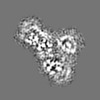
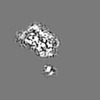
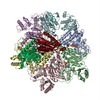
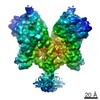
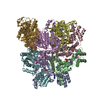
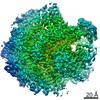
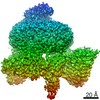
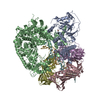
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-4166タイトル Cryo-EM structure of TRIP13 in complex with ATP gamma S, p31comet, C-Mad2 and Cdc20 TRIP13:p31-Substrate map 複合体 : TRIP13 hexamer in complex with ATP gamma S, p31comet, C-Mad2 and Cdc20複合体 : MAD2L1-binding protein, Pachytene checkpoint protein 2 homologタンパク質・ペプチド : Pachytene checkpoint protein 2 homologタンパク質・ペプチド : MAD2L1-binding protein複合体 : Cell division cycle protein 20 homolog, Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2Aタンパク質・ペプチド : Cell division cycle protein 20 homologタンパク質・ペプチド : Mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint protein MAD2Aリガンド : PHOSPHOTHIOPHOSPHORIC ACID-ADENYLATE ESTER / / / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 4.6 Å Alfieri C / Chang L 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 Cancer Research UK C576/A14109
ジャーナル : Nature / 年 : 2018タイトル : Mechanism for remodelling of the cell cycle checkpoint protein MAD2 by the ATPase TRIP13.著者 : Claudio Alfieri / Leifu Chang / David Barford / 要旨 : The maintenance of genome stability during mitosis is coordinated by the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) through its effector the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), an inhibitor of the anaphase- ... The maintenance of genome stability during mitosis is coordinated by the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) through its effector the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), an inhibitor of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C, also known as the cyclosome). Unattached kinetochores control MCC assembly by catalysing a change in the topology of the β-sheet of MAD2 (an MCC subunit), thereby generating the active closed MAD2 (C-MAD2) conformer. Disassembly of free MCC, which is required for SAC inactivation and chromosome segregation, is an ATP-dependent process driven by the AAA+ ATPase TRIP13. In combination with p31, an SAC antagonist, TRIP13 remodels C-MAD2 into inactive open MAD2 (O-MAD2). Here, we present a mechanism that explains how TRIP13-p31 disassembles the MCC. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of the TRIP13-p31-C-MAD2-CDC20 complex reveal that p31 recruits C-MAD2 to a defined site on the TRIP13 hexameric ring, positioning the N terminus of C-MAD2 (MAD2) to insert into the axial pore of TRIP13 and distorting the TRIP13 ring to initiate remodelling. Molecular modelling suggests that by gripping MAD2 within its axial pore, TRIP13 couples sequential ATP-driven translocation of its hexameric ring along MAD2 to push upwards on, and simultaneously rotate, the globular domains of the p31-C-MAD2 complex. This unwinds a region of the αA helix of C-MAD2 that is required to stabilize the C-MAD2 β-sheet, thus destabilizing C-MAD2 in favour of O-MAD2 and dissociating MAD2 from p31. Our study provides insights into how specific substrates are recruited to AAA+ ATPases through adaptor proteins and suggests a model of how translocation through the axial pore of AAA+ ATPases is coupled to protein remodelling. 履歴 登録 2017年11月20日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2017年11月29日 - マップ公開 2018年5月2日 - 更新 2025年10月1日 - 現状 2025年10月1日 処理サイト : PDBe / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 英国, 1件
英国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2018
ジャーナル: Nature / 年: 2018

 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_4166.map.gz
emd_4166.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-4166-v30.xml
emd-4166-v30.xml emd-4166.xml
emd-4166.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_4166.png
emd_4166.png emd-4166.cif.gz
emd-4166.cif.gz emd_4166_additional_1.map.gz
emd_4166_additional_1.map.gz emd_4166_additional_2.map.gz
emd_4166_additional_2.map.gz emd_4166_additional_3.map.gz
emd_4166_additional_3.map.gz emd_4166_additional_4.map.gz
emd_4166_additional_4.map.gz emd_4166_additional_5.map.gz
emd_4166_additional_5.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4166
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4166 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4166
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-4166 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
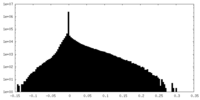
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_4166.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 10.5 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_4166.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 10.5 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
Trichoplusia ni (イラクサキンウワバ)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー


















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)