+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-4387 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
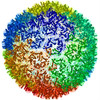
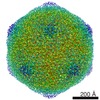
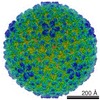
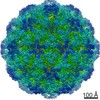
| Title | Aged P22 Empty Procapsid | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Aged P22 Empty Procapsid | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Enterobacteria phage P22 (virus) Enterobacteria phage P22 (virus) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 17.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | McCoy K / Selivanovitch E / Luque D / Lee B / Edwards E / Caston JR / Douglas T | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Biomacromolecules / Year: 2018 Journal: Biomacromolecules / Year: 2018Title: Cargo Retention inside P22 Virus-Like Particles. Authors: Kimberly McCoy / Ekaterina Selivanovitch / Daniel Luque / Byeongdu Lee / Ethan Edwards / José R Castón / Trevor Douglas /   Abstract: Viral protein cages, with their regular and programmable architectures, are excellent platforms for the development of functional nanomaterials. The ability to transform a virus into a material with ...Viral protein cages, with their regular and programmable architectures, are excellent platforms for the development of functional nanomaterials. The ability to transform a virus into a material with intended structure and function relies on the existence of a well-understood model system, a noninfectious virus-like particle (VLP) counterpart. Here, we study the factors important to the ability of P22 VLP to retain or release various protein cargo molecules depending on the nature of the cargo, the capsid morphology, and the environmental conditions. Because the interaction between the internalized scaffold protein (SP) and the capsid coat protein (CP) is noncovalent, we have studied the efficiency with which a range of SP variants can dissociate from the interior of different P22 VLP morphologies and exit by traversing the porous capsid. Understanding the types of cargos that are either retained or released from the P22 VLP will aid in the rational design of functional nanomaterials. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_4387.map.gz emd_4387.map.gz | 20.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-4387-v30.xml emd-4387-v30.xml emd-4387.xml emd-4387.xml | 9 KB 9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_4387.png emd_4387.png | 207.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4387 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4387 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4387 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4387 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_4387.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_4387.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 22.2 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Aged P22 Empty Procapsid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 4.32 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Enterobacteria phage P22
| Entire | Name:  Enterobacteria phage P22 (virus) Enterobacteria phage P22 (virus) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Enterobacteria phage P22
| Supramolecule | Name: Enterobacteria phage P22 / type: virus / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / NCBI-ID: 10754 / Sci species name: Enterobacteria phage P22 / Virus type: VIRUS-LIKE PARTICLE / Virus isolate: OTHER / Virus enveloped: No / Virus empty: Yes |
|---|---|
| Host (natural) | Organism:  Salmonella enterica (bacteria) Salmonella enterica (bacteria) |
| Host system | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/2 / Material: COPPER/RHODIUM / Mesh: 300 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TECNAI F20 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI EAGLE (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 20.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai F20 / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









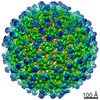
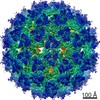

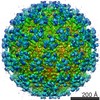
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)