+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Mammalian ternary complex of an 80S ribosome, NAC and NatA/E | ||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | translation / ribosome / N-terminal acetyltransferase / NatA / NatE / NAC | ||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||||||||
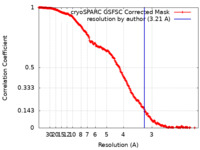
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.21 Å | ||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Yudin D / Scaiola A / Ban N | ||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, United States,  Germany, Germany,  Switzerland, European Union, 5 items Switzerland, European Union, 5 items
| ||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2024 Journal: Nature / Year: 2024Title: NAC guides a ribosomal multienzyme complex for nascent protein processing. Authors: Alfred M Lentzsch / Denis Yudin / Martin Gamerdinger / Sowmya Chandrasekar / Laurenz Rabl / Alain Scaiola / Elke Deuerling / Nenad Ban / Shu-Ou Shan /    Abstract: Approximately 40% of the mammalian proteome undergoes N-terminal methionine excision and acetylation, mediated sequentially by methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP) and N-acetyltransferase A (NatA), ...Approximately 40% of the mammalian proteome undergoes N-terminal methionine excision and acetylation, mediated sequentially by methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP) and N-acetyltransferase A (NatA), respectively. Both modifications are strictly cotranslational and essential in higher eukaryotic organisms. The interaction, activity and regulation of these enzymes on translating ribosomes are poorly understood. Here we perform biochemical, structural and in vivo studies to demonstrate that the nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC) orchestrates the action of these enzymes. NAC assembles a multienzyme complex with MetAP1 and NatA early during translation and pre-positions the active sites of both enzymes for timely sequential processing of the nascent protein. NAC further releases the inhibitory interactions from the NatA regulatory protein huntingtin yeast two-hybrid protein K (HYPK) to activate NatA on the ribosome, enforcing cotranslational N-terminal acetylation. Our results provide a mechanistic model for the cotranslational processing of proteins in eukaryotic cells. | ||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_50130.map.gz emd_50130.map.gz | 337 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-50130-v30.xml emd-50130-v30.xml emd-50130.xml emd-50130.xml | 39.4 KB 39.4 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_50130_fsc.xml emd_50130_fsc.xml | 20.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
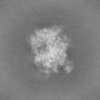
| Images |  emd_50130.png emd_50130.png | 162.4 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_50130_msk_1.map emd_50130_msk_1.map | 669.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-50130.cif.gz emd-50130.cif.gz | 4.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_50130_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50130_half_map_1.map.gz emd_50130_half_map_2.map.gz emd_50130_half_map_2.map.gz | 622.3 MB 622.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50130 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50130 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50130 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-50130 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_50130.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 669.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_50130.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 669.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_50130_msk_1.map emd_50130_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
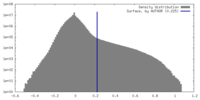
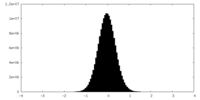
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: halfmap A
| File | emd_50130_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | halfmap A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
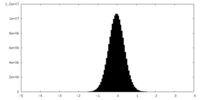
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: halfmap B
| File | emd_50130_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | halfmap B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Ternary complex of a translating ribosome, NAC and NatA/E
| Entire | Name: Ternary complex of a translating ribosome, NAC and NatA/E |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Ternary complex of a translating ribosome, NAC and NatA/E
| Supramolecule | Name: Ternary complex of a translating ribosome, NAC and NatA/E type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#89 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #2: Rabbit ribosome-nascent chain complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Rabbit ribosome-nascent chain complex / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #2-#10, #13-#74, #76-#79, #81-#89 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #3: Human NAC heterodimer
| Supramolecule | Name: Human NAC heterodimer / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1, #75 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #4: Human NatA/E complex
| Supramolecule | Name: Human NatA/E complex / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #11-#12, #80 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #5: Human NatA
| Supramolecule | Name: Human NatA / type: complex / ID: 5 / Parent: 4 / Macromolecule list: #12, #80 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #6: Human NatE
| Supramolecule | Name: Human NatE / type: complex / ID: 6 / Parent: 4 / Macromolecule list: #11 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.4 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.6 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)