[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-43563: Cryo-EM structure of a type I ZorAB complex from Shewanella sp. s... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of a type I ZorAB complex from Shewanella sp. strain ANA-3, composite map | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | composite map generated from sharpened consensus and local refinement of peptidoglycan-binding domain | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | phage defense / zorya / phage / membrane protein complex / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | : / OmpA-like domain profile. / OmpA-like domain superfamily / OmpA family / OmpA-like domain / membrane / MotA/TolQ/ExbB proton channel domain-containing protein / Chemotaxis protein MotB-related protein Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Deme JC / Lea SM | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2025Title: Modularity of Zorya defense systems during phage inhibition. Authors: Giuseppina Mariano / Justin C Deme / Jennifer J Readshaw / Matthew J Grobbelaar / Mackenzie Keenan / Yasmin El-Masri / Lindsay Bamford / Suraj Songra / Tim R Blower / Tracy Palmer / Susan M Lea /   Abstract: Bacteria have evolved an extraordinary diversity of defense systems against bacteriophage (phage) predation. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying these anti-phage systems often remain elusive. ...Bacteria have evolved an extraordinary diversity of defense systems against bacteriophage (phage) predation. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying these anti-phage systems often remain elusive. Here, we provide mechanistic and structural insights into Zorya phage defense systems. Using cryo-EM structural analyses, we show that the Zorya type I and II core components, ZorA and ZorB, assemble in a 5:2 complex that is similar to inner-membrane ion-driven, rotary motors that power flagellar rotation, type 9 secretion, gliding and the Ton nutrient uptake systems. The ZorAB complex has an elongated cytoplasmic tail assembled by bundling the C-termini of the five ZorA subunits. Mutagenesis demonstrates that peptidoglycan binding by the periplasmic domains of ZorB, the structured cytoplasmic tail of ZorA, and ion flow through the motor is important for function in both type I and II systems. Furthermore, we identify ZorE as the effector module of the Zorya II system, possessing nickase activity. Our work reveals the molecular basis of the activity of Zorya systems and highlights the ZorE nickase as crucial for population-wide immunity in the type II system. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_43563.map.gz emd_43563.map.gz | 387.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-43563-v30.xml emd-43563-v30.xml emd-43563.xml emd-43563.xml | 17 KB 17 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_43563.png emd_43563.png | 105 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-43563.cif.gz emd-43563.cif.gz | 6.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_43563_additional_1.map.gz emd_43563_additional_1.map.gz | 201.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43563 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43563 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-43563 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 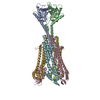 8vvnMC 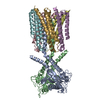 8vviC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_43563.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_43563.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | composite map generated from sharpened consensus and local refinement of peptidoglycan-binding domain | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.723 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: composite map generated from unsharpened consensus and local...
| File | emd_43563_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | composite map generated from unsharpened consensus and local refinement of peptidoglycan-binding domain | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : ZorAB complex
| Entire | Name: ZorAB complex |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: ZorAB complex
| Supramolecule | Name: ZorAB complex / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Chemotaxis protein MotB-related protein
| Macromolecule | Name: Chemotaxis protein MotB-related protein / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 32.12708 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MDRLFTRGST KVDEENPYWM SFSDLMSGLL VIFILAAVAL IIELTQKSEQ IDASIEELKK AEEARRNILI DIKEELAKQN IHVEIVEND TVLRIPESTL SFESGKDTLP ENTTVKNEVR LIGIALHKAI TTNERWKYLD TVFVEGHTDS NGIWYRGKGN W GLSTDRAV ...String: MDRLFTRGST KVDEENPYWM SFSDLMSGLL VIFILAAVAL IIELTQKSEQ IDASIEELKK AEEARRNILI DIKEELAKQN IHVEIVEND TVLRIPESTL SFESGKDTLP ENTTVKNEVR LIGIALHKAI TTNERWKYLD TVFVEGHTDS NGIWYRGKGN W GLSTDRAV SIWKLWQTEI NVAPKLSVLT NYNGQLLFSV SGYADTRRVD LQETTEEQRA RNRRIDIRFT VKKPKIEDYE KA KNVENLY FQGQFGSWSH PQFEKGGGSG GGSGGGSWSH PQFEK UniProtKB: Chemotaxis protein MotB-related protein |
-Macromolecule #2: MotA/TolQ/ExbB proton channel domain-containing protein
| Macromolecule | Name: MotA/TolQ/ExbB proton channel domain-containing protein type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 5 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) Shewanella sp. ANA-3 (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 77.102953 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MATERQIELS WLLPDFSHLS FHPQTGTALS SLFVAITLTV TLLFIAYLLY KSIDVVLKIN WLQKALEPLE RKDVAQKKEV LYQLAKSKS KGKSKGIGFL WMEFDETLVE VRKGDQIEIR NTLDAGHFFN TYTLANSVTE NRLIAAVPGF LTALGVIGTF M GLQLGLAD ...String: MATERQIELS WLLPDFSHLS FHPQTGTALS SLFVAITLTV TLLFIAYLLY KSIDVVLKIN WLQKALEPLE RKDVAQKKEV LYQLAKSKS KGKSKGIGFL WMEFDETLVE VRKGDQIEIR NTLDAGHFFN TYTLANSVTE NRLIAAVPGF LTALGVIGTF M GLQLGLAD LKLGAGVDVT TMQDGVAGVV NGAKIAFLTS VWGVALSVFF NFFEKLCEQF IRSKIRELED KVDFLFPRVR PE EQLQIIS ENSSESRNVL QGLAEKIGEK MQEAMVTATQ GIQSSLESSL SKIMAPAINK LVDETSQGNQ KALEGLLESF MDR FGQAGN LQRSALDDVS NKVNQSVEAM QLTMSNFVEQ LQKSQAESGD REKALIADIS HQVSKLSSQS EDIHQKLTSY VENQ IGKIS SQMQIREEAS AKRDSELVNV IGQQVNELVN NSRRQGELLT SFVETQLNNL TKSFDERDKR STELETTRNN KIEKQ TEAI VKISNELIST VEKSVSEQLA AVKHLVSQGE TLQNSVNASV EAAAQATQAM KESSIELRVS ADHMRVLSSH VNDAGN KLS GAIKSAVDST ADLANQNQIS AQRIENARES LMKDVSRFSE LSDQIKALIT SASSTFTELK STQRDFIGNL KEEVESL SR KMTDMLEEYS QQANGQTAEH LKIWSQSVTD YSTQMNSAVK ALSSVVDEMQ VKLG UniProtKB: MotA/TolQ/ExbB proton channel domain-containing protein |
-Macromolecule #3: SODIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: SODIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 22.99 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 140 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON IV (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 54.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)




























