+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: PDB / ID: 7xnl | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state A | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Components Components |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | MEMBRANE PROTEIN / potassium voltage-gated channel / ML277 / PIP2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationgastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / iodide transport / regulation of gastric acid secretion ...gastrin-induced gastric acid secretion / corticosterone secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / basolateral part of cell / lumenal side of membrane / negative regulation of voltage-gated potassium channel activity / rhythmic behavior / stomach development / iodide transport / regulation of gastric acid secretion / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / transporter inhibitor activity / Phase 3 - rapid repolarisation / membrane repolarization during atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / membrane repolarization during action potential / Phase 2 - plateau phase / regulation of atrial cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / intracellular chloride ion homeostasis / membrane repolarization during ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / negative regulation of delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / membrane repolarization during cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion export across plasma membrane / renal sodium ion absorption / voltage-gated potassium channel activity involved in ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential repolarization / atrial cardiac muscle cell action potential / auditory receptor cell development / regulation of membrane repolarization / protein phosphatase 1 binding / detection of mechanical stimulus involved in sensory perception of sound / delayed rectifier potassium channel activity / ventricular cardiac muscle cell action potential / potassium ion homeostasis / Voltage gated Potassium channels / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / regulation of ventricular cardiac muscle cell membrane repolarization / positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transport / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / non-motile cilium assembly / outward rectifier potassium channel activity / cardiac muscle cell contraction / intestinal absorption / inner ear morphogenesis / response to corticosterone / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / adrenergic receptor signaling pathway / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / ciliary base / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / presynaptic endocytosis / protein kinase A regulatory subunit binding / renal absorption / nitric-oxide synthase binding / protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / regulation of heart contraction / calcineurin-mediated signaling / potassium ion import across plasma membrane / inner ear development / regulation of heart rate by cardiac conduction / adenylate cyclase binding / action potential / protein phosphatase activator activity / cochlea development / social behavior / monoatomic ion channel complex / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / detection of calcium ion / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / catalytic complex / postsynaptic cytosol / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / positive regulation of heart rate / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / transport vesicle / presynaptic cytosol / cardiac muscle contraction / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / sperm midpiece / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / positive regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / calcium channel complex / cellular response to epinephrine stimulus / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / cytoplasmic vesicle membrane / response to amphetamine / calyx of Held / cellular response to cAMP / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / erythrocyte differentiation / regulation of cytokinesis Similarity search - Function | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Method | ELECTRON MICROSCOPY / single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Ma, D. / Guo, J. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 6items China, 6items
| |||||||||||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2022Title: Structural mechanisms for the activation of human cardiac KCNQ1 channel by electro-mechanical coupling enhancers. Authors: Demin Ma / Ling Zhong / Zhenzhen Yan / Jing Yao / Yan Zhang / Fan Ye / Yuan Huang / Dongwu Lai / Wei Yang / Panpan Hou / Jiangtao Guo /  Abstract: The cardiac KCNQ1 potassium channel carries the important current and controls the heart rhythm. Hundreds of mutations in KCNQ1 can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Although KCNQ1 ...The cardiac KCNQ1 potassium channel carries the important current and controls the heart rhythm. Hundreds of mutations in KCNQ1 can cause life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Although KCNQ1 structures have been recently resolved, the structural basis for the dynamic electro-mechanical coupling, also known as the voltage sensor domain-pore domain (VSD-PD) coupling, remains largely unknown. In this study, utilizing two VSD-PD coupling enhancers, namely, the membrane lipid phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP) and a small-molecule ML277, we determined 2.5-3.5 Å resolution cryo-electron microscopy structures of full-length human KCNQ1-calmodulin (CaM) complex in the apo closed, ML277-bound open, and ML277-PIP-bound open states. ML277 binds at the "elbow" pocket above the S4-S5 linker and directly induces an upward movement of the S4-S5 linker and the opening of the activation gate without affecting the C-terminal domain (CTD) of KCNQ1. PIP binds at the cleft between the VSD and the PD and brings a large structural rearrangement of the CTD together with the CaM to activate the PD. These findings not only elucidate the structural basis for the dynamic VSD-PD coupling process during KCNQ1 gating but also pave the way to develop new therapeutics for anti-arrhythmia. | |||||||||||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Structure viewer | Molecule:  Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
- Download
Download
| PDBx/mmCIF format |  7xnl.cif.gz 7xnl.cif.gz | 683.2 KB | Display |  PDBx/mmCIF format PDBx/mmCIF format |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB format |  pdb7xnl.ent.gz pdb7xnl.ent.gz | 558.3 KB | Display |  PDB format PDB format |
| PDBx/mmJSON format |  7xnl.json.gz 7xnl.json.gz | Tree view |  PDBx/mmJSON format PDBx/mmJSON format | |
| Others |  Other downloads Other downloads |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  7xnl_validation.pdf.gz 7xnl_validation.pdf.gz | 1.8 MB | Display |  wwPDB validaton report wwPDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  7xnl_full_validation.pdf.gz 7xnl_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.8 MB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  7xnl_validation.xml.gz 7xnl_validation.xml.gz | 63 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  7xnl_validation.cif.gz 7xnl_validation.cif.gz | 89.8 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xn/7xnl https://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xn/7xnl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xn/7xnl ftp://data.pdbj.org/pub/pdb/validation_reports/xn/7xnl | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  33318MC  7xniC  7xnkC  7xnnC M: map data used to model this data C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
- Assembly
Assembly
| Deposited unit | 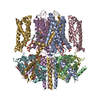
|
|---|---|
| 1 |
|
- Components
Components
| #1: Protein | Mass: 76487.297 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNQ1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1 / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: KCNQ1, KCNA8, KCNA9, KVLQT1 / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P51787 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P51787#2: Protein | Mass: 19615.445 Da / Num. of mol.: 4 Source method: isolated from a genetically manipulated source Source: (gene. exp.)  Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII / Production host: Homo sapiens (human) / Gene: CALM3, CALML2, CAM3, CAMC, CAMIII / Production host:  Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DP25 Homo sapiens (human) / References: UniProt: P0DP25#3: Chemical | ChemComp-K / #4: Chemical | ChemComp-I0S / ( #5: Chemical | ChemComp-PIO / [( Has ligand of interest | Y | |
|---|
-Experimental details
-Experiment
| Experiment | Method: ELECTRON MICROSCOPY |
|---|---|
| EM experiment | Aggregation state: PARTICLE / 3D reconstruction method: single particle reconstruction |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Component | Name: human KCNQ1-CaM-ML277-PIP2 complex in state A / Type: ORGANELLE OR CELLULAR COMPONENT / Entity ID: #1-#2 / Source: RECOMBINANT |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Source (recombinant) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Buffer solution | pH: 8 |
| Specimen | Embedding applied: NO / Shadowing applied: NO / Staining applied: NO / Vitrification applied: YES |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy imaging
Electron microscopy imaging
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
|---|---|
| Microscopy | Model: FEI TITAN KRIOS |
| Electron gun | Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM FIELD EMISSION GUN / Accelerating voltage: 300 kV / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM |
| Electron lens | Mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: -1300 nm / Nominal defocus min: -1100 nm |
| Image recording | Electron dose: 64 e/Å2 / Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) |
- Processing
Processing
| CTF correction | Type: PHASE FLIPPING AND AMPLITUDE CORRECTION |
|---|---|
| 3D reconstruction | Resolution: 3.1 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Num. of particles: 103745 / Symmetry type: POINT |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller






 PDBj
PDBj