synapse / protein-containing complex disassembly / regulation of establishment of protein localization / positive regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis / ribbon synapse / positive regulation of intracellular protein transport / regulation of vesicle-mediated transport / vesicle docking / Cargo recognition for clathrin-mediated endocytosis / chloride channel inhibitor activity / secretion by cell / regulation of exocytosis / Clathrin-mediated endocytosis / SNARE complex / SNAP receptor activity / calcium-ion regulated exocytosis / vesicle fusion / positive regulation of ATP-dependent activity / ATP-dependent protein disaggregase activity / actomyosin / hormone secretion / LGI-ADAM interactions / positive regulation of hormone secretion / intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport / Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport / ATP-dependent protein binding / Golgi stack / response to cholesterol / neurotransmitter secretion / protein localization to membrane / clathrin-coated vesicle / apical protein localization / syntaxin binding / vesicle-fusing ATPase / syntaxin-1 binding / insulin secretion / Neutrophil degranulation / regulation of synaptic vesicle recycling / endosomal transport / SNARE complex assembly / myosin binding / positive regulation of neurotransmitter secretion / neurotransmitter transport / regulation of synapse assembly / response to gravity / regulation of neuron projection development / synaptic vesicle priming / neuron projection terminus / exocytosis / positive regulation of receptor recycling / protein sumoylation / positive regulation of exocytosis / synaptic vesicle exocytosis / modulation of excitatory postsynaptic potential / associative learning / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / synaptic vesicle endocytosis / long-term memory / postsynaptic cytosol / response to glucose / axonal growth cone / calcium channel inhibitor activity / vesicle-mediated transport Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 7.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zhao M / Wu S / Zhou Q / Vivona S / Cipriano DJ / Cheng Y / Brunger AT | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2015 Journal: Nature / Year: 2015Title: Mechanistic insights into the recycling machine of the SNARE complex. Authors: Minglei Zhao / Shenping Wu / Qiangjun Zhou / Sandro Vivona / Daniel J Cipriano / Yifan Cheng / Axel T Brunger /  Abstract: Evolutionarily conserved SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptors) proteins form a complex that drives membrane fusion in eukaryotes. The ATPase NSF (N- ...Evolutionarily conserved SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor attachment protein receptors) proteins form a complex that drives membrane fusion in eukaryotes. The ATPase NSF (N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor), together with SNAPs (soluble NSF attachment protein), disassembles the SNARE complex into its protein components, making individual SNAREs available for subsequent rounds of fusion. Here we report structures of ATP- and ADP-bound NSF, and the NSF/SNAP/SNARE (20S) supercomplex determined by single-particle electron cryomicroscopy at near-atomic to sub-nanometre resolution without imposing symmetry. Large, potentially force-generating, conformational differences exist between ATP- and ADP-bound NSF. The 20S supercomplex exhibits broken symmetry, transitioning from six-fold symmetry of the NSF ATPase domains to pseudo four-fold symmetry of the SNARE complex. SNAPs interact with the SNARE complex with an opposite structural twist, suggesting an unwinding mechanism. The interfaces between NSF, SNAPs, and SNAREs exhibit characteristic electrostatic patterns, suggesting how one NSF/SNAP species can act on many different SNARE complexes. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_6206.map.gz emd_6206.map.gz | 6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-6206-v30.xml emd-6206-v30.xml emd-6206.xml emd-6206.xml | 17.4 KB 17.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_6206.png emd_6206.png | 119.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_6206_additional_1.map.gz emd_6206_additional_1.map.gz | 7.4 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6206 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6206 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6206 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-6206 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 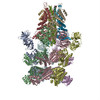 3j96MC 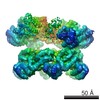 6204C  6205C 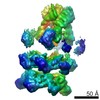 6207C 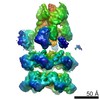 6208C 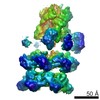 6209C 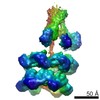 6210C 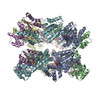 3j94C 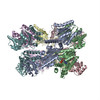 3j95C 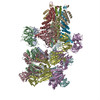 3j97C  3j98C  3j99C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_6206.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 7.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_6206.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 7.8 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
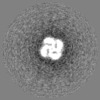
| Annotation | Map of 20S supercomplex, state I. This map is unsharpened and unfiltered. The map was normalized using the program MAPMAN. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
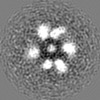
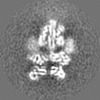
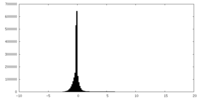
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 2.4312 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
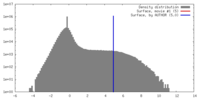
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Supplemental map: emd 6206 additional 1.map
| File | emd_6206_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
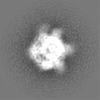
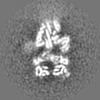
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
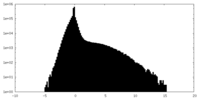
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : 20S supercomplex consisting of truncated neuronal SNARE complex, ...
| Entire | Name: 20S supercomplex consisting of truncated neuronal SNARE complex, alpha-SNAP, and N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor (NSF) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: 20S supercomplex consisting of truncated neuronal SNARE complex, ...
| Supramolecule | Name: 20S supercomplex consisting of truncated neuronal SNARE complex, alpha-SNAP, and N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor (NSF) type: sample / ID: 1000 Oligomeric state: One hexamer of NSF + four alpha-SNAP molecules + one SNARE complex Number unique components: 5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 660 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor
| Macromolecule | Name: N-ethylmaleimide sensitive factor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: NSF / Number of copies: 6 / Oligomeric state: hexamer / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 83 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Vesicle-fusing ATPase |
-Macromolecule #2: alpha Soluble NSF Attachment Protein
| Macromolecule | Name: alpha Soluble NSF Attachment Protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: alpha-SNAP / Number of copies: 4 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 33 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Alpha-soluble NSF attachment protein |
-Macromolecule #3: Syntaxin-1A
| Macromolecule | Name: Syntaxin-1A / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: Stx-1A / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Syntaxin-1A |
-Macromolecule #4: Synaptobrevin-2
| Macromolecule | Name: Synaptobrevin-2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Name.synonym: Syb-2, VAMP-2 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Vesicle-associated membrane protein 2 |
-Macromolecule #5: Synaptosomal-associated protein 25
| Macromolecule | Name: Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 5 / Name.synonym: SNAP-25 / Number of copies: 1 / Recombinant expression: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | UniProtKB: Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 15 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 Details: 50 mM Tris-Cl, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM AMPPNP, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT, 0.05% v/v Nonident P-40 |
| Grid | Details: Holey carbon on top of 400 mesh copper grid |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 90 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I / Method: Blot for 3.5 seconds before plunging. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Date | Jan 28, 2014 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 44 e/Å2 Details: Gatan K2 Summit in super-resolution counting mode. Motion correction as described in Li et al. (2013) Nature Methods. |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.3 mm / Nominal defocus max: -2.8 µm / Nominal defocus min: -1.8 µm / Nominal magnification: 31000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: OTHER |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Details | 3D classification, refinement, and reconstruction were performed using RELION. |
|---|---|
| CTF correction | Details: Each particle |
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 7.6 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: RELION / Number images used: 29717 |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, PHENIX |
| Details | D2 domain of NSF was from crystal structure 1NSF. D1 domain of NSF was from related entry EMD-6204. N domain of NSF was from crystal structure 1QCS. aSNAP was a homology model. SNARE complex was from crystal structure 1N7S. |
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: R-factor |
| Output model |  PDB-3j96: |
-Atomic model buiding 2
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - Chain ID: A |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, PHENIX |
| Details | D2 domain of NSF was from crystal structure 1NSF. D1 domain of NSF was from related entry EMD-6204. N domain of NSF was from crystal structure 1QCS. aSNAP was a homology model. SNARE complex was from crystal structure 1N7S. |
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: R-factor |
| Output model |  PDB-3j96: |
-Atomic model buiding 3
| Initial model | PDB ID: Chain - #0 - Chain ID: A / Chain - #1 - Chain ID: B / Chain - #2 - Chain ID: C / Chain - #3 - Chain ID: D |
|---|---|
| Software | Name: Chimera, PHENIX |
| Details | D2 domain of NSF was from crystal structure 1NSF. D1 domain of NSF was from related entry EMD-6204. N domain of NSF was from crystal structure 1QCS. aSNAP was a homology model. SNARE complex was from crystal structure 1N7S. |
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: R-factor |
| Output model |  PDB-3j96: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)