[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
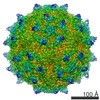
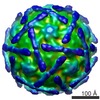
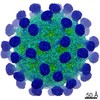
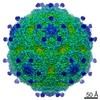
Yorodumi- EMDB-3880: Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1-D2 fragment of ICAM-1 -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3880 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1-D2 fragment of ICAM-1 | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1-D2 fragment of ICAM-1 | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Enterovirus / Receptor / Complex / picornavirus / VIRUS | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationregulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity / T cell extravasation / positive regulation of cellular extravasation / regulation of ruffle assembly / T cell antigen processing and presentation / membrane to membrane docking / T cell activation via T cell receptor contact with antigen bound to MHC molecule on antigen presenting cell / adhesion of symbiont to host / establishment of endothelial barrier / heterophilic cell-cell adhesion ...regulation of leukocyte mediated cytotoxicity / T cell extravasation / positive regulation of cellular extravasation / regulation of ruffle assembly / T cell antigen processing and presentation / membrane to membrane docking / T cell activation via T cell receptor contact with antigen bound to MHC molecule on antigen presenting cell / adhesion of symbiont to host / establishment of endothelial barrier / heterophilic cell-cell adhesion / cell adhesion mediated by integrin / leukocyte migration / leukocyte cell-cell adhesion / Interleukin-10 signaling / symbiont-mediated suppression of host cytoplasmic pattern recognition receptor signaling pathway via inhibition of RIG-I activity / immunological synapse / Integrin cell surface interactions / negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process / negative regulation of extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway via death domain receptors / cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor / picornain 2A / symbiont-mediated suppression of host mRNA export from nucleus / symbiont genome entry into host cell via pore formation in plasma membrane / picornain 3C / T=pseudo3 icosahedral viral capsid / cellular response to glucose stimulus / host cell cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / : / integrin binding / cellular response to amyloid-beta / Interferon gamma signaling / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / ribonucleoside triphosphate phosphatase activity / viral capsid / transmembrane signaling receptor activity / nucleoside-triphosphate phosphatase / signaling receptor activity / host cell / channel activity / virus receptor activity / Interleukin-4 and Interleukin-13 signaling / monoatomic ion transmembrane transport / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade / RNA helicase activity / cell adhesion / membrane raft / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / external side of plasma membrane / symbiont-mediated activation of host autophagy / RNA-directed RNA polymerase / focal adhesion / cysteine-type endopeptidase activity / viral RNA genome replication / RNA-directed RNA polymerase activity / symbiont entry into host cell / DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / host cell nucleus / structural molecule activity / cell surface / proteolysis / extracellular space / RNA binding / extracellular exosome / zinc ion binding / ATP binding / membrane / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Coxsackievirus A24 / Coxsackievirus A24 /  homo sapiens (human) / homo sapiens (human) /  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.9 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hurdiss DL / Ranson NA | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  Netherlands, Netherlands,  Germany, Germany,  United Kingdom, 3 items United Kingdom, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2018 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2018Title: Role of enhanced receptor engagement in the evolution of a pandemic acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis virus. Authors: Jim Baggen / Daniel L Hurdiss / Georg Zocher / Nitesh Mistry / Richard W Roberts / Jasper J Slager / Hongbo Guo / Arno L W van Vliet / Maryam Wahedi / Kimberley Benschop / Erwin Duizer / ...Authors: Jim Baggen / Daniel L Hurdiss / Georg Zocher / Nitesh Mistry / Richard W Roberts / Jasper J Slager / Hongbo Guo / Arno L W van Vliet / Maryam Wahedi / Kimberley Benschop / Erwin Duizer / Cornelis A M de Haan / Erik de Vries / José M Casasnovas / Raoul J de Groot / Niklas Arnberg / Thilo Stehle / Neil A Ranson / Hendrik Jan Thibaut / Frank J M van Kuppeveld /      Abstract: Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (AHC) is a painful, contagious eye disease, with millions of cases in the last decades. Coxsackievirus A24 (CV-A24) was not originally associated with human disease, ...Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (AHC) is a painful, contagious eye disease, with millions of cases in the last decades. Coxsackievirus A24 (CV-A24) was not originally associated with human disease, but in 1970 a pathogenic "variant" (CV-A24v) emerged, which is now the main cause of AHC. Initially, this variant circulated only in Southeast Asia, but it later spread worldwide, accounting for numerous AHC outbreaks and two pandemics. While both CV-A24 variant and nonvariant strains still circulate in humans, only variant strains cause AHC for reasons that are yet unknown. Since receptors are important determinants of viral tropism, we set out to map the CV-A24 receptor repertoire and establish whether changes in receptor preference have led to the increased pathogenicity and rapid spread of CV-A24v. Here, we identify ICAM-1 as an essential receptor for both AHC-causing and non-AHC strains. We provide a high-resolution cryo-EM structure of a virus-ICAM-1 complex, which revealed critical ICAM-1-binding residues. These data could help identify a possible conserved mode of receptor engagement among ICAM-1-binding enteroviruses and rhinoviruses. Moreover, we identify a single capsid substitution that has been adopted by all pandemic CV-A24v strains and we reveal that this adaptation enhances the capacity of CV-A24v to bind sialic acid. Our data elucidate the CV-A24v receptor repertoire and point to a role of enhanced receptor engagement in the adaptation to the eye, possibly enabling pandemic spread. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3880.map.gz emd_3880.map.gz | 219.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3880-v30.xml emd-3880-v30.xml emd-3880.xml emd-3880.xml | 19.5 KB 19.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3880_fsc.xml emd_3880_fsc.xml | 15.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3880.png emd_3880.png | 237.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3880.cif.gz emd-3880.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_3880_additional.map.gz emd_3880_additional.map.gz | 302.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3880 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3880 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3880 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3880 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  6eitMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3880.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 381.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3880.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 381.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1-D2 fragment of ICAM-1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.0651 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1-D2 fragment...
| File | emd_3880_additional.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1-D2 fragment of ICAM-1 (unsharpened map). | ||||||||||||
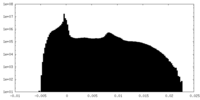
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
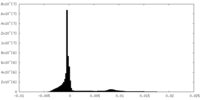
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1 and D2 domains of ICAM-1
| Entire | Name: Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1 and D2 domains of ICAM-1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1 and D2 domains of ICAM-1
| Supramolecule | Name: Coxsackievirus A24v in complex with the D1 and D2 domains of ICAM-1 type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 8 MDa |
-Supramolecule #2: Coxsackievirus A24
| Supramolecule | Name: Coxsackievirus A24 / type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #1-#3 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Coxsackievirus A24 Coxsackievirus A24 |
-Supramolecule #3: D1 and D2 domains of ICAM-1
| Supramolecule | Name: D1 and D2 domains of ICAM-1 / type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 / Macromolecule list: #4 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  homo sapiens (human) homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: VP1
| Macromolecule | Name: VP1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Coxsackievirus A24 Coxsackievirus A24 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 34.378371 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GIEETIDTVI TNALQLSQPK PQKQPTAQST PLTSGVNSQE VPALTAVETG ASGQAVPSDV IETRHVVNYK TRSESTLESF FGRSACVTI LEVENFNATT DADRKKQFTT WAITYTDTVQ LRRKLEFFTY SRFDLEMTFV ITERYYASNT GHARNQVYQL M YIPPGAPR ...String: GIEETIDTVI TNALQLSQPK PQKQPTAQST PLTSGVNSQE VPALTAVETG ASGQAVPSDV IETRHVVNYK TRSESTLESF FGRSACVTI LEVENFNATT DADRKKQFTT WAITYTDTVQ LRRKLEFFTY SRFDLEMTFV ITERYYASNT GHARNQVYQL M YIPPGAPR PTAWDDYTWQ SSSNPSVFYT YGSAPPRMSI PYVGIANAYS HFYDGFARVP LKDETVDSGD TYYGLVTIND FG TLAVRVV NEYNPARITS KIRVYMKPKH VRCWCPRPPR AVPYRGEGVD FKQDSITPLT AVENINTF UniProtKB: Genome polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #2: VP2
| Macromolecule | Name: VP2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Coxsackievirus A24 Coxsackievirus A24 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 29.817412 KDa |
| Sequence | String: SPNVEACGYS DRVRQITLGN STITTQEAAN AVVAYGEWPS YLDDKEANPI DAPTEPDVSS NRFYTLDSVQ WKSTSRGWWW KLPDALKDM GMFGQNMYYH YLGRSGYTVH VQCNASKFHQ GALGVFAIPE YVMACNTEAK TSYVSYVNAN PGEKGGVFDN A YNPSAEAS ...String: SPNVEACGYS DRVRQITLGN STITTQEAAN AVVAYGEWPS YLDDKEANPI DAPTEPDVSS NRFYTLDSVQ WKSTSRGWWW KLPDALKDM GMFGQNMYYH YLGRSGYTVH VQCNASKFHQ GALGVFAIPE YVMACNTEAK TSYVSYVNAN PGEKGGVFDN A YNPSAEAS EGRKFAALDY LLGCGVLAGN AFVYPHQIIN LRTNNSATLV LPYVNSLAID CMAKHNNWGL VILPLCKLDY AP NSSTEIP ITVTIAPMFT EFNGLRNITV PATQ UniProtKB: Genome polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #3: VP3
| Macromolecule | Name: VP3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Coxsackievirus A24 Coxsackievirus A24 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 26.637746 KDa |
| Sequence | String: GLPTMLTPGS SQFLTSDDFQ SPCALPNFDV TPPIHIPGEV FNMMELAEID SMIPMNSVTG KANTMEMYPI PLDDKGSATP IFSISLSPA SDKRLQYTML GEILNYYTHW TGSLRFTFLF CGSMMATGKI LLSYSPPGAK PPTTRKDAML GTHIIWDLGL Q SSCTMLAP ...String: GLPTMLTPGS SQFLTSDDFQ SPCALPNFDV TPPIHIPGEV FNMMELAEID SMIPMNSVTG KANTMEMYPI PLDDKGSATP IFSISLSPA SDKRLQYTML GEILNYYTHW TGSLRFTFLF CGSMMATGKI LLSYSPPGAK PPTTRKDAML GTHIIWDLGL Q SSCTMLAP WISNTVYRRC IKDDFTEGGY ITCFYQTRIV VPSGTPTSMF MLAFVSACPD FSVRLLRDTN HISQRTLFAR AQ UniProtKB: Genome polyprotein |
-Macromolecule #4: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 9.2976 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: QTSVSPSKVI LPRGGSVLVT CSTSCDQPKL LGIETPLPKK ELLLPGNNRK VYELSNVQED SQPMCYSNCP DGQSTAKTFL TVYWT UniProtKB: Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 10 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: TBS buffer (Coxsackievirus A24v) Phosphate buffer (ICAM-1 D1-D2) |
| Grid | Model: Lacey grids coated in a 3 nm carbon film (Agar Scientific, UK) Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: CONTINUOUS / Support film - Film thickness: 3 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 80 % / Chamber temperature: 8 K / Instrument: LEICA EM GP Details: On-grid binding of the receptor was performed by applying 3 microliters of ICAM-1 (9.85 mg/ml) to the pre-blotted, virus-containing grid, and leaving for 30 seconds before blotting and freezing. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 2652 / Average exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-6eit: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller














 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)