[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-47338: Cryo-EM structure of the C. neoformans lipid flippase Apt1-Cdc50 ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
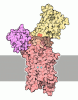
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the C. neoformans lipid flippase Apt1-Cdc50 bound with butyrolactol A in the E2P state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Composite map | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cryptococcus neoformans / lipid flippase / P4-ATPase / Cdc50 protein / butyrolactol A / TRANSLOCASE-INHIBITOR complex | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / magnesium ion binding / endoplasmic reticulum / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.72 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Duan HD / Li H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025 Journal: bioRxiv / Year: 2025Title: Butyrolactol A potentiates caspofungin efficacy against resistant fungi via phospholipid flippase inhibition. Authors: Xuefei Chen / H Diessel Duan / Michael J Hoy / Kalinka Koteva / Michaela Spitzer / Allison K Guitor / Emily Puumala / Aline A Fiebig / Guanggan Hu / Bonnie Yiu / Sommer Chou / Zhuyun Bian / ...Authors: Xuefei Chen / H Diessel Duan / Michael J Hoy / Kalinka Koteva / Michaela Spitzer / Allison K Guitor / Emily Puumala / Aline A Fiebig / Guanggan Hu / Bonnie Yiu / Sommer Chou / Zhuyun Bian / Yeseul Choi / Amelia Bing Ya Guo / Wenliang Wang / Sheng Sun / Nicole Robbins / Anna Floyd Averette / Michael A Cook / Ray Truant / Lesley T MacNeil / Eric D Brown / James W Kronstad / Brian K Coombes / Leah E Cowen / Joseph Heitman / Huilin Li / Gerard D Wright /   Abstract: Fungal infections cause millions of deaths annually and are challenging to treat due to limited therapeutic options and rising resistance. Cryptococci are intrinsically resistant to the latest ...Fungal infections cause millions of deaths annually and are challenging to treat due to limited therapeutic options and rising resistance. Cryptococci are intrinsically resistant to the latest generation of antifungals, echinocandins, while , a notorious global threat, is also increasingly resistant. We performed a natural product extract screen to rescue caspofungin fungicidal activity against H99 and identified butyrolactol A, which restores echinocandin efficacy against resistant fungal pathogens, including multidrug-resistant . Mode of action studies revealed that butyrolactol A inhibits the phospholipid flippase Apt1-Cdc50, blocking phospholipid transport. Cryo-electron microscopy analysis of the Apt1•butyrolactol A complex revealed that the flippase is trapped in a dead-end state. Apt1 inhibition disrupts membrane asymmetry, vesicular trafficking, and cytoskeletal organization, thereby enhancing echinocandin uptake and potency. This study identifies lipid flippases as promising antifungal targets and demonstrates the potential of revisiting natural products to expand the antifungal arsenal and combat resistance. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_47338.map.gz emd_47338.map.gz | 2.5 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-47338-v30.xml emd-47338-v30.xml emd-47338.xml emd-47338.xml | 19.8 KB 19.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_47338_fsc.xml emd_47338_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_47338.png emd_47338.png | 38.6 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-47338.cif.gz emd-47338.cif.gz | 7.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47338 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47338 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47338 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-47338 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_47338_validation.pdf.gz emd_47338_validation.pdf.gz | 385.5 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_47338_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_47338_full_validation.pdf.gz | 385.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_47338_validation.xml.gz emd_47338_validation.xml.gz | 11.4 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_47338_validation.cif.gz emd_47338_validation.cif.gz | 15.2 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47338 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47338 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47338 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-47338 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9dzuMC  9dzvC  9omvC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_47338.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_47338.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Composite map | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.828 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Apt1-Cdc50 heterodimer bound with butyrolactol A
| Entire | Name: Apt1-Cdc50 heterodimer bound with butyrolactol A |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Apt1-Cdc50 heterodimer bound with butyrolactol A
| Supramolecule | Name: Apt1-Cdc50 heterodimer bound with butyrolactol A / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 222 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Transcription regulator
| Macromolecule | Name: Transcription regulator / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 45.937961 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAIFNRKPKA RLDGEPAPTE KEKVKWSKRP ANTAFKQQRL KAWQPILTPK SVLPTLLIIG IIFAPIGALI VWGSGKVTTI TLDYTECDV DAPTDGSYQA MPNSAYQYDL ATSSSVSESS IASPTWTFSN DSSREVGETA RCEIEFEVPY DLGPGLFLYY K LTNYYQNH ...String: MAIFNRKPKA RLDGEPAPTE KEKVKWSKRP ANTAFKQQRL KAWQPILTPK SVLPTLLIIG IIFAPIGALI VWGSGKVTTI TLDYTECDV DAPTDGSYQA MPNSAYQYDL ATSSSVSESS IASPTWTFSN DSSREVGETA RCEIEFEVPY DLGPGLFLYY K LTNYYQNH RRYSSSFDAT QLIGDSRSLS QINGGNCKPI TSRDGKPYYP CGLIANSLFN DTFPSVVLLN PTNGAQNQTY NF SESGIAW GGIKKNYAST LTYISPSDVL PPPNWALKYP NGYVDGFPNL REDEHFQVWM RVAALPTFRK LWARNDGEIM SQG RYRIVA NMNYPVKQFS GTKSIVISTV SWIGGKQPFL GWAYIAAAIL CVVLAVAGLI RHLVKPRKLG DMSLLSWNQP NANG LHHHH HHHHHH UniProtKB: Transcription regulator |
-Macromolecule #2: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase
| Macromolecule | Name: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) Cryptococcus neoformans var. grubii H99 (fungus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 176.534609 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGASKPPLVP RSKKHNPSWL DRNIVKPLES LAPSKLFARR RSPPVPRSVF INEPLPSEYY DKKGKILRAH HFATNQNVTS KYTVITFIP KNLFEQFRRV ANCFFLAISI LQFFPKFSTI SPGLVILPLI IVLAITALKD GYEDIKRHQA DHRTNHAIVH V LGGQDYTN ...String: MGASKPPLVP RSKKHNPSWL DRNIVKPLES LAPSKLFARR RSPPVPRSVF INEPLPSEYY DKKGKILRAH HFATNQNVTS KYTVITFIP KNLFEQFRRV ANCFFLAISI LQFFPKFSTI SPGLVILPLI IVLAITALKD GYEDIKRHQA DHRTNHAIVH V LGGQDYTN QNPMASKDKT FIPAIPLPKR RSKKAKKAEE EAALNMQGRS SSTENFAAEP VPGAEPRGQD ELQRMRSQVS NW DEDPEAG DSPGELGWHR TIWEDVKVGD FVKIYENEQF PADIVICATS EEEDVAYIET KNLDGETNLK SRNGVPGLSH LNT AEACAK AHLCIDLDAP ESNMFRLNGA VINLEEYDED EQHPIHPITL ETTMLRGCVL KNTAWVIGII VYTGEDTKII RNAG ATPSK RSKVEKQMNP QVIINLVILA AIAVVCAIVD HVNEVEWDRQ QAYWMLFADT SGDNPNINGL VTFANAFITF QNIVP ISLY ISIEAVRTIQ AAFIYWDRDI KYKKDGVTTR TTARSWNLSD DLGQIEYIFS DKTGTLTQNA MIFRQCSVGG KIYTGD GLP PSHPTITHQH QPPPVHQHDD QDDPIAKSAS ESDDSDPKKI STEDPDEIKV TLPKEVLATF HDAELDKDLE AHDSEQS RI LHGFFAVLGL CHTVLAAETE PGVIEYKAQS PDEAALVQSA ADVGFVFRGR DHNILRMSTP FSDVSDEYEL LHVLEFNS A RKRMSVILRK LDEDGRIFLL CKGADNVIFE RLTKDSNQRE MREKTDQDLQ YFASEGLRTL CLAYRILDPQ VYEQWAKEY HNATVALQDR EERIESVSSS IERDLILLGA TAIEDKLQDG VPDTISDLKR AGIKVWVATG DKLETAVAIG YTTNLLTKDT NLIVVREGR HSIGDQLREA LEEFFGEDAG LRTTLSRIDS RRNSMDPPRL TRVNTGVRSL VGRDNGTRPG GFSLVIEGHA L AHCFDDEE TEALLLALST RCNTVICCRV SPLQKAQIVH LIKDNLGVMC LAIGDGANDV SMIQAADVGV GISGEEGLQA VN SSDYAIA QFRYLKRLLL VHGHWSYFRN SSMILNFFYK NIIGIGVLFW FMIYCGWSTT YVFAYVYLLF WNVFWTLVPV IAI GLFDRN IDDETLMALP ELYRASREGK YFGLMRFAYY IFEGVYQSAV IYFFLNYTYV TTTARGDGYD VYMYEMSTTQ AIGA VMVAN LFSGLNIDAW TGWVWFAIWF GPFLIWVFTA VYSVIPPSSF YTGVYGNDVF LFRSAAYWFG WPFVTIIALL PRYLI KTFR QNIFPNDVDT MRLVRKYHPE VDLYNHPMLG GKLAPKKDED ESDYGEEPFD GPEGRRSSIK MANLRHSHGA FGRGDQ AGD MELGMGRKSL GNRPGLRSSM DSSRFGIHSG ARGSTVDMST GLEQPPSRGF GFTMEEGGVA IQRMQSRLSQ TSSHASR SR WPRFNNNSSS SHPFETKPPS SMSKLRSRAG SILTRKRADT TDTRNSDDKS LSSPVKTGFF GRHMPGQNHG QHEGRSMG T PLKSETGRGD NWEEEELEDE SLGRGFGVGQ NMAPPEIPRM DYKDDDDKI UniProtKB: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase |
-Macromolecule #5: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #6: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION
| Macromolecule | Name: BERYLLIUM TRIFLUORIDE ION / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: BEF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 66.007 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-BEF: |
-Macromolecule #7: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #8: (3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(1R,2R,3S,4S,5R,6R,8E,10E,14E,16Z)-1,...
| Macromolecule | Name: (3R,4R,5S)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-[(1R,2R,3S,4S,5R,6R,8E,10E,14E,16Z)-1,2,3,4,5-pentahydroxy-6,20,20-trimethylhenicosa-8,10,14,16-tetraen-1-yl]oxolan-2-one type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: A1BD6 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 526.659 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.7 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.3 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




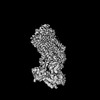



 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















