[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-3663: RsgA-GDPNP bound to the 30S ribosomal subunit (RsgA assembly inte... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3663 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | RsgA-GDPNP bound to the 30S ribosomal subunit (RsgA assembly intermediate with uS3) | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Postprocessed merged map_rlnFinalResolution 5.833443_rlnBfactorUsedForSharpening -100.000000 | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | ribosome | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationguanosine tetraphosphate binding / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; In phosphorus-containing anhydrides / four-way junction DNA binding / regulation of mRNA stability / negative regulation of translational initiation ...guanosine tetraphosphate binding / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; In phosphorus-containing anhydrides / four-way junction DNA binding / regulation of mRNA stability / negative regulation of translational initiation / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / positive regulation of RNA splicing / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA endonuclease activity / DNA-templated transcription termination / maintenance of translational fidelity / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / GDP binding / regulation of translation / ribosome biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / response to antibiotic / hydrolase activity / GTPase activity / mRNA binding / GTP binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / metal ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.16 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Lopez-Alonso JP / Kaminishi T | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2017 Journal: Nucleic Acids Res / Year: 2017Title: RsgA couples the maturation state of the 30S ribosomal decoding center to activation of its GTPase pocket. Authors: Jorge Pedro López-Alonso / Tatsuya Kaminishi / Takeshi Kikuchi / Yuya Hirata / Idoia Iturrioz / Neha Dhimole / Andreas Schedlbauer / Yoichi Hase / Simon Goto / Daisuke Kurita / Akira Muto / ...Authors: Jorge Pedro López-Alonso / Tatsuya Kaminishi / Takeshi Kikuchi / Yuya Hirata / Idoia Iturrioz / Neha Dhimole / Andreas Schedlbauer / Yoichi Hase / Simon Goto / Daisuke Kurita / Akira Muto / Shu Zhou / Chieko Naoe / Deryck J Mills / David Gil-Carton / Chie Takemoto / Hyouta Himeno / Paola Fucini / Sean R Connell /    Abstract: During 30S ribosomal subunit biogenesis, assembly factors are believed to prevent accumulation of misfolded intermediate states of low free energy that slowly convert into mature 30S subunits, ...During 30S ribosomal subunit biogenesis, assembly factors are believed to prevent accumulation of misfolded intermediate states of low free energy that slowly convert into mature 30S subunits, namely, kinetically trapped particles. Among the assembly factors, the circularly permuted GTPase, RsgA, plays a crucial role in the maturation of the 30S decoding center. Here, directed hydroxyl radical probing and single particle cryo-EM are employed to elucidate RsgA΄s mechanism of action. Our results show that RsgA destabilizes the 30S structure, including late binding r-proteins, providing a structural basis for avoiding kinetically trapped assembly intermediates. Moreover, RsgA exploits its distinct GTPase pocket and specific interactions with the 30S to coordinate GTPase activation with the maturation state of the 30S subunit. This coordination validates the architecture of the decoding center and facilitates the timely release of RsgA to control the progression of 30S biogenesis. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3663.map.gz emd_3663.map.gz | 5.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3663-v30.xml emd-3663-v30.xml emd-3663.xml emd-3663.xml | 38.6 KB 38.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_3663_fsc.xml emd_3663_fsc.xml | 8.9 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_3663.png emd_3663.png | 114.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3663.cif.gz emd-3663.cif.gz | 9.5 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_3663_half_map_1.map.gz emd_3663_half_map_1.map.gz emd_3663_half_map_2.map.gz emd_3663_half_map_2.map.gz | 49.6 MB 49.6 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3663 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3663 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3663 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3663 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5no4MC 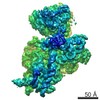 3661C 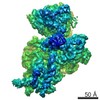 3662C  5no2C 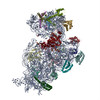 5no3C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3663.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3663.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Postprocessed merged map_rlnFinalResolution 5.833443_rlnBfactorUsedForSharpening -100.000000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.39 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Half map: Note calibrated pixel size is 1.39: use this...
| File | emd_3663_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Note calibrated pixel size is 1.39: use this value for post-processing | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_3663_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
+Entire : 30S ribosomal subunit bound by RsgA
+Supramolecule #1: 30S ribosomal subunit bound by RsgA
+Macromolecule #1: 16S ribosomal RNA
+Macromolecule #2: 30S ribosomal protein S3
+Macromolecule #3: 30S ribosomal protein S4
+Macromolecule #4: 30S ribosomal protein S5
+Macromolecule #5: 30S ribosomal protein S6
+Macromolecule #6: 30S ribosomal protein S7
+Macromolecule #7: 30S ribosomal protein S8
+Macromolecule #8: 30S ribosomal protein S9
+Macromolecule #9: 30S ribosomal protein S10
+Macromolecule #10: 30S ribosomal protein S11
+Macromolecule #11: 30S ribosomal protein S12
+Macromolecule #12: 30S ribosomal protein S13
+Macromolecule #13: 30S ribosomal protein S14
+Macromolecule #14: 30S ribosomal protein S15
+Macromolecule #15: 30S ribosomal protein S16
+Macromolecule #16: 30S ribosomal protein S17
+Macromolecule #17: 30S ribosomal protein S18
+Macromolecule #18: 30S ribosomal protein S19
+Macromolecule #19: 30S ribosomal protein S20
+Macromolecule #20: Small ribosomal subunit biogenesis GTPase RsgA
+Macromolecule #21: MAGNESIUM ION
+Macromolecule #22: ZINC ION
+Macromolecule #23: PHOSPHOAMINOPHOSPHONIC ACID-GUANYLATE ESTER
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 Component:
| |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R2/1 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 200 / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 50 sec. / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Pretreatment - Pressure: 0.02 kPa | |||||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 95 % / Chamber temperature: 278 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK II |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON II (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Digitization - Dimensions - Width: 2048 pixel / Digitization - Dimensions - Height: 2048 pixel / Number real images: 3408 / Average exposure time: 1.5 sec. / Average electron dose: 2.3 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 101000 / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 59000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Protocol: BACKBONE TRACE |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5no4: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



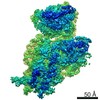
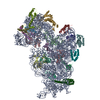
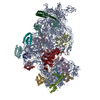

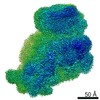




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)