+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
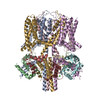
| Title | human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state B | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | potassium voltage-gated channel / ML277 / PIP2 / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationgastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / regulation of gastric acid secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization ...gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / regulation of gastric acid secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / iodide transport / transporter inhibitor activity / Phase 3 - rapid repolarisation / membrane repolarization during action potential / membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion export across plasma membrane / renal sodium ion absorption / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / auditory receptor cell development / regulation of membrane repolarization / protein phosphatase 1 binding / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion homeostasis / Voltage gated Potassium channels / : / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / non-motile cilium assembly / cardiac muscle cell contraction / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / intestinal absorption / inner ear morphogenesis / response to corticosterone / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / renal absorption / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / nitric-oxide synthase binding / ciliary base / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / regulation of heart contraction / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / calcineurin-mediated signaling / inner ear development / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / adenylate cyclase binding / action potential / protein phosphatase activator activity / cochlea development / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / monoatomic ion channel complex / social behavior / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / postsynaptic cytosol / catalytic complex / positive regulation of heart rate / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / transport vesicle / cardiac muscle contraction / presynaptic cytosol / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / sperm midpiece / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / cellular response to cAMP / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / calyx of Held / response to amphetamine / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of cytokinesis / erythrocyte differentiation Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.5 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ma D / Guo J | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 6 items China, 6 items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: Structural mechanisms for the activation of human cardiac KCNQ1 channel by electro-mechanical coupling enhancers. Authors: Demin Ma / Ling Zhong / Zhenzhen Yan / Jing Yao / Yan Zhang / Fan Ye / Yuan Huang / Dongwu Lai / Wei Yang / Panpan Hou / Jiangtao Guo /  Abstract: The cardiac KCNQ1 potassium channel carries the important current and controls the heart rhythm. Hundreds of mutations in KCNQ1 can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Although KCNQ1 ...The cardiac KCNQ1 potassium channel carries the important current and controls the heart rhythm. Hundreds of mutations in KCNQ1 can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Although KCNQ1 structures have been recently resolved, the structural basis for the dynamic electro-mechanical coupling, also known as the voltage sensor domain-pore domain (VSD-PD) coupling, remains largely unknown. In this study, utilizing two VSD-PD coupling enhancers, namely, the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP) and a small-molecule ML277, we determined 2.5-3.5 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length human KCNQ1-calmodulin (CaM) complex in the apo closed, ML277-bound open, and ML277-PIP-bound open states. ML277 binds at the "elbow" pocket above the S4-S5 linker and directly induces an upward movement of the S4-S5 linker and the opening of the activation gate without affecting the C-terminal domain (CTD) of KCNQ1. PIP binds at the cleft between the VSD and the PD and brings a large structural rearrangement of the CTD together with the CaM to activate the PD. These findings not only elucidate the structural basis for the dynamic VSD-PD coupling process during KCNQ1 gating but also pave the way to develop new therapeutics for anti-arrhythmia. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_33319.map.gz emd_33319.map.gz | 41.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-33319-v30.xml emd-33319-v30.xml emd-33319.xml emd-33319.xml | 17.5 KB 17.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_33319.png emd_33319.png | 67.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-33319.cif.gz emd-33319.cif.gz | 6.1 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_33319_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33319_half_map_1.map.gz emd_33319_half_map_2.map.gz emd_33319_half_map_2.map.gz | 37.1 MB 37.1 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33319 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33319 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33319 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-33319 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_33319_validation.pdf.gz emd_33319_validation.pdf.gz | 731.7 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_33319_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_33319_full_validation.pdf.gz | 731.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_33319_validation.xml.gz emd_33319_validation.xml.gz | 11.5 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_33319_validation.cif.gz emd_33319_validation.cif.gz | 13.5 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33319 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33319 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33319 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-33319 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7xnnMC  7xniC  7xnkC  7xnlC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_33319.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_33319.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.014 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_33319_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_33319_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state B
| Entire | Name: human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state B |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state B
| Supramolecule | Name: human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state B / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Calmodulin-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 19.615445 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK LEGGSSGGLV P RGSGGSSG GHHHHHHHH UniProtKB: Calmodulin-3 |
-Macromolecule #2: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1
| Macromolecule | Name: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 76.487297 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MAAASSPPRA ERKRWGWGRL PGARRGSAGL AKKCPFSLEL AEGGPAGGAL YAPIAPGAPG PAPPASPAAP AAPPVASDLG PRPPVSLDP RVSIYSTRRP VLARTHVQGR VYNFLERPTG WKCFVYHFAV FLIVLVCLIF SVLSTIEQYA ALATGTLFWM E IVLVVFFG ...String: MAAASSPPRA ERKRWGWGRL PGARRGSAGL AKKCPFSLEL AEGGPAGGAL YAPIAPGAPG PAPPASPAAP AAPPVASDLG PRPPVSLDP RVSIYSTRRP VLARTHVQGR VYNFLERPTG WKCFVYHFAV FLIVLVCLIF SVLSTIEQYA ALATGTLFWM E IVLVVFFG TEYVVRLWSA GCRSKYVGLW GRLRFARKPI SIIDLIVVVA SMVVLCVGSK GQVFATSAIR GIRFLQILRM LH VDRQGGT WRLLGSVVFI HRQELITTLY IGFLGLIFSS YFVYLAEKDA VNESGRVEFG SYADALWWGV VTVTTIGYGD KVP QTWVGK TIASCFSVFA ISFFALPAGI LGSGFALKVQ QKQRQKHFNR QIPAAASLIQ TAWRCYAAEN PDSSTWKIYI RKAP RSHTL LSPSPKPKKS VVVKKKKFKL DKDNGVTPGE KMLTVPHITC DPPEERRLDH FSVDGYDSSV RKSPTLLEVS MPHFM RTNS FAEDLDLEGE TLLTPITHIS QLREHHRATI KVIRRMQYFV AKKKFQQARK PYDVRDVIEQ YSQGHLNLMV RIKELQ RRL DQSIGKPSLF ISVSEKSKDR GSNTIGARLN RVEDKVTQLD QRLALITDML HQLLSLHGGS TPGSGGPPRE GGAHITQ PC GSGGSVDPEL FLPSNTLPTY EQLTVPRRGP DEGSLEGGSS GGWSHPQFEK UniProtKB: Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 1 |
-Macromolecule #3: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #4: (2R)-N-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-1-(4-methylbenzene-...
| Macromolecule | Name: (2R)-N-[4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]-1-(4-methylbenzene-1-sulfonyl)piperidine-2-carboxamide type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: I0S |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 471.592 Da |
| Chemical component information | 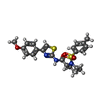 ChemComp-I0S: |
-Macromolecule #5: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(o...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-2-octanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phosphoryl]oxy-propyl] octanoate type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: PIO |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 746.566 Da |
| Chemical component information | 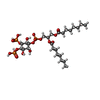 ChemComp-PIO: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 64.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: -1.3 µm / Nominal defocus min: -1.1 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: PDB ENTRY PDB model - PDB ID: |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 2.5 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Number images used: 257550 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
| Final angle assignment | Type: MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller








 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)