[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-30999: Cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type S-Trimer from a sub... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30999 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of the SARS-CoV-2 wild-type S-Trimer from a subunit vaccine candidate | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | spike protein / COVID-19 / vaccine / VIRAL PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcollagen type I trimer / cellular response to vitamin E / tooth mineralization / cellular response to fluoride / Anchoring fibril formation / intramembranous ossification / Crosslinking of collagen fibrils / collagen biosynthetic process / Collagen chain trimerization / Defective VWF binding to collagen type I ...collagen type I trimer / cellular response to vitamin E / tooth mineralization / cellular response to fluoride / Anchoring fibril formation / intramembranous ossification / Crosslinking of collagen fibrils / collagen biosynthetic process / Collagen chain trimerization / Defective VWF binding to collagen type I / platelet-derived growth factor binding / bone trabecula formation / Enhanced cleavage of VWF variant by ADAMTS13 / Defective VWF cleavage by ADAMTS13 variant / extracellular matrix structural constituent conferring tensile strength / Enhanced binding of GP1BA variant to VWF multimer:collagen / Defective binding of VWF variant to GPIb:IX:V / Extracellular matrix organization / embryonic skeletal system development / cartilage development involved in endochondral bone morphogenesis / skin morphogenesis / Collagen biosynthesis and modifying enzymes / collagen-activated tyrosine kinase receptor signaling pathway / endochondral ossification / Platelet Adhesion to exposed collagen / collagen fibril organization / response to steroid hormone / face morphogenesis / Assembly of collagen fibrils and other multimeric structures / MET activates PTK2 signaling / Scavenging by Class A Receptors / GP1b-IX-V activation signalling / Syndecan interactions / blood vessel development / Platelet Aggregation (Plug Formation) / RUNX2 regulates osteoblast differentiation / Collagen degradation / Non-integrin membrane-ECM interactions / negative regulation of cell-substrate adhesion / response to hyperoxia / ECM proteoglycans / response to cAMP / Integrin cell surface interactions / positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition / cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus / protein localization to nucleus / GPVI-mediated activation cascade / cellular response to retinoic acid / cellular response to fibroblast growth factor stimulus / visual perception / secretory granule / cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus / Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall / skeletal system development / cellular response to amino acid stimulus / response to hydrogen peroxide / cellular response to glucose stimulus / cellular response to mechanical stimulus / sensory perception of sound / response to insulin / : / Immunoregulatory interactions between a Lymphoid and a non-Lymphoid cell / osteoblast differentiation / cellular response to tumor necrosis factor / response to estradiol / positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway / protein transport / protease binding / symbiont-mediated disruption of host tissue / Maturation of spike protein / Translation of Structural Proteins / Virion Assembly and Release / host cell surface / host extracellular space / symbiont-mediated-mediated suppression of host tetherin activity / Induction of Cell-Cell Fusion / structural constituent of virion / membrane fusion / Attachment and Entry / entry receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment membrane / positive regulation of viral entry into host cell / receptor-mediated virion attachment to host cell / host cell surface receptor binding / symbiont-mediated suppression of host innate immune response / positive regulation of cell migration / endocytosis involved in viral entry into host cell / endoplasmic reticulum lumen / response to xenobiotic stimulus / receptor ligand activity / fusion of virus membrane with host plasma membrane / fusion of virus membrane with host endosome membrane / viral envelope / symbiont entry into host cell / positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription / virion attachment to host cell / host cell plasma membrane / SARS-CoV-2 activates/modulates innate and adaptive immune responses / virion membrane / extracellular space Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |   Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
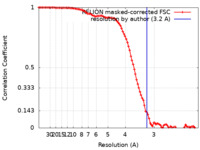
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.2 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Zheng S / Ma J | |||||||||
| Funding support |  China, 1 items China, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: J Virol / Year: 2021 Journal: J Virol / Year: 2021Title: Cryo-EM structure of S-Trimer, a subunit vaccine candidate for COVID-19. Authors: Jiahao Ma / Danmei Su / Yinyan Sun / Xueqin Huang / Ying Liang / Linqiang Fang / Yan Ma / Wenhui Li / Peng Liang / Sanduo Zheng /  Abstract: Within a year after its emergence, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has infected over 100 million people worldwide with a death toll over 2 million. Vaccination ...Within a year after its emergence, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has infected over 100 million people worldwide with a death toll over 2 million. Vaccination remains the best hope to ultimately put this pandemic to an end. Here, using Trimer-Tag technology, we produced both wild-type (WT) and furin site mutant (MT) S-Trimers for COVID-19 vaccine studies. Cryo-EM structures of the WT and MT S-Trimers, determined at 3.2 Å and 2.6 Å respectively, revealed that both antigens adopt a tightly closed conformation and their structures are essentially identical to that of the previously solved full-length WT S protein in detergent. The tightly closed conformation is stabilized by fatty acid and polysorbate 80 binding at the receptor binding domains (RBDs) and the N terminal domains (NTDs) respectively. Additionally, we identified an important pH switch in the WT S-Trimer that shows dramatic conformational change and accounts for its increased stability at lower pH. These results validate Trimer-Tag as a platform technology in production of metastable WT S-Trimer as a candidate for COVID-19 subunit vaccine.Effective vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 is critical to end the COVID-19 pandemic. Here, using Trimer-Tag technology, we are able to produce stable and large quantities of WT S-Trimer, a subunit vaccine candidate for COVID-19 with high safety and efficacy from animal and Phase 1 clinical trial studies. Cryo-EM structures of the S-Trimer subunit vaccine candidate show that it predominately adopts tightly closed pre-fusion state, and resembles that of the native and full-length spike in detergent, confirming its structural integrity. WT S-Trimer is currently being evaluated in global Phase 2/3 clinical trial. Combining with published structures of the S protein, we also propose a model to dissect the conformation change of the spike protein before receptor binding. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30999.map.gz emd_30999.map.gz | 8.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30999-v30.xml emd-30999-v30.xml emd-30999.xml emd-30999.xml | 18.1 KB 18.1 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_30999_fsc.xml emd_30999_fsc.xml | 10 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_30999.png emd_30999.png | 38.7 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-30999.cif.gz emd-30999.cif.gz | 7.5 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30999 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30999 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30999 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30999 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7e7dMC  7e7bC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30999.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30999.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.087 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : SARS-CoV-2 spike protein fused to the C-terminal region of human ...
| Entire | Name: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein fused to the C-terminal region of human type 1a collagen |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein fused to the C-terminal region of human ...
| Supramolecule | Name: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein fused to the C-terminal region of human type 1a collagen type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Spike glycoprotein,Collagen alpha-1(I) chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Spike glycoprotein,Collagen alpha-1(I) chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: Chimeric protein / Number of copies: 3 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 168.164328 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MFVFLVLLPL VSSQCVNLTT RTQLPPAYTN SFTRGVYYPD KVFRSSVLHS TQDLFLPFFS NVTWFHAIHV SGTNGTKRFD NPVLPFNDG VYFASTEKSN IIRGWIFGTT LDSKTQSLLI VNNATNVVIK VCEFQFCNDP FLGVYYHKNN KSWMESEFRV Y SSANNCTF ...String: MFVFLVLLPL VSSQCVNLTT RTQLPPAYTN SFTRGVYYPD KVFRSSVLHS TQDLFLPFFS NVTWFHAIHV SGTNGTKRFD NPVLPFNDG VYFASTEKSN IIRGWIFGTT LDSKTQSLLI VNNATNVVIK VCEFQFCNDP FLGVYYHKNN KSWMESEFRV Y SSANNCTF EYVSQPFLMD LEGKQGNFKN LREFVFKNID GYFKIYSKHT PINLVRDLPQ GFSALEPLVD LPIGINITRF QT LLALHRS YLTPGDSSSG WTAGAAAYYV GYLQPRTFLL KYNENGTITD AVDCALDPLS ETKCTLKSFT VEKGIYQTSN FRV QPTESI VRFPNITNLC PFGEVFNATR FASVYAWNRK RISNCVADYS VLYNSASFST FKCYGVSPTK LNDLCFTNVY ADSF VIRGD EVRQIAPGQT GKIADYNYKL PDDFTGCVIA WNSNNLDSKV GGNYNYLYRL FRKSNLKPFE RDISTEIYQA GSTPC NGVE GFNCYFPLQS YGFQPTNGVG YQPYRVVVLS FELLHAPATV CGPKKSTNLV KNKCVNFNFN GLTGTGVLTE SNKKFL PFQ QFGRDIADTT DAVRDPQTLE ILDITPCSFG GVSVITPGTN TSNQVAVLYQ DVNCTEVPVA IHADQLTPTW RVYSTGS NV FQTRAGCLIG AEHVNNSYEC DIPIGAGICA SYQTQTNSPR RARSVASQSI IAYTMSLGAE NSVAYSNNSI AIPTNFTI S VTTEILPVSM TKTSVDCTMY ICGDSTECSN LLLQYGSFCT QLNRALTGIA VEQDKNTQEV FAQVKQIYKT PPIKDFGGF NFSQILPDPS KPSKRSFIED LLFNKVTLAD AGFIKQYGDC LGDIAARDLI CAQKFNGLTV LPPLLTDEMI AQYTSALLAG TITSGWTFG AGAALQIPFA MQMAYRFNGI GVTQNVLYEN QKLIANQFNS AIGKIQDSLS STASALGKLQ DVVNQNAQAL N TLVKQLSS NFGAISSVLN DILSRLDKVE AEVQIDRLIT GRLQSLQTYV TQQLIRAAEI RASANLAATK MSECVLGQSK RV DFCGKGY HLMSFPQSAP HGVVFLHVTY VPAQEKNFTT APAICHDGKA HFPREGVFVS NGTHWFVTQR NFYEPQIITT DNT FVSGNC DVVIGIVNNT VYDPLQPELD SFKEELDKYF KNHTSPDVDL GDISGINASV VNIQKEIDRL NEVAKNLNES LIDL QELGK YEQYIKRSNG LPGPIGPPGP RGRTGDAGPV GPPGPPGPPG PPGPPSAGFD FSFLPQPPQE KAHDGGRYYR ANDAN VVRD RDLEVDTTLK SLSQQIENIR SPEGSRKNPA RTCRDLKMCH SDWKSGEYWI DPNQGCNLDA IKVFCNMETG ETCVYP TQP SVAQKNWYIS KNPKDKRHVW FGESMTDGFQ FEYGGQGSDP ADVAIQLTFL RLMSTEASQN ITYHCKNSVA YMDQQTG NL KKALLLKGSN EIEIRAEGNS RFTYSVTVDG CTSHTGAWGK TVIEYKTTKS SRLPIIDVAP LDVGAPDQEF GFDVGPVC UniProtKB: Spike glycoprotein, Collagen alpha-1(I) chain |
-Macromolecule #3: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose
| Macromolecule | Name: 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-beta-D-glucopyranose / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 19 / Formula: NAG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 221.208 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-NAG: |
-Macromolecule #4: Elaidic acid
| Macromolecule | Name: Elaidic acid / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: ELA |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 282.461 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 0.3 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Support film - #0 - Film type ID: 1 / Support film - #0 - Material: CARBON / Support film - #0 - topology: HOLEY / Support film - #1 - Film type ID: 2 / Support film - #1 - Material: GRAPHENE OXIDE / Support film - #1 - topology: CONTINUOUS |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 282 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK I Details: blot time 2 seconds, blot force 4, waiting time 8 seconds. |
| Details | monodisperse |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Number grids imaged: 2 / Number real images: 2000 / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated defocus max: 2.8000000000000003 µm / Calibrated defocus min: 0.6 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 0.0 mm / Nominal magnification: 64000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



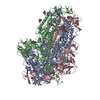
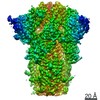

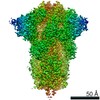
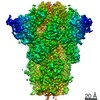
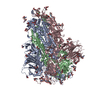
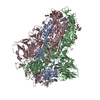
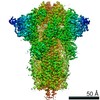
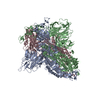























 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)