+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-30245 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
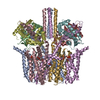
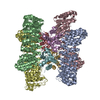
| Title | Cryo-EM structure of human KCNQ4 with retigabine | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | KCNQ / Channel / Calmodulin / PIP2 / retigabine / MEMBRANE PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationtransporter inhibitor activity / Voltage gated Potassium channels / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / inner ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / response to corticosterone / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane ...transporter inhibitor activity / Voltage gated Potassium channels / establishment of protein localization to mitochondrial membrane / type 3 metabotropic glutamate receptor binding / Sensory processing of sound by outer hair cells of the cochlea / Sensory processing of sound by inner hair cells of the cochlea / inner ear morphogenesis / negative regulation of high voltage-gated calcium channel activity / response to corticosterone / negative regulation of calcium ion export across plasma membrane / regulation of cardiac muscle cell action potential / nitric-oxide synthase binding / presynaptic endocytosis / regulation of cell communication by electrical coupling involved in cardiac conduction / regulation of synaptic vesicle exocytosis / calcineurin-mediated signaling / adenylate cyclase binding / protein phosphatase activator activity / catalytic complex / voltage-gated potassium channel activity / regulation of synaptic vesicle endocytosis / detection of calcium ion / potassium channel activity / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction / postsynaptic cytosol / regulation of cardiac muscle contraction by regulation of the release of sequestered calcium ion / phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding / presynaptic cytosol / regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol by sarcoplasmic reticulum / titin binding / sperm midpiece / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / voltage-gated potassium channel complex / potassium ion transmembrane transport / calcium channel complex / substantia nigra development / regulation of heart rate / basal plasma membrane / calyx of Held / response to amphetamine / bioluminescence / adenylate cyclase activator activity / sarcomere / nitric-oxide synthase regulator activity / protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity / regulation of cytokinesis / generation of precursor metabolites and energy / spindle microtubule / calcium channel regulator activity / sensory perception of sound / response to calcium ion / mitochondrial membrane / potassium ion transport / Schaffer collateral - CA1 synapse / G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle / long-term synaptic potentiation / spindle pole / calcium-dependent protein binding / synaptic vesicle membrane / myelin sheath / growth cone / vesicle / transmembrane transporter binding / G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway / protein domain specific binding / calcium ion binding / centrosome / protein kinase binding / protein-containing complex / nucleus / plasma membrane / cytoplasm Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.1 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Shen H / Li T | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021 Journal: Mol Cell / Year: 2021Title: Structural Basis for the Modulation of Human KCNQ4 by Small-Molecule Drugs. Authors: Tian Li / Kun Wu / Zhenlei Yue / Yifei Wang / Fan Zhang / Huaizong Shen /  Abstract: Among the five KCNQ channels, also known as the K7 voltage-gated potassium (K) channels, KCNQ2-KCNQ5 control neuronal excitability. Dysfunctions of KCNQ2-KCNQ5 are associated with neurological ...Among the five KCNQ channels, also known as the K7 voltage-gated potassium (K) channels, KCNQ2-KCNQ5 control neuronal excitability. Dysfunctions of KCNQ2-KCNQ5 are associated with neurological disorders such as epilepsy, deafness, and neuropathic pain. Here, we report the cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human KCNQ4 and its complexes with the opener retigabine or the blocker linopirdine at overall resolutions of 2.5, 3.1, and 3.3 Å, respectively. In all structures, a phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP) molecule inserts its head group into a cavity within each voltage-sensing domain (VSD), revealing an unobserved binding mode for PIP. Retigabine nestles in each fenestration, inducing local shifts. Instead of staying within the central pore, linopirdine resides in a cytosolic cavity underneath the inner gate. Electrophysiological analyses of various mutants corroborated the structural observations. Our studies reveal the molecular basis for the modulatory mechanism of neuronal KCNQ channels and provide a framework for structure-facilitated drug discovery targeting these important channels. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_30245.map.gz emd_30245.map.gz | 114 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-30245-v30.xml emd-30245-v30.xml emd-30245.xml emd-30245.xml | 17.8 KB 17.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_30245.png emd_30245.png | 102.2 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-30245.cif.gz emd-30245.cif.gz | 6.6 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_30245_additional_1.map.gz emd_30245_additional_1.map.gz | 115.3 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30245 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30245 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30245 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-30245 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_30245_validation.pdf.gz emd_30245_validation.pdf.gz | 472.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_30245_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_30245_full_validation.pdf.gz | 471.9 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_30245_validation.xml.gz emd_30245_validation.xml.gz | 6.3 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_30245_validation.cif.gz emd_30245_validation.cif.gz | 7.4 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-30245 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-30245 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-30245 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-30245 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7bymMC  7bylC  7bynC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
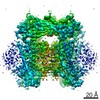
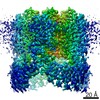
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_30245.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_30245.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 125 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.087 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
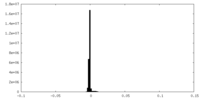
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_30245_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Complex of human KCNQ4 and retigabine
| Entire | Name: Complex of human KCNQ4 and retigabine |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Complex of human KCNQ4 and retigabine
| Supramolecule | Name: Complex of human KCNQ4 and retigabine / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Macromolecule #1: Green fluorescent protein,Potassium voltage-gated channel subfami...
| Macromolecule | Name: Green fluorescent protein,Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4 type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 109.327836 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHHHA ADYKDHDIDY KDDDDKSAMV SKGEELFTGV VPILVELDGD VNGHKFSVSG EGEGDATYGK LTLKFICTTG KLPVPWPTL VTTLTYGVQC FSRYPDHMKQ HDFFKSAMPE GYVQERTIFF KDDGNYTTRA EVKFEGDTLV NRIELKGIDF K EDGNILGH ...String: MHHHHHHHHA ADYKDHDIDY KDDDDKSAMV SKGEELFTGV VPILVELDGD VNGHKFSVSG EGEGDATYGK LTLKFICTTG KLPVPWPTL VTTLTYGVQC FSRYPDHMKQ HDFFKSAMPE GYVQERTIFF KDDGNYTTRA EVKFEGDTLV NRIELKGIDF K EDGNILGH KLEYNYNSHN VYIMADKQKN GIKVNFKIRH NIEDGSVQLA DHYQQNTPIG DGPVLLPDNH YLSTQSKLSK DP NEKRDHM VLLEFVTAAG ITLGMDELYK SGLRSGLEVL FQGPGGRMAE APPRRLGLGP PPGDAPRAEL VALTAVQSEQ GEA GGGGSP RRLGLLGSPL PPGAPLPGPG SGSGSACGQR SSAAHKRYRR LQNWVYNVLE RPRGWAFVYH VFIFLLVFSC LVLS VLSTI QEHQELANEC LLILEFVMIV VFGLEYIVRV WSAGCCCRYR GWQGRFRFAR KPFCVIDFIV FVASVAVIAA GTQGN IFAT SALRSMRFLQ ILRMVRMDRR GGTWKLLGSV VYAHSKELIT AWYIGFLVLI FASFLVYLAE KDANSDFSSY ADSLWW GTI TLTTIGYGDK TPHTWLGRVL AAGFALLGIS FFALPAGILG SGFALKVQEQ HRQKHFEKRR MPAANLIQAA WRLYSTD MS RAYLTATWYY YDSILPSFRE LALLFEHVQR ARNGGLRPLE VRRAPVPDGA PSRYPPVATC HRPGSTSFCP GESSRMGI K DRIRMGSSQR RTGPSKQHLA PPTMPTSPSS EQVGEATSPT KVQKSWSFND RTRFRASLRL KPRTSAEDAP SEEVAEEKS YQCELTVDDI MPAVKTVIRS IRILKFLVAK RKFKETLRPY DVKDVIEQYS AGHLDMLGRI KSLQTRVDQI VGRGPGDRKA REKGDKGPS DAEVVDEISM MGRVVKVEKQ VQSIEHKLDL LLGFYSRCLR SGTSASLGAV QVPLFDPDIT SDYHSPVDHE D ISVSAQTL SISRSVSTNM D UniProtKB: Green fluorescent protein, Potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily KQT member 4 |
-Macromolecule #2: Calmodulin-3
| Macromolecule | Name: Calmodulin-3 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 4 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 16.852545 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MADQLTEEQI AEFKEAFSLF DKDGDGTITT KELGTVMRSL GQNPTEAELQ DMINEVDADG NGTIDFPEFL TMMARKMKDT DSEEEIREA FRVFDKDGNG YISAAELRHV MTNLGEKLTD EEVDEMIREA DIDGDGQVNY EEFVQMMTAK UniProtKB: Calmodulin-3 |
-Macromolecule #3: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tr...
| Macromolecule | Name: [(2R)-1-octadecanoyloxy-3-[oxidanyl-[(1R,2R,3S,4R,5R,6S)-2,3,6-tris(oxidanyl)-4,5-diphosphonooxy-cyclohexyl]oxy-phospho ryl]oxy-propan-2-yl] (8Z)-icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoate type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: PT5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 1.047088 KDa |
-Macromolecule #4: ethyl N-[2-azanyl-4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylamino]phenyl]carbamate
| Macromolecule | Name: ethyl N-[2-azanyl-4-[(4-fluorophenyl)methylamino]phenyl]carbamate type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: FBX |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 303.331 Da |
| Chemical component information | 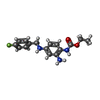 ChemComp-FBX: |
-Macromolecule #5: POTASSIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: POTASSIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 3 / Formula: K |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 39.098 Da |
-Macromolecule #6: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 4 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)