[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-28272: CryoEM structure of the high pH turnover-inactivated nitrogenase ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry |  | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | CryoEM structure of the high pH turnover-inactivated nitrogenase MoFe-protein | ||||||||||||
 Map data Map data | Primary map sharpened by a B-factor of 50 angstroms. | ||||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| ||||||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | nitrogenase / nitrogen fixation / reductase / MoFe / OXIDOREDUCTASE | ||||||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationmolybdenum-iron nitrogenase complex / nitrogenase / nitrogenase activity / nitrogen fixation / iron-sulfur cluster binding / ATP binding / metal ion binding Similarity search - Function | ||||||||||||
| Biological species |  Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) | ||||||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 2.37 Å | ||||||||||||
 Authors Authors | Warmack RA / Maggiolo AO / Rees DC | ||||||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 3 items United States, 3 items
| ||||||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2023Title: Structural consequences of turnover-induced homocitrate loss in nitrogenase. Authors: Rebeccah A Warmack / Ailiena O Maggiolo / Andres Orta / Belinda B Wenke / James B Howard / Douglas C Rees /  Abstract: Nitrogenase catalyzes the ATP-dependent reduction of dinitrogen to ammonia during the process of biological nitrogen fixation that is essential for sustaining life. The active site FeMo-cofactor ...Nitrogenase catalyzes the ATP-dependent reduction of dinitrogen to ammonia during the process of biological nitrogen fixation that is essential for sustaining life. The active site FeMo-cofactor contains a [7Fe:1Mo:9S:1C] metallocluster coordinated with an R-homocitrate (HCA) molecule. Here, we establish through single particle cryoEM and chemical analysis of two forms of the Azotobacter vinelandii MoFe-protein - a high pH turnover inactivated species and a ∆NifV variant that cannot synthesize HCA - that loss of HCA is coupled to α-subunit domain and FeMo-cofactor disordering, and formation of a histidine coordination site. We further find a population of the ∆NifV variant complexed to an endogenous protein identified through structural and proteomic approaches as the uncharacterized protein NafT. Recognition by endogenous NafT demonstrates the physiological relevance of the HCA-compromised form, perhaps for cofactor insertion or repair. Our results point towards a dynamic active site in which HCA plays a role in enabling nitrogenase catalysis by facilitating activation of the FeMo-cofactor from a relatively stable form to a state capable of reducing dinitrogen under ambient conditions. | ||||||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_28272.map.gz emd_28272.map.gz | 374.3 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-28272-v30.xml emd-28272-v30.xml emd-28272.xml emd-28272.xml | 22.8 KB 22.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_28272.png emd_28272.png | 73.8 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-28272.cif.gz emd-28272.cif.gz | 6.8 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_28272_additional_1.map.gz emd_28272_additional_1.map.gz emd_28272_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28272_half_map_1.map.gz emd_28272_half_map_2.map.gz emd_28272_half_map_2.map.gz | 372.7 MB 676.2 MB 676.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28272 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28272 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28272 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-28272 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8enlMC 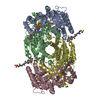 8crsC  8dbxC  8enmC  8ennC  8enoC C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_28272.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 729 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_28272.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 729 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Primary map sharpened by a B-factor of 50 angstroms. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.65 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
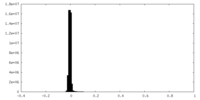
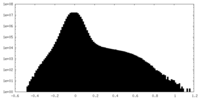
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: Secondary blurred map.
| File | emd_28272_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Secondary blurred map. | ||||||||||||
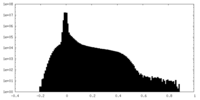
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
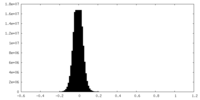
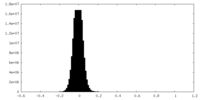
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_28272_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
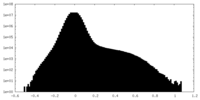
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_28272_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Heterotetrameric nitrogenase MoFe-protein
| Entire | Name: Heterotetrameric nitrogenase MoFe-protein |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Heterotetrameric nitrogenase MoFe-protein
| Supramolecule | Name: Heterotetrameric nitrogenase MoFe-protein / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) |
-Macromolecule #1: Nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein alpha chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein alpha chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: nitrogenase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 54.000559 KDa |
| Sequence | String: MSREEVESLI QEVLEVYPEK ARKDRNKHLA VNDPAVTQSK KCIISNKKSQ PGLMTIRGCA YAGSKGVVWG PIKDMIHISH GPVGCGQYS RAGRRNYYIG TTGVNAFVTM NFTSDFQEKD IVFGGDKKLA KLIDEVETLF PLNKGISVQS ECPIGLIGDD I ESVSKVKG ...String: MSREEVESLI QEVLEVYPEK ARKDRNKHLA VNDPAVTQSK KCIISNKKSQ PGLMTIRGCA YAGSKGVVWG PIKDMIHISH GPVGCGQYS RAGRRNYYIG TTGVNAFVTM NFTSDFQEKD IVFGGDKKLA KLIDEVETLF PLNKGISVQS ECPIGLIGDD I ESVSKVKG AELSKTIVPV RCEGFRGVSQ SLGHHIANDA VRDWVLGKRD EDTTFASTPY DVAIIGDYNI GGDAWSSRIL LE EMGLRCV AQWSGDGSIS EIELTPKVKL NLVHCYRSMN YISRHMEEKY GIPWMEYNFF GPTKTIESLR AIAAKFDESI QKK CEEVIA KYKPEWEAVV AKYRPRLEGK RVMLYIGGLR PRHVIGAYED LGMEVVGTGY EFAHNDDYDR TMKEMGDSTL LYDD VTGYE FEEFVKRIKP DLIGSGIKEK FIFQKMGIPF REMHSWDYSG PYHGFDGFAI FARDMDMTLN NPCWKKLQAP WE UniProtKB: Nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein alpha chain |
-Macromolecule #2: Nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein beta chain
| Macromolecule | Name: Nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein beta chain / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: nitrogenase |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) Azotobacter vinelandii (bacteria) |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 59.404684 KDa |
| Sequence | String: SQQVDKIKAS YPLFLDQDYK DMLAKKRDGF EEKYPQDKID EVFQWTTTKE YQELNFQREA LTVNPAKACQ PLGAVLCALG FEKTMPYVH GSQGCVAYFR SYFNRHFREP VSCVSDSMTE DAAVFGGQQN MKDGLQNCKA TYKPDMIAVS TTCMAEVIGD D LNAFINNS ...String: SQQVDKIKAS YPLFLDQDYK DMLAKKRDGF EEKYPQDKID EVFQWTTTKE YQELNFQREA LTVNPAKACQ PLGAVLCALG FEKTMPYVH GSQGCVAYFR SYFNRHFREP VSCVSDSMTE DAAVFGGQQN MKDGLQNCKA TYKPDMIAVS TTCMAEVIGD D LNAFINNS KKEGFIPDEF PVPFAHTPSF VGSHVTGWDN MFEGIARYFT LKSMDDKVVG SNKKINIVPG FETYLGNFRV IK RMLSEMG VGYSLLSDPE EVLDTPADGQ FRMYAGGTTQ EEMKDAPNAL NTVLLQPWHL EKTKKFVEGT WKHEVPKLNI PMG LDWTDE FLMKVSEISG QPIPASLTKE RGRLVDMMTD SHTWLHGKRF ALWGDPDFVM GLVKFLLELG CEPVHILCHN GNKR WKKAV DAILAASPYG KNATVYIGKD LWHLRSLVFT DKPDFMIGNS YGKFIQRDTL HKGKEFEVPL IRIGFPIFDR HHLHR STTL GYEGAMQILT TLVNSILERL DEETRGMQAT DYNHDLVR UniProtKB: Nitrogenase molybdenum-iron protein beta chain |
-Macromolecule #3: iron-sulfur-molybdenum cluster with interstitial carbon
| Macromolecule | Name: iron-sulfur-molybdenum cluster with interstitial carbon type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: ICS |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 787.451 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ICE: |
-Macromolecule #4: UNKNOWN ATOM OR ION
| Macromolecule | Name: UNKNOWN ATOM OR ION / type: ligand / ID: 4 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: UNX |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 671.215 Da |
-Macromolecule #5: FE(8)-S(7) CLUSTER
| Macromolecule | Name: FE(8)-S(7) CLUSTER / type: ligand / ID: 5 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: CLF |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 671.215 Da |
| Chemical component information | 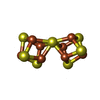 ChemComp-CLF: |
-Macromolecule #6: CHAPSO
| Macromolecule | Name: CHAPSO / type: ligand / ID: 6 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: 1N7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 631.884 Da |
| Chemical component information | 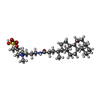 ChemComp-1N7: |
-Macromolecule #7: FE (III) ION
| Macromolecule | Name: FE (III) ION / type: ligand / ID: 7 / Number of copies: 2 / Formula: FE |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 55.845 Da |
-Macromolecule #8: water
| Macromolecule | Name: water / type: ligand / ID: 8 / Number of copies: 926 / Formula: HOH |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 18.015 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-HOH: |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.8 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE-PROPANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: OTHER / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: -3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: -0.8 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)