+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30808 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of DgpB-C at 2.85 angstrom resolution | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
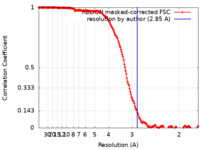
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.85 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Mori T / Moriya T / Adachi N / Kawasaki M / Senda T / Abe I | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Japan, 1 items Japan, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: C-Glycoside metabolism in the gut and in nature: Identification, characterization, structural analyses and distribution of C-C bond-cleaving enzymes. Authors: Takahiro Mori / Takuto Kumano / Haibing He / Satomi Watanabe / Miki Senda / Toshio Moriya / Naruhiko Adachi / Sanae Hori / Yuzu Terashita / Masato Kawasaki / Yoshiteru Hashimoto / Takayoshi ...Authors: Takahiro Mori / Takuto Kumano / Haibing He / Satomi Watanabe / Miki Senda / Toshio Moriya / Naruhiko Adachi / Sanae Hori / Yuzu Terashita / Masato Kawasaki / Yoshiteru Hashimoto / Takayoshi Awakawa / Toshiya Senda / Ikuro Abe / Michihiko Kobayashi /  Abstract: C-Glycosides, in which a sugar moiety is linked via a carbon-carbon (C-C) bond to a non-sugar moiety (aglycone), are found in our food and medicine. The C-C bond is cleaved by intestinal microbes and ...C-Glycosides, in which a sugar moiety is linked via a carbon-carbon (C-C) bond to a non-sugar moiety (aglycone), are found in our food and medicine. The C-C bond is cleaved by intestinal microbes and the resulting aglycones exert various bioactivities. Although the enzymes responsible for the reactions have been identified, their catalytic mechanisms and the generality of the reactions in nature remain to be explored. Here, we present the identification and structural basis for the activation of xenobiotic C-glycosides by heterocomplex C-deglycosylation enzymes from intestinal and soil bacteria. They are found to be metal-dependent enzymes exhibiting broad substrate specificity toward C-glycosides. X-ray crystallographic and cryo-electron microscopic analyses, as well as structure-based mutagenesis, reveal the structural details of these enzymes and the detailed catalytic mechanisms of their remarkable C-C bond cleavage reactions. Furthermore, bioinformatic and biochemical analyses suggest that the C-deglycosylation enzymes are widely distributed in the gut, soil, and marine bacteria. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30808.map.gz emd_30808.map.gz | 388.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30808-v30.xml emd-30808-v30.xml emd-30808.xml emd-30808.xml | 17.5 KB 17.5 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_30808_fsc.xml emd_30808_fsc.xml | 17 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_30808.png emd_30808.png | 109.5 KB | ||
| Masks |  emd_30808_msk_1.map emd_30808_msk_1.map | 421.9 MB |  Mask map Mask map | |
| Others |  emd_30808_half_map_1.map.gz emd_30808_half_map_1.map.gz emd_30808_half_map_2.map.gz emd_30808_half_map_2.map.gz | 388.6 MB 337.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30808 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30808 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30808 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30808 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7drdMC  7bvrC  7bvsC  7dreC  7exbC  7exzC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | |
| EM raw data |  EMPIAR-11124 (Title: Cryo-EM structure of DgpB-C at 2.85 angstrom resolution EMPIAR-11124 (Title: Cryo-EM structure of DgpB-C at 2.85 angstrom resolutionData size: 1.9 TB Data #1: Cryo-EM structure of DgpB-C at 2.85 angstrom resolution [micrographs - multiframe]) |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30808.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30808.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 421.9 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.88 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
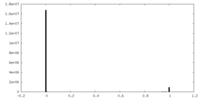
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Mask #1
| File |  emd_30808_msk_1.map emd_30808_msk_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
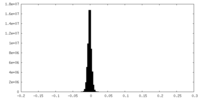
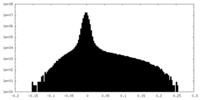
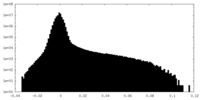
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_30808_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_30808_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : DgpB-C
| Entire | Name: DgpB-C |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: DgpB-C
| Supramolecule | Name: DgpB-C / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 / Details: heterodimer complex of DpgB and DpbC |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 250 KDa |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Component:
| |||||||||
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 300 / Support film - Material: CARBON / Support film - topology: HOLEY / Pretreatment - Type: GLOW DISCHARGE / Pretreatment - Atmosphere: AIR / Details: The grid was washed by acetone prior to use. | |||||||||
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 291 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV / Details: Blotting time was 5 seconds (blot force 20). | |||||||||
| Details | This sample was mono-disperse. |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS TALOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: FEI FALCON III (4k x 4k) / Detector mode: COUNTING / Number grids imaged: 1 / Number real images: 2122 / Average exposure time: 54.23 sec. / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.5 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm / Nominal magnification: 120000 |
| Sample stage | Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: OTHER |
|---|---|
| Output model |  PDB-7drd: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller




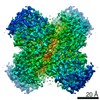
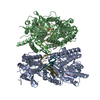
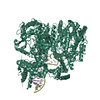
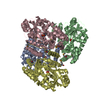
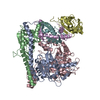



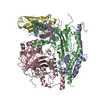
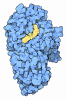
 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)