+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Full length EcPKS2 - acylated dataset with three ACP positions | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Unsharpened map for FL EcPKS2 - acylated dataset | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | polyketide adenosyl transferase beta-keto-synthase dehydratase keto-reductase Acyl carrier protein / BIOSYNTHETIC PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Elysia chlorotica (eastern emerald elysia) Elysia chlorotica (eastern emerald elysia) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Schubert HL / Hill CP | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2025Title: The structure of full-length AFPK supports the ACP linker in a role that regulates iterative polyketide and fatty acid assembly. Authors: Heidi L Schubert / Feng Li / Christopher P Hill / Eric W Schmidt /  Abstract: The polyketide synthases (PKSs) in microbes and the cytoplasmic fatty acid synthases in humans (FASs) are related enzymes that have been well studied. As a result, there is a paradigm explaining in ...The polyketide synthases (PKSs) in microbes and the cytoplasmic fatty acid synthases in humans (FASs) are related enzymes that have been well studied. As a result, there is a paradigm explaining in general terms how FASs repeatedly use a set of enzymatic domains to produce simple fats, while PKSs use the domains in a much more complex manner to produce pharmaceuticals and other elaborate molecules. However, most animals also have PKSs that do not conform to the rules described in microbes, including a large family of enzymes that bridge fatty acid and polyketide metabolism, the animal FAS-like PKSs (AFPKs). Here, we present the cryoelectron microscopy structures of two AFPKs from sea slugs. While the AFPK resemble mammalian FASs, their chemical products mimic those of PKSs in complexity. How then does the architecture of AFPKs facilitate this structural complexity? Unexpectedly, chemical complexity is controlled not solely by the enzymatic domains but is aided by the dynamics of the acyl carrier protein (ACP), a shuttle that moves intermediates between these domains. We observed interactions between enzyme domains and the linker-ACP domain, which, when manipulated, altered the kinetic properties of the enzyme to change the resulting chemical products. This unveils elaborate mechanisms and enzyme motions underlying lipid and polyketide biochemistry across the domains of life. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_45913.map.gz emd_45913.map.gz | 52.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-45913-v30.xml emd-45913-v30.xml emd-45913.xml emd-45913.xml | 20.7 KB 20.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_45913_fsc.xml emd_45913_fsc.xml | 9.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_45913.png emd_45913.png | 104 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_45913_msk_1.map emd_45913_msk_1.map | 103 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-45913.cif.gz emd-45913.cif.gz | 8.2 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_45913_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45913_half_map_1.map.gz emd_45913_half_map_2.map.gz emd_45913_half_map_2.map.gz | 95.5 MB 95.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45913 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45913 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45913 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-45913 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  9ctoMC  9cq1C  9cq9C  9ctiC  9ctkC  9ctlC  9ctmC  9ctnC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_45913.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_45913.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Unsharpened map for FL EcPKS2 - acylated dataset | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_45913_msk_1.map emd_45913_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half B
| File | emd_45913_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half B | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Half A
| File | emd_45913_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Half A | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Homodimer of EcPKS2
| Entire | Name: Homodimer of EcPKS2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Homodimer of EcPKS2
| Supramolecule | Name: Homodimer of EcPKS2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Elysia chlorotica (eastern emerald elysia) Elysia chlorotica (eastern emerald elysia) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 350 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Polyketide synthase 2
| Macromolecule | Name: Polyketide synthase 2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Elysia chlorotica (eastern emerald elysia) Elysia chlorotica (eastern emerald elysia) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 253.035688 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MAPQEQASSS QQDDAPPKTP NVVEPYKGEV AICGLSGRYP ESANVGELEY NLFNKIDMVT IDNRRWEPGY LGTPERMGKV KTITDFDAE FFGVHTKGAQ TMDPMLRNLL EVVYEAIVDA GESLESMKGT RTGVYIGVSN NEVDTAYMKN WTDDDAYMVQ G CHHSMYPN ...String: MAPQEQASSS QQDDAPPKTP NVVEPYKGEV AICGLSGRYP ESANVGELEY NLFNKIDMVT IDNRRWEPGY LGTPERMGKV KTITDFDAE FFGVHTKGAQ TMDPMLRNLL EVVYEAIVDA GESLESMKGT RTGVYIGVSN NEVDTAYMKN WTDDDAYMVQ G CHHSMYPN WISFFFDFSG PSTAYNTA(SCY)S TSLVCLDAAE RHLRMGVIDN AIVGGSNFIY RPATTKLFMG MNFLGSST C KAFDESGDGF VRGEVASAIL LKKADTAKRV YCTLVGSMLN NDGNQTNGIL YPNSEAQEQL MTDIYSTHKI DANEVKYFE CHGTGTQAGD PNETRAICNA VCKGKKDPLL IGSIKSNLGH GETASGINGI SKVIITMHSR QIPPNLHFKN PNPKIPGLFD GRLKVVTET TPFDGGLIAI NSFGMGGTNA HAIFRSFDKR AEPHPASDKP RLFTYCARTE EGLQKIFEEA HKHASNVEFH A LCQESANT KPKSLPYRGA TILNAEGEYT EIQKCPSKAR EVWFVYSGMG SQWVGMGRSL MALDVFRQSI EETAAILSPF GV DLMSLLM DGTEDKLKEI MPPFICINAI QLALTDLLNS MGIVPDGLVG HSLGEVGCAY ADGCLTRREA ILSAFWRAKA VID CEVKPG KMAAVELTWE EAKRLCPPGV VAACHNSQDS VTISGGAQEM TKFMAELSAQ GVTVKEVNSN NISYHSSFMT EPAA YLKKG LEKEIVPKPR SKKWISTSIP EERWGNPEAQ TADASYQANN LLSSVLFYEG LQKIPSNAIA IEIAPAGLLQ SVIKK SLGQ DCTIVALQKR KSPNNLEVFF SALGKCYSHG VPMNPLGLYP AVQFPVSIDT PMLSSMVSEA WDHSAKWRVP LVEEFE YGS GSSSDNVIDI DLSEDSPENY LLEHAVDGRM LFPATGTLVL AWKTLAKLKG VEFEQLGVQM TNVQIHQALF LNPGGKT TV SVSVMPITGE FQVRDGESLI SSGVITSSEG RLLETDQHMK KGSVLDGKPD KELLFTKEIY REFLLRGYEY GAAFQGIQ R ASLDATDTDI RWDGRWISYL DTVLQMYLLS KPGTHQALPT LLESVTIDPR VHPAQPPEGT TEFQVLPGKW DPVLQIAAA GGVEIRSCHS IRASRRLNHD PPILEDFAFA PYVDPRPSDR SAAAVTPALR DYADACFEFS RQGMKRWLEN DKNNVLPNKE EIKEALAMA NKHASTPQAA SNFASAKATL EALVNNKNGH RLPNHGLFEM LDIAFSEPLE GDYWDRLRMK LHDVRTYLWD D PIIAALES PDIVKLVMET VSDNVNQQVM EILEVGAARG PYYRQAIPKA LEYFSIKDWQ YTVADQGFVE DAAEFPVKMM QF DPLDPAN FPAELTESCD LLVLKWNLQM QVDLDAAITE FSKMIKPGGF LLVLENGTRL STFFPIKAIV SASLGGKGGP EGD RAMGCF YTDAQWSALF ARHGFEQIMH IPDGIAVSMF LLRKPFEPSV APIIINVDDL ECSWLEEVQA RCAELQDSHK DSRL WLVAN TELSGVLGFL RSLVWEFGSE KLRCIQIDDA TAGPNPPKIS ADSADFKELV RKDLAYNVFK NGKWGTYRGF VISDA DRQK ERPSEYVYAD WLSAGDMSSL RWFDSPLKTG HNNGMLGSKM AHKLETETCS VYYAGLNLRD IILANGTIQR DILPEE TFF KEGVLGVEFS GRNSSGKRVM GLCPPPALAT TVKCPVSSLW SVPDQWTLEE AATVPLAYAT AYYCLVSEGG VQKGATV FI HAGASVVGQA SIAVALSYNC EIFTLTKNSD ETALLKSMYP QLNDRNFCSS EDCSFEKYIR KETKGSGVDV VINTLRGK F LKASRRLLSK KGKFVDIGFK VDSNTQIAYY TREHPDLRFQ LDALLESQGP EWTRLFDLVQ AGIHSGVVKP LKRAVYSMD KIVDAFKTVE AEREAGKIVI KIRDEERQKV CPTPRTSFPA IHRTCFHPDK SHILVGGMGG MGLETAHWMV LRGAKKLILT SRYGITTGY QARKIAFFKQ LGVEVEVLAL SVNTRKAADK VFEHALKMGP VGGIFNMAMV LYNDDFLKMN REQFLKPLES K ITMTMLLD DKSREKPVRD TLDHFVMFSS LIVSGGHLGQ ANYAFGSTVL EKICERRKRD GLPVTTPQWA SIADVGTVAL MG TGNETII CRKYPQRFFN VLSVFDFMMS SDNVVTISYV LVEKSMGVAA GEESMVDQVL RAVGKVLGIK DVSSVDGDKE FID MGVDSL MSVEIKQALE RDAGLVISTK DTQLMTFNTL RSMVKGSHVH HHHHH |
-Macromolecule #2: NADPH DIHYDRO-NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: NADPH DIHYDRO-NICOTINAMIDE-ADENINE-DINUCLEOTIDE PHOSPHATE type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: NDP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 745.421 Da |
| Chemical component information | 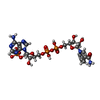 ChemComp-NDP: |
-Macromolecule #3: ~{S}-[2-[3-[[(2~{R})-3,3-dimethyl-2-oxidanyl-4-phosphonooxy-butan...
| Macromolecule | Name: ~{S}-[2-[3-[[(2~{R})-3,3-dimethyl-2-oxidanyl-4-phosphonooxy-butanoyl]amino]propanoylamino]ethyl] ethanethioate type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 6VG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 400.385 Da |
| Chemical component information | 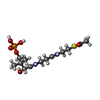 ChemComp-6VG: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 6.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
Details: pH measured at 4 degrees C | ||||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: GOLD / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: GOLD / Support film - topology: HOLEY ARRAY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 25 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR | ||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 278 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP / Details: single application, single blot. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Average electron dose: 40.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.8 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.8 µm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model | Chain - Source name: AlphaFold / Chain - Initial model type: in silico model |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: RIGID BODY FIT |
| Output model |  PDB-9cto: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)













































