[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-37474: Human L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.2 in the presence... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Human L-type voltage-gated calcium channel Cav1.2 in the presence of calciseptine, amlodipine and pinaverium at 2.9 Angstrom resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Cav1.2 / Channels / Calcium Ion-Selective / TRANSPORT PROTEIN / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationpositive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / immune system development / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / Phase 2 - plateau phase ...positive regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in AV node cell action potential / voltage-gated calcium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential / immune system development / positive regulation of adenylate cyclase activity / Presynaptic depolarization and calcium channel opening / regulation of membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane depolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / Phase 2 - plateau phase / high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / membrane depolarization during AV node cell action potential / membrane depolarization during bundle of His cell action potential / cardiac conduction / L-type voltage-gated calcium channel complex / membrane depolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / positive regulation of muscle contraction / cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / NCAM1 interactions / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / camera-type eye development / cardiac muscle cell action potential involved in contraction / embryonic forelimb morphogenesis / calcium ion transport into cytosol / regulation of calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel / voltage-gated calcium channel complex / Mechanical load activates signaling by PIEZO1 and integrins in osteocytes / Phase 0 - rapid depolarisation / alpha-actinin binding / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / calcium ion import across plasma membrane / regulation of calcium ion transport / neuronal dense core vesicle / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / voltage-gated calcium channel activity / presynaptic active zone membrane / sarcoplasmic reticulum / protein localization to plasma membrane / calcium channel regulator activity / Regulation of insulin secretion / postsynaptic density membrane / calcium ion transmembrane transport / GABA-ergic synapse / Z disc / cellular response to amyloid-beta / calcium ion transport / Adrenaline,noradrenaline inhibits insulin secretion / T cell receptor signaling pathway / toxin activity / heart development / positive regulation of cytosolic calcium ion concentration / chemical synaptic transmission / perikaryon / calmodulin binding / postsynaptic density / cilium / dendrite / synapse / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / nucleoplasm / metal ion binding / membrane / plasma membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) Dendroaspis polylepis polylepis (black mamba) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Gao S / Yao X / Yan N | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell / Year: 2023 Journal: Cell / Year: 2023Title: Structural basis for human Ca1.2 inhibition by multiple drugs and the neurotoxin calciseptine. Authors: Shuai Gao / Xia Yao / Jiaofeng Chen / Gaoxingyu Huang / Xiao Fan / Lingfeng Xue / Zhangqiang Li / Tong Wu / Yupeng Zheng / Jian Huang / Xueqin Jin / Yan Wang / Zhifei Wang / Yong Yu / Lei ...Authors: Shuai Gao / Xia Yao / Jiaofeng Chen / Gaoxingyu Huang / Xiao Fan / Lingfeng Xue / Zhangqiang Li / Tong Wu / Yupeng Zheng / Jian Huang / Xueqin Jin / Yan Wang / Zhifei Wang / Yong Yu / Lei Liu / Xiaojing Pan / Chen Song / Nieng Yan /   Abstract: Ca1.2 channels play crucial roles in various neuronal and physiological processes. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human Ca1.2, both in its apo form and in complex with several drugs, as well ...Ca1.2 channels play crucial roles in various neuronal and physiological processes. Here, we present cryo-EM structures of human Ca1.2, both in its apo form and in complex with several drugs, as well as the peptide neurotoxin calciseptine. Most structures, apo or bound to calciseptine, amlodipine, or a combination of amiodarone and sofosbuvir, exhibit a consistent inactivated conformation with a sealed gate, three up voltage-sensing domains (VSDs), and a down VSD. Calciseptine sits on the shoulder of the pore domain, away from the permeation path. In contrast, when pinaverium bromide, an antispasmodic drug, is inserted into a cavity reminiscent of the IFM-binding site in Na channels, a series of structural changes occur, including upward movement of VSD coupled with dilation of the selectivity filter and its surrounding segments in repeat III. Meanwhile, S4-5 merges with S5 to become a single helix, resulting in a widened but still non-conductive intracellular gate. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_37474.map.gz emd_37474.map.gz | 79.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-37474-v30.xml emd-37474-v30.xml emd-37474.xml emd-37474.xml | 24.8 KB 24.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_37474.png emd_37474.png | 41.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-37474.cif.gz emd-37474.cif.gz | 9.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_37474_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37474_half_map_1.map.gz emd_37474_half_map_2.map.gz emd_37474_half_map_2.map.gz | 77.7 MB 77.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37474 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37474 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37474 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-37474 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8we8MC  8fhsC  8we6C  8we7C  8we9C  8weaC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_37474.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_37474.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.114 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_37474_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
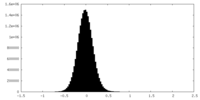
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_37474_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : Cav1.2
+Supramolecule #1: Cav1.2
+Macromolecule #1: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit alpha-1C
+Macromolecule #2: Voltage-dependent calcium channel subunit alpha-2/delta-1
+Macromolecule #3: Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-3
+Macromolecule #4: Calciseptin
+Macromolecule #8: CALCIUM ION
+Macromolecule #9: CHOLESTEROL
+Macromolecule #10: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
+Macromolecule #11: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tr...
+Macromolecule #12: 1,2-Distearoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
+Macromolecule #13: amlodipine
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 281 K |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.1 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.9000000000000001 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




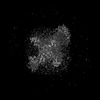


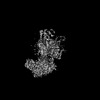

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)