[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-3589: Cryo-EM structure of tsA201 cell alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb mi... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-3589 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
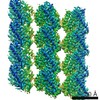
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of tsA201 cell alpha1B and betaI and betaIVb microtubules | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | HEK cell tubulin microtubule cryo-EM reconstruction | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Microtubules Dynamics Tubulin Isoform / structural protein | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationodontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Intraflagellar transport / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / Gap junction assembly ...odontoblast differentiation / Post-chaperonin tubulin folding pathway / Cilium Assembly / cytoskeleton-dependent intracellular transport / Carboxyterminal post-translational modifications of tubulin / Microtubule-dependent trafficking of connexons from Golgi to the plasma membrane / Sealing of the nuclear envelope (NE) by ESCRT-III / Intraflagellar transport / Formation of tubulin folding intermediates by CCT/TriC / Gap junction assembly / Kinesins / GTPase activating protein binding / Assembly and cell surface presentation of NMDA receptors / COPI-independent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / COPI-dependent Golgi-to-ER retrograde traffic / natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity / regulation of synapse organization / nuclear envelope lumen / Recycling pathway of L1 / MHC class I protein binding / RHOH GTPase cycle / RHO GTPases activate IQGAPs / microtubule-based process / Hedgehog 'off' state / intercellular bridge / COPI-mediated anterograde transport / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / cytoplasmic microtubule / spindle assembly / Loss of Nlp from mitotic centrosomes / Loss of proteins required for interphase microtubule organization from the centrosome / Recruitment of mitotic centrosome proteins and complexes / MHC class II antigen presentation / Mitotic Prometaphase / Recruitment of NuMA to mitotic centrosomes / cellular response to interleukin-4 / Anchoring of the basal body to the plasma membrane / EML4 and NUDC in mitotic spindle formation / HSP90 chaperone cycle for steroid hormone receptors (SHR) in the presence of ligand / AURKA Activation by TPX2 / Resolution of Sister Chromatid Cohesion / Translocation of SLC2A4 (GLUT4) to the plasma membrane / RHO GTPases Activate Formins / PKR-mediated signaling / structural constituent of cytoskeleton / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / HCMV Early Events / Aggrephagy / azurophil granule lumen / The role of GTSE1 in G2/M progression after G2 checkpoint / mitotic spindle / Separation of Sister Chromatids / Regulation of PLK1 Activity at G2/M Transition / mitotic cell cycle / double-stranded RNA binding / microtubule cytoskeleton / cell body / Hydrolases; Acting on acid anhydrides; Acting on GTP to facilitate cellular and subcellular movement / Potential therapeutics for SARS / microtubule / cytoskeleton / cilium / membrane raft / protein domain specific binding / cell division / GTPase activity / ubiquitin protein ligase binding / Neutrophil degranulation / GTP binding / protein-containing complex binding / structural molecule activity / protein-containing complex / extracellular exosome / extracellular region / metal ion binding / nucleus / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Vemu A / Atherton J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United Kingdom, United Kingdom,  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Biol Cell / Year: 2017 Journal: Mol Biol Cell / Year: 2017Title: Tubulin isoform composition tunes microtubule dynamics. Authors: Annapurna Vemu / Joseph Atherton / Jeffrey O Spector / Carolyn A Moores / Antonina Roll-Mecak /   Abstract: Microtubules polymerize and depolymerize stochastically, a behavior essential for cell division, motility, and differentiation. While many studies advanced our understanding of how microtubule- ...Microtubules polymerize and depolymerize stochastically, a behavior essential for cell division, motility, and differentiation. While many studies advanced our understanding of how microtubule-associated proteins tune microtubule dynamics in trans, we have yet to understand how tubulin genetic diversity regulates microtubule functions. The majority of in vitro dynamics studies are performed with tubulin purified from brain tissue. This preparation is not representative of tubulin found in many cell types. Here we report the 4.2-Å cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure and in vitro dynamics parameters of α1B/βI+βIVb microtubules assembled from tubulin purified from a human embryonic kidney cell line with isoform composition characteristic of fibroblasts and many immortalized cell lines. We find that these microtubules grow faster and transition to depolymerization less frequently compared with brain microtubules. Cryo-EM reveals that the dynamic ends of α1B/βI+βIVb microtubules are less tapered and that these tubulin heterodimers display lower curvatures. Interestingly, analysis of EB1 distributions at dynamic ends suggests no differences in GTP cap sizes. Last, we show that the addition of recombinant α1A/βIII tubulin, a neuronal isotype overexpressed in many tumors, proportionally tunes the dynamics of α1B/βI+βIVb microtubules. Our study is an important step toward understanding how tubulin isoform composition tunes microtubule dynamics. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_3589.map.gz emd_3589.map.gz | 2.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-3589-v30.xml emd-3589-v30.xml emd-3589.xml emd-3589.xml | 13.6 KB 13.6 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_3589.png emd_3589.png | 213.9 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-3589.cif.gz emd-3589.cif.gz | 6.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3589 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3589 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3589 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-3589 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  5n5nMC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_3589.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 11.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_3589.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 11.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | HEK cell tubulin microtubule cryo-EM reconstruction | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. generated in cubic-lattice coordinate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.221 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Human tsA201 cell tubulin microtubules
| Entire | Name: Human tsA201 cell tubulin microtubules |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Human tsA201 cell tubulin microtubules
| Supramolecule | Name: Human tsA201 cell tubulin microtubules / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 Details: Microtubules formed from tsA201 cell tubulin (14pf) with bound GTP analogue GMPCPP. Tubulin was purified via TOG affinity. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Tubulin beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: GMPCPP (GTP-analogue) bound / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 47.735793 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLDRISVY YNEATGGKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS ...String: MREIVHIQAG QCGNQIGAKF WEVISDEHGI DPTGTYHGDS DLQLDRISVY YNEATGGKYV PRAILVDLEP GTMDSVRSGP FGQIFRPDN FVFGQSGAGN NWAKGHYTEG AELVDSVLDV VRKEAESCDC LQGFQLTHSL GGGTGSGMGT LLISKIREEY P DRIMNTFS VVPSPKVSDT VVEPYNATLS VHQLVENTDE TYCIDNEALY DICFRTLKLT TPTYGDLNHL VSATMSGVTT CL RFPGQLN ADLRKLAVNM VPFPRLHFFM PGFAPLTSRG SQQYRALTVP ELTQQVFDAK NMMAACDPRH GRYLTVAAVF RGR MSMKEV DEQMLNVQNK NSSYFVEWIP NNVKTAVCDI PPRGLKMAVT FIGNSTAIQE LFKRISEQFT AMFRRKAFLH WYTG EGMDE MEFTEAESNM NDLVSEYQQY Q UniProtKB: Tubulin beta chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Tubulin alpha-1B chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Tubulin alpha-1B chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Details: GTP-bound / Number of copies: 6 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 48.665027 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE ...String: MRECISIHVG QAGVQIGNAC WELYCLEHGI QPDGQMPSDK TIGGGDDSFN TFFSETGAGK HVPRAVFVDL EPTVIDEVRT GTYRQLFHP EQLITGKEDA ANNYARGHYT IGKEIIDLVL DRIRKLADQC TGLQGFLVFH SFGGGTGSGF TSLLMERLSV D YGKKSKLE FSIYPAPQVS TAVVEPYNSI LTTHTTLEHS DCAFMVDNEA IYDICRRNLD IERPTYTNLN RLISQIVSSI TA SLRFDGA LNVDLTEFQT NLVPYPRIHF PLATYAPVIS AEKAYHEQLS VAEITNACFE PANQMVKCDP RHGKYMACCL LYR GDVVPK DVNAAIATIK TKRSIQFVDW CPTGFKVGIN YQPPTVVPGG DLAKVQRAVC MLSNTTAIAE AWARLDHKFD LMYA KRAFV HWYVGEGMEE GEFSEAREDM AALEKDYEEV GV UniProtKB: Tubulin alpha-1B chain |
-Macromolecule #3: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID GUANYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: G2P |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 521.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 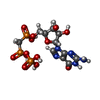 ChemComp-G2P: |
-Macromolecule #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 12 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| Macromolecule | Name: GUANOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 6 / Formula: GTP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 523.18 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-GTP: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 6.8 Details: BRB80 with GMPCPP (80mM PIPES, 2mM MgCl2, 1mM EGTA, 1mM DTT, 1mM GMPCPP) |
| Grid | Model: C-flat-2/2 / Material: COPPER / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK III |
| Details | Microtubules polymerised at 25mg/ml in BRB80 with GMPCPP and diluted to a final concentration of 2.5mg/ml |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI POLARA 300 |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: DIRECT ELECTRON DE-20 (5k x 3k) / Detector mode: INTEGRATING / Average electron dose: 25.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Tecnai Polara / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.2 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: FREALIGN Details: Gold-standard high-resolution noise substitution test employed in resolution estimation (Chen et al., 2013) Number images used: 13000 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING / Software - Name: FREALIGN |
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-5n5n: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















