[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-48525: Inactive Mu-Opioid Receptor with Nb6M, NabFab, and isoquinuclidin... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Inactive Mu-Opioid Receptor with Nb6M, NabFab, and isoquinuclidine compound#020_E1 | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | G-protein coupled receptor / Mu-opioid / isoquinuclidine / antagonist / nanobodies / fabs / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationOpioid Signalling / beta-endorphin receptor activity / morphine receptor activity / negative regulation of Wnt protein secretion / regulation of cellular response to stress / G protein-coupled opioid receptor signaling pathway / behavioral response to ethanol / negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / sensory perception / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway ...Opioid Signalling / beta-endorphin receptor activity / morphine receptor activity / negative regulation of Wnt protein secretion / regulation of cellular response to stress / G protein-coupled opioid receptor signaling pathway / behavioral response to ethanol / negative regulation of nitric oxide biosynthetic process / sensory perception / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled acetylcholine receptor signaling pathway / regulation of NMDA receptor activity / neuropeptide binding / positive regulation of neurogenesis / negative regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / G-protein alpha-subunit binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway, coupled to cyclic nucleotide second messenger / neuropeptide signaling pathway / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / MECP2 regulates neuronal receptors and channels / sensory perception of pain / Peptide ligand-binding receptors / G protein-coupled receptor activity / adenylate cyclase-inhibiting G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / G-protein activation / G-protein beta-subunit binding / Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 signaling / G alpha (i) signalling events / phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / perikaryon / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / endosome / neuron projection / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of cell population proliferation / axon / synapse / dendrite / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) Homo sapiens (human) / synthetic construct (others) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.3 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Kim JY / Vigneron SF / Billesbolle C / Manglik A / Shoichet BK | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: Docking 14 million virtual isoquinuclidines against the mu and kappa opioid receptors reveals dual antagonists-inverse agonists with reduced withdrawal effects. Authors: Seth F Vigneron / Shohei Ohno / Joao Braz / Joseph Y Kim / Oh Sang Kweon / Chase Webb / Christian Billesbølle / Karnika Bhardwaj / John Irwin / Aashish Manglik / Allan I Basbaum / Jonathan ...Authors: Seth F Vigneron / Shohei Ohno / Joao Braz / Joseph Y Kim / Oh Sang Kweon / Chase Webb / Christian Billesbølle / Karnika Bhardwaj / John Irwin / Aashish Manglik / Allan I Basbaum / Jonathan A Ellman / Brian K Shoichet /  Abstract: Large library docking of tangible molecules has revealed potent ligands across many targets. While make-on-demand libraries now exceed 75 billion enumerated molecules, their synthetic routes are ...Large library docking of tangible molecules has revealed potent ligands across many targets. While make-on-demand libraries now exceed 75 billion enumerated molecules, their synthetic routes are dominated by a few reaction types, reducing diversity and inevitably leaving many interesting bioactive-like chemotypes unexplored. Here, we investigate the large-scale enumeration and targeted docking of isoquinuclidines. These "natural-product-like" molecules are rare in the current libraries and are functionally congested, making them interesting as receptor probes. Using a modular, four-component reaction scheme, we built and docked a virtual library of over 14.6 million isoquinuclidines against both the μ- and -opioid receptors (MOR and KOR, respectively). Synthesis and experimental testing of 18 prioritized compounds found nine ligands with low μM affinities. Structure-based optimization revealed low- and sub-nM antagonists and inverse agonists targeting both receptors. Cryo-electron microscopy (cryoEM) structures illuminate the origins of activity on each target. In mouse behavioral studies, a potent member of the series with joint MOR-antagonist and KOR-inverse-agonist activity reversed morphine-induced analgesia, phenocopying the MOR-selective anti-overdose agent naloxone. Encouragingly, the new molecule induced less severe opioid-induced withdrawal symptoms compared to naloxone during withdrawal precipitation, and did not induce conditioned-place aversion, likely reflecting a reduction of dysphoria due to the compound's KOR-inverse agonism. The strengths and weaknesses of bespoke library docking, and of docking for opioid receptor polypharmacology, will be considered. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_48525.map.gz emd_48525.map.gz | 168 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-48525-v30.xml emd-48525-v30.xml emd-48525.xml emd-48525.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_48525.png emd_48525.png | 54.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-48525.cif.gz emd-48525.cif.gz | 7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_48525_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48525_half_map_1.map.gz emd_48525_half_map_2.map.gz emd_48525_half_map_2.map.gz | 165.1 MB 165.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48525 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48525 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48525 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-48525 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9mqiMC  9mqhC  9mqjC  9mqkC  9mqlC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_48525.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_48525.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 178 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.8189 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
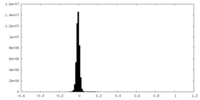
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_48525_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_48525_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human Mu-Opioid Receptor
| Entire | Name: Human Mu-Opioid Receptor |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human Mu-Opioid Receptor
| Supramolecule | Name: Human Mu-Opioid Receptor / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Mu-type opioid receptor
| Macromolecule | Name: Mu-type opioid receptor / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 46.081359 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: DYKDDDDASI DMDSSAAPTN ASNCTDALAY SSCSPAPSPG SWVNLSHLDG NLSDPCGPNR TDLGGRDSLC PPTGSPSMIT AITIMALYS IVCVVGLFGN FLVMYVIVRY TKMKTATNIY IFNLALADAL ATSTLPFQSV NYLMGTWPFG TILCKIVISI D YYNMFTSI ...String: DYKDDDDASI DMDSSAAPTN ASNCTDALAY SSCSPAPSPG SWVNLSHLDG NLSDPCGPNR TDLGGRDSLC PPTGSPSMIT AITIMALYS IVCVVGLFGN FLVMYVIVRY TKMKTATNIY IFNLALADAL ATSTLPFQSV NYLMGTWPFG TILCKIVISI D YYNMFTSI FTLCTMSVDR YIAVCHPVKA LDFRTPRNAK IINVCNWILS SAIGLPVMFM ATTKYRQGSI DCTLTFSHPT WY WENLLKI CVFIFAFIMP VLIITVCYGL MILRLKSVRL LSGSREKDRN LRRITRMVLV VVAVFIVCWT PIHIYVIIKA LVT IPETTF QTVSWHFCIA LGYTNSCLNP VLYAFLDENF KRCFREFCIP TSSNIEQQNS TRIRQNTRDH PSTANTVDRT NHQL ENLEA ETAPLP UniProtKB: Mu-type opioid receptor |
-Macromolecule #2: Nanobody 6M
| Macromolecule | Name: Nanobody 6M / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 14.418919 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QRQLVESGGG LVQPGGSLRL SCAASGTIFR LYDMGWFRQA PGKEREGVAS ITSGGSTKYA DSVKGRFTIS RDNAKNTVYL QMNSLEPED TAVYYCNAEY RTGIWEELLD GWGKGTPVTV SSHHHHHHEP EA |
-Macromolecule #3: NabFab Heavy Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: NabFab Heavy Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25.684463 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NFSYYSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VAYISSSSSY TSYADSVKGR FTISADTSKN TAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARGYQYWQYH ASWYWNGGLD YWGQGTLVTV SSASTKGPSV FPLAPSSKST SGGTAALGCL V KDYFPEPV ...String: EISEVQLVES GGGLVQPGGS LRLSCAASGF NFSYYSIHWV RQAPGKGLEW VAYISSSSSY TSYADSVKGR FTISADTSKN TAYLQMNSL RAEDTAVYYC ARGYQYWQYH ASWYWNGGLD YWGQGTLVTV SSASTKGPSV FPLAPSSKST SGGTAALGCL V KDYFPEPV TVSWNSGALT SGVHTFPAVL QSSGLYSLSS VVTVPSSSLG TQTYICNVNH KPSNTKVDKK VEPKSCDKTH T |
-Macromolecule #4: NabFab Light Chain
| Macromolecule | Name: NabFab Light Chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 23.258783 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQSSSSLITF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD ...String: SDIQMTQSPS SLSASVGDRV TITCRASQSV SSAVAWYQQK PGKAPKLLIY SASSLYSGVP SRFSGSRSGT DFTLTISSLQ PEDFATYYC QQSSSSLITF GQGTKVEIKR TVAAPSVFIF PPSDSQLKSG TASVVCLLNN FYPREAKVQW KVDNALQSGN S QESVTEQD SKDSTYSLSS TLTLSKADYE KHKVYACEVT HQGLSSPVTK SFNRGEC |
-Macromolecule #5: methyl (1S,3R,4S,6S,8M)-2-[(1-ethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methyl]-8-(3-...
| Macromolecule | Name: methyl (1S,3R,4S,6S,8M)-2-[(1-ethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)methyl]-8-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dimethyl-2-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-7-ene-6-carboxylate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: A1BNM |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 395.495 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: UltrAuFoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Specialist optics | Phase plate: OTHER |
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 47.7 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: INSILICO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Algorithm: FOURIER SPACE / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 3.3 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 259816 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller





















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)