[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-32215: Cryo-EM structure of Depo32, a Klebsiella phage depolymerase targ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of Depo32, a Klebsiella phage depolymerase targets the K2 serotype K. pneumoniae | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | |||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Depolymerase / Klebsiella pneumoniae / K2 capsular type / Capsular polysaccharides / LYASE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology | biological process involved in interaction with host / Pectin lyase fold/virulence factor / viral life cycle / virion component / Depolymerase Function and homology information Function and homology information | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Klebsiella phage 020009 (virus) / Klebsiella phage 020009 (virus) /  Klebsiella phage GH-K3 (virus) Klebsiella phage GH-K3 (virus) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.32 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Cai R / Ren Z | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 3 items China, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Microbiol Spectr / Year: 2023 Journal: Microbiol Spectr / Year: 2023Title: Structural biology and functional features of phage-derived depolymerase Depo32 on with K2 serotype capsular polysaccharides. Authors: Ruopeng Cai / Zhuolu Ren / Rihong Zhao / Yan Lu / Xinwu Wang / Zhimin Guo / Jinming Song / Wentao Xiang / Rui Du / Xiaokang Zhang / Wenyu Han / Heng Ru / Jingmin Gu /  Abstract: Hypervirulent with capsular polysaccharides (CPSs) causes severe nosocomial- and community-acquired infections. Phage-derived depolymerases can degrade CPSs from to attenuate bacterial virulence, ...Hypervirulent with capsular polysaccharides (CPSs) causes severe nosocomial- and community-acquired infections. Phage-derived depolymerases can degrade CPSs from to attenuate bacterial virulence, but their antimicrobial mechanisms and clinical potential are not well understood. In the present study, phage GH-K3-derived depolymerase Depo32 (encoded by gene ) was identified to exhibit high efficiency in specifically degrading the CPSs of K2 serotype . The cryo-electron microscopy structure of trimeric Depo32 at a resolution up to 2.32 Å revealed potential catalytic centers in the cleft of each of the two adjacent subunits. subjected to Depo32 became more sensitive to phagocytosis by RAW264.7 cells and activated the cells by the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. In addition, intranasal inoculation with Depo32 (a single dose of 200 µg, 20 µg daily for 3 days, or in combination with gentamicin) rescued all C57BL/6J mice infected with a lethal dose of K7 without interference from its neutralizing antibody. In summary, this work elaborates on the mechanism by which Depo32 targets the degradation of K2 serotype CPSs and its potential as an antivirulence agent. IMPORTANCE Depolymerases specific to more than 20 serotypes of spp. have been identified, but most studies only evaluated the single-dose treatment of depolymerases with relatively simple clinical evaluation indices and did not reveal the anti-infection mechanism of these depolymerases in depth. On the basis of determining the biological characteristics, the structure of Depo32 was analyzed by cryo-electron microscopy, and the potential active center was further identified. In addition, the effects of Depo32 on macrophage phagocytosis, signaling pathway activation, and serum killing were revealed, and the efficacy of the depolymerase (single treatment, multiple treatments, or in combination with gentamicin) against acute pneumonia caused by was evaluated. Moreover, the roles of the active sites of Depo32 were also elucidated in the and studies. Therefore, through structural biology, cell biology, and experiments, this study demonstrated the mechanism by which Depo32 targets K2 serotype . infection. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_32215.map.gz emd_32215.map.gz | 56.8 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-32215-v30.xml emd-32215-v30.xml emd-32215.xml emd-32215.xml | 20.3 KB 20.3 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_32215_fsc.xml emd_32215_fsc.xml | 9.1 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_32215.png emd_32215.png | 115 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-32215.cif.gz emd-32215.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_32215_additional_1.map.gz emd_32215_additional_1.map.gz emd_32215_half_map_1.map.gz emd_32215_half_map_1.map.gz emd_32215_half_map_2.map.gz emd_32215_half_map_2.map.gz | 56.8 MB 49.7 MB 49.7 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32215 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32215 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32215 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-32215 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7vyvMC  7vz3C M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_32215.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_32215.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.087 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: sharpened by B-factor -50
| File | emd_32215_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | sharpened by B-factor -50 | ||||||||||||
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
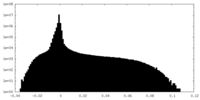
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_32215_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_32215_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Tail spike protein Depo32
| Entire | Name: Tail spike protein Depo32 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Tail spike protein Depo32
| Supramolecule | Name: Tail spike protein Depo32 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Klebsiella phage 020009 (virus) / Strain: vB_KpnS_GH-K3 Klebsiella phage 020009 (virus) / Strain: vB_KpnS_GH-K3 |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 300 KDa |
-Macromolecule #1: Depolymerase
| Macromolecule | Name: Depolymerase / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Klebsiella phage GH-K3 (virus) Klebsiella phage GH-K3 (virus) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 98.645289 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MALYREGKAA MAADGTVTGT GTKWQSSLSL IRPGATIMFL SSPIQMAVVN KVVSDTEIKA ITTNGAVVAS TDYAILLSDS LTVDGLAQD VAETLRYYQS QETVIADAVE FFKEFDFESL QNLANQIKAD SEASESSAAA AAASESKAKT SEDNAKSSEN A AKNSEVAA ...String: MALYREGKAA MAADGTVTGT GTKWQSSLSL IRPGATIMFL SSPIQMAVVN KVVSDTEIKA ITTNGAVVAS TDYAILLSDS LTVDGLAQD VAETLRYYQS QETVIADAVE FFKEFDFESL QNLANQIKAD SEASESSAAA AAASESKAKT SEDNAKSSEN A AKNSEVAA ETTRDQIQQI IDNAGDQSTL VVLAQPDGFD SIGRVSSFAA LRNLKPKKSG QHVLLTSYYD GWAAENKMPT GG GEFISSI GTATDDGGYI AAGPGYYWTR VVNNNSFTAE DFGCKTTATP PPNFNVLPAE LFDNTARMQA AFNLAISKSF KLN LSAGTY YFESSDTLRI TGPIHIEGRP GTVFYHNPSN KANPKTDAFM NISGCSMGRI SSINCFSNSY LGKGINFDRS VGDN RKLVL EHVYVDTFRW GFYVGEPECI NQIEFHSCRA QSNYFQGIFI ESFKEGQEYG HSAPVHFFNT ICNGNGPTSF ALGAT YKTT KNEYIKVMDS VNDVGCQAYF QGLSNVQYIG GQLSGHGSPR NTSLATITQC NSFIIYGTDL EDINGFTTDG TAITAD NID TIESNYLKDI SGAAIVVSSC LGFKIDSPHI FKIKTLSTIK LMNNTYNYEI GGFTPDEALK YNVWDANGLA TNRISGV IH PRLVNSRLGI NSVAFDNMSN KLDVSSLIHN ETSQIIGLTP STGSNVPHTR IMWSNGAMYS STDLNNGFRL NYLSNHNE P LTPMHLYNEF SVSEFGGSVT ESNALDEIKY IFIQTTYANS GDGRFIIQAL DASGSVLSSN WYSPQSFNST FPISGFVRF DVPTGAKKIR YGFVNSANYT GSLRSHFMSG FAYNKRFFLK IYAVYNDLGR YGQFEPPYSV AIDRFRVGDN TTQMPSIPAS SATDVAGVN EVINSLLASL KANGFMSS UniProtKB: Depolymerase |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.5 mg/mL | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| ||||||||||||
| Grid | Model: C-flat-1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Time: 30 sec. | ||||||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 285.15 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: blot 3.5 to 4 seconds before plunging. | ||||||||||||
| Details | This sample was monodisperse. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average exposure time: 2.56 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 81000 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DARK FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.5 µm |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Protocol: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7vyv: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)