+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Microtubule-TTLL6 map | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule, locally sharpened | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | tubulin post-translational modifications / microtubules / TTLL / LIGASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationodontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Intraflagellar transport / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / Gap junction assembly ...odontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Intraflagellar transport / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / Gap junction assembly / Kinesins / GTPase activating protein binding / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / regulation of synapse organization / nuclear envelope lumen / Recycling pathway of L1 / MHC class I protein binding / RHOH GTPase cycle / microtubule-based process / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / Hedgehog 'off' state / intercellular bridge / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cytoplasmic microtubule / spindle assembly / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / Mitotic Prometaphase / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / cellular response to interleukin-4 / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / PKR-mediated signaling / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell body / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Potential therapeutics for SARS / microtubule / cytoskeleton / cilium / membrane raft / protein domain specific binding / cell division / GTPase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / protein-containing complex / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mahalingan KK / Grotjahn D / Li Y / Lander GC / Zehr EA / Roll-Mecak A | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024 Journal: Nat Chem Biol / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for α-tubulin-specific and modification state-dependent glutamylation. Authors: Kishore K Mahalingan / Danielle A Grotjahn / Yan Li / Gabriel C Lander / Elena A Zehr / Antonina Roll-Mecak /  Abstract: Microtubules have spatiotemporally complex posttranslational modification patterns. Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) enzymes introduce the most prevalent modifications on α-tubulin and β-tubulin. ...Microtubules have spatiotemporally complex posttranslational modification patterns. Tubulin tyrosine ligase-like (TTLL) enzymes introduce the most prevalent modifications on α-tubulin and β-tubulin. How TTLLs specialize for specific substrate recognition and ultimately modification-pattern generation is largely unknown. TTLL6, a glutamylase implicated in ciliopathies, preferentially modifies tubulin α-tails in microtubules. Cryo-electron microscopy, kinetic analysis and single-molecule biochemistry reveal an unprecedented quadrivalent recognition that ensures simultaneous readout of microtubule geometry and posttranslational modification status. By binding to a β-tubulin subunit, TTLL6 modifies the α-tail of the longitudinally adjacent tubulin dimer. Spanning two tubulin dimers along and across protofilaments (PFs) ensures fidelity of recognition of both the α-tail and the microtubule. Moreover, TTLL6 reads out and is stimulated by glutamylation of the β-tail of the laterally adjacent tubulin dimer, mediating crosstalk between α-tail and β-tail. This positive feedback loop can generate localized microtubule glutamylation patterns. Our work uncovers general principles that generate tubulin chemical and topographic complexity. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_42884.map.gz emd_42884.map.gz | 14 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-42884-v30.xml emd-42884-v30.xml emd-42884.xml emd-42884.xml | 27 KB 27 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_42884_fsc.xml emd_42884_fsc.xml | 20.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_42884.png emd_42884.png | 128.6 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_42884_msk_1.map emd_42884_msk_1.map | 699 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-42884.cif.gz emd-42884.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_42884_additional_1.map.gz emd_42884_additional_1.map.gz emd_42884_additional_2.map.gz emd_42884_additional_2.map.gz emd_42884_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42884_half_map_1.map.gz emd_42884_half_map_2.map.gz emd_42884_half_map_2.map.gz | 561.7 MB 11.1 MB 564.1 MB 564.9 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42884 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42884 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42884 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-42884 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 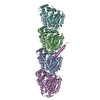 8t42C  8u3zC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_42884.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 699 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_42884.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 699 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
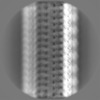
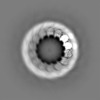
| Annotation | Map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule, locally sharpened | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
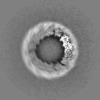
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.15 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_42884_msk_1.map emd_42884_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
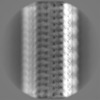
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
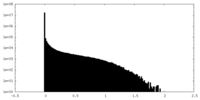
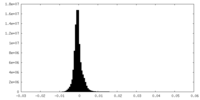
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Raw map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule
| File | emd_42884_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
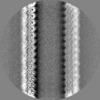
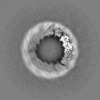
| Annotation | Raw map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
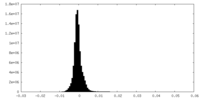
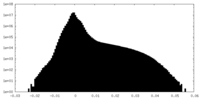
| Density Histograms |
-Additional map: Map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule,...
| File | emd_42884_additional_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule, post-processed with DeepEMhancer | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: Second half-map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule
| File | emd_42884_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Second half-map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: First half-map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule
| File | emd_42884_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | First half-map of alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubule | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : TTLL6 bound to unmodified human microtubules
| Entire | Name: TTLL6 bound to unmodified human microtubules |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: TTLL6 bound to unmodified human microtubules
| Supramolecule | Name: TTLL6 bound to unmodified human microtubules / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: Microtubules were decorated with TTLL6 on electron microscopy grids |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 300 KDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1B, betaI and betaIVb
| Supramolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1B, betaI and betaIVb / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: kidney / Location in cell: cytoplasm Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: kidney / Location in cell: cytoplasm |
-Supramolecule #3: Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL6
| Supramolecule | Name: Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL6 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin alpha-1B chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1B chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: a-tubulin from tsA201 cell line / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: kidney Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: kidney |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLISQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRIHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRSIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YQPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GVDSVEGEGE EEGEEY UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1B chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin beta-I/IVb chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta-I/IVb chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: kidney Homo sapiens (human) / Organ: kidney |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLDRISVY YNEATGGKYV PRAILVDLE PGTMDSVRSG PFGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV V RKEAESCD CLQGFQLTHS LGGGTGSGMG TLLISKIREE YPDRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLDRISVY YNEATGGKYV PRAILVDLE PGTMDSVRSG PFGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV V RKEAESCD CLQGFQLTHS LGGGTGSGMG TLLISKIREE YPDRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VV EPYNATL SVHQLVENTD ETYCIDNEAL YDICFRTLKL TTPTYGDLNH LVSATMSGVT TCL RFPGQL NADLRKLAVN MVPFPRLHFF MPGFAPLTSR GSQQYRALTV PELTQQVFDA KNMM AACDP RHGRYLTVAA VFRGRMSMKE VDEQMLNVQN KNSSYFVEWI PNNVKTAVCD IPPRG LKMA VTFIGNSTAI QELFKRISEQ FTAMFRRKAF LHWYTGEGMD EMEFTEAESN MNDLVS EYQ QYQDATAEEE EDFGEEAEEE A UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #3: Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL6
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin polyglutamylase TTLL6 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO EC number: Ligases; Forming carbon-nitrogen bonds; Acid-amino-acid ligases (peptide synthases) |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: GKKKRKKKRL VINLSNCRYD SVRRAAQQYG LREAGDNDDW TLYWTDYSVS LERVMEMKSY QKINHFPGMS EICRKDLLAR NMSRMLKLFP KDFHFFPRTW CLPADWGDLQ TYSRTRKNKT YICKPDSGCQ GRGIFITRSV KEIKPGEDMI CQLYISKPFI IDGFKFDLRV ...String: GKKKRKKKRL VINLSNCRYD SVRRAAQQYG LREAGDNDDW TLYWTDYSVS LERVMEMKSY QKINHFPGMS EICRKDLLAR NMSRMLKLFP KDFHFFPRTW CLPADWGDLQ TYSRTRKNKT YICKPDSGCQ GRGIFITRSV KEIKPGEDMI CQLYISKPFI IDGFKFDLRV YVLVTSCDPL RVFVYNEGLA RFATTSYSHP NLDNLDEICM HLTNYSINKH SSNFVQDAFS GSKRKLSTFN SYMKTHGYDV EQIWRGIEDV IIKTLISAHP VIKHNYHTCF PSHTLNSACF EILGFDILLD RKLKPWLLEV NHSPSFSTDS KLDKEVKDSL LYDALVLINL GNCDKKKVLE EERQRGRFLQ QCPNREIRLE EVKGFQAMRL QKTEEYEKKN CGGFRLIYPG LNLEKYDKFF QDNSSLFQNT VASRARELYA RQLIQELRQK QEKKVFLKKA RKA |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.1 mg/mL | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7 Component:
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 303 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: The sample was blotted with Whatman #5 blotting paper on both sides of the grid for 3 s with a blot offset of -1 using a Vitrobot Mark IV (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with a chamber set to 30C ...Details: The sample was blotted with Whatman #5 blotting paper on both sides of the grid for 3 s with a blot offset of -1 using a Vitrobot Mark IV (Thermo Fisher Scientific) with a chamber set to 30C at 100% humidity and subsequently plunged into liquid ethane.. | ||||||||||||||||||
| Details | TTLL6 decoration of microtubule was heterogenous. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Digitization - Frames/image: 1-39 / Number real images: 2771 / Average exposure time: 9.75 sec. / Average electron dose: 42.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 36000 |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
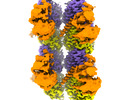
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Initial model |
| ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT / Target criteria: Cross-correlation |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller


































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)