[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-52109: SV40 LTAg complex with ADP and DNA (3D variability component_000,... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | SV40 LTAg complex with ADP and DNA (3D variability component_000, frame_019). | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Intermediate map from continuous heterogeneity analysis, postprocessed by EMReady2. Frame_019 (of frames _000 thru _019) along principal component_000 (of components _000, 001, & _002). | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | AAA+ superfamily Helicase Substrate translocation DNA unwinding / DNA BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Betapolyomavirus macacae / synthetic construct (others) Betapolyomavirus macacae / synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.4 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shahid T | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, 2 items United Kingdom, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2025 Journal: Nature / Year: 2025Title: Structural dynamics of DNA unwinding by a replicative helicase. Authors: Taha Shahid / Ammar U Danazumi / Muhammad Tehseen / Lubna Alhudhali / Alice R Clark / Christos G Savva / Samir M Hamdan / Alfredo De Biasio /   Abstract: Hexameric helicases are nucleotide-driven molecular machines that unwind DNA to initiate replication across all domains of life. Despite decades of intensive study, several critical aspects of their ...Hexameric helicases are nucleotide-driven molecular machines that unwind DNA to initiate replication across all domains of life. Despite decades of intensive study, several critical aspects of their function remain unresolved: the site and mechanism of DNA strand separation, the mechanics of unwinding propagation, and the dynamic relationship between nucleotide hydrolysis and DNA movement. Here, using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), we show that the simian virus 40 large tumour antigen (LTag) helicase assembles in the form of head-to-head hexamers at replication origins, melting DNA at two symmetrically positioned sites to establish bidirectional replication forks. Through continuous heterogeneity analysis, we characterize the conformational landscape of LTag on forked DNA under catalytic conditions, demonstrating coordinated motions that drive DNA translocation and unwinding. We show that the helicase pulls the tracking strand through DNA-binding loops lining the central channel, while directing the non-tracking strand out of the rear, in a cyclic process. ATP hydrolysis functions as an 'entropy switch', removing blocks to translocation rather than directly powering DNA movement. Our structures show the allosteric couplings between nucleotide turnover and subunit motions that enable DNA unwinding while maintaining dedicated exit paths for the separated strands. These findings provide a comprehensive model for replication fork establishment and progression that extends from viral to eukaryotic systems. More broadly, they introduce fundamental principles of the mechanism by which ATP-dependent enzymes achieve efficient mechanical work through entropy-driven allostery. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_52109.map.gz emd_52109.map.gz | 6.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-52109-v30.xml emd-52109-v30.xml emd-52109.xml emd-52109.xml | 16.6 KB 16.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_52109.png emd_52109.png | 61 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-52109.cif.gz emd-52109.cif.gz | 4.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_52109_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52109_half_map_1.map.gz emd_52109_half_map_2.map.gz emd_52109_half_map_2.map.gz | 200.6 MB 200.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52109 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52109 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52109 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-52109 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9evhC  9evpC  9exdC  9f3tC  9f3uC  9f5iC  9f73C  9f74C  9f75C  9f7nC  9f9nC  9f9oC  9f9wC  9f9xC  9fa1C  9fa2C  9fb0C  9fb4C  9fb5C  9fb6C  9kaeC  9kakC C: citing same article ( |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_52109.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_52109.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 27 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
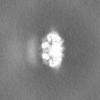
| Annotation | Intermediate map from continuous heterogeneity analysis, postprocessed by EMReady2. Frame_019 (of frames _000 thru _019) along principal component_000 (of components _000, 001, & _002). | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.67 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Unfiltered and unmasked gold-standard half-map (consensus refinement)....
| File | emd_52109_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
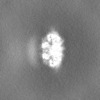
| Annotation | Unfiltered and unmasked gold-standard half-map (consensus refinement). | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
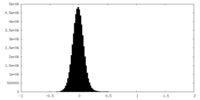
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Unfiltered and unmasked gold-standard half-map (consensus refinement)....
| File | emd_52109_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unfiltered and unmasked gold-standard half-map (consensus refinement). | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Large T antigen with DNA in presence of ADP.
| Entire | Name: Large T antigen with DNA in presence of ADP. |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Large T antigen with DNA in presence of ADP.
| Supramolecule | Name: Large T antigen with DNA in presence of ADP. / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Large T antigen
| Supramolecule | Name: Large T antigen / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Betapolyomavirus macacae Betapolyomavirus macacae |
-Supramolecule #3: DNA
| Supramolecule | Name: DNA / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 8 / Details: 200 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 1 mM ADP. |
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil / Material: GOLD / Support film - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 277 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Energy filter - Name: GIF Bioquantum / Energy filter - Slit width: 20 eV |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 9737 / Average exposure time: 2.0 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 105000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)