+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2868 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Reconstruction of nucleoplasmin isolated from oocytes | |||||||||
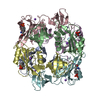
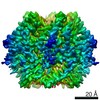
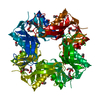
 Map data Map data | reconstruction of nucleoplamsin | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | nucleoplasmin oocyte | |||||||||
| Biological species | ||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / negative staining / Resolution: 19.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Onikubo T / Nicklay JJ / Xing L / Warren C / Anson B / Wang WL / Burgos ES / Ruff SE / Shabanowitz J / Cheng RH ...Onikubo T / Nicklay JJ / Xing L / Warren C / Anson B / Wang WL / Burgos ES / Ruff SE / Shabanowitz J / Cheng RH / Hunt DF / Shechter D | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2015 Journal: Cell Rep / Year: 2015Title: Developmentally Regulated Post-translational Modification of Nucleoplasmin Controls Histone Sequestration and Deposition. Authors: Takashi Onikubo / Joshua J Nicklay / Li Xing / Christopher Warren / Brandon Anson / Wei-Lin Wang / Emmanuel S Burgos / Sophie E Ruff / Jeffrey Shabanowitz / R Holland Cheng / Donald F Hunt / David Shechter /  Abstract: Nucleoplasmin (Npm) is an abundant histone chaperone in vertebrate oocytes and embryos. During embryogenesis, regulation of Npm histone binding is critical for its function in storing and releasing ...Nucleoplasmin (Npm) is an abundant histone chaperone in vertebrate oocytes and embryos. During embryogenesis, regulation of Npm histone binding is critical for its function in storing and releasing maternal histones to establish and maintain the zygotic epigenome. Here, we demonstrate that Xenopus laevis Npm post-translational modifications (PTMs) specific to the oocyte and egg promote either histone deposition or sequestration, respectively. Mass spectrometry and Npm phosphomimetic mutations used in chromatin assembly assays identified hyperphosphorylation on the N-terminal tail as a critical regulator for sequestration. C-terminal tail phosphorylation and PRMT5-catalyzed arginine methylation enhance nucleosome assembly by promoting histone interaction with the second acidic tract of Npm. Electron microscopy reconstructions of Npm and TTLL4 activity toward the C-terminal tail demonstrate that oocyte- and egg-specific PTMs cause Npm conformational changes. Our results reveal that PTMs regulate Npm chaperoning activity by modulating Npm conformation and Npm-histone interaction, leading to histone sequestration in the egg. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2868.map.gz emd_2868.map.gz | 2.6 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2868-v30.xml emd-2868-v30.xml emd-2868.xml emd-2868.xml | 7.9 KB 7.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2868.png EMD-2868.png | 58.9 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2868 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2868 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2868 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2868 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2868.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 6.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2868.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 6.4 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | reconstruction of nucleoplamsin | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.25 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : nucleoplasmin isolated from Xenopus oocyte
| Entire | Name: nucleoplasmin isolated from Xenopus oocyte |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: nucleoplasmin isolated from Xenopus oocyte
| Supramolecule | Name: nucleoplasmin isolated from Xenopus oocyte / type: sample / ID: 1000 / Oligomeric state: pentamer / Number unique components: 1 |
|---|
-Macromolecule #1: nucleoplasmin
| Macromolecule | Name: nucleoplasmin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Oligomeric state: pentamer / Recombinant expression: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | negative staining |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Staining | Type: NEGATIVE / Details: uranyl acetate staining |
|---|---|
| Grid | Details: 300 mesh copper grid coated with carbon film |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: NONE / Instrument: OTHER |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | JEOL 2100F |
|---|---|
| Date | Mar 20, 2013 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: TVIPS TEMCAM-F415 (4k x 4k) / Number real images: 80 / Average electron dose: 10 e/Å2 / Bits/pixel: 16 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 1.25 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.9 µm / Nominal magnification: 80000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: JEOL |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C5 (5 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 19.0 Å / Resolution method: OTHER / Software - Name: EMAN / Number images used: 1306 |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















