+ データを開く
データを開く
- 基本情報
基本情報
| 登録情報 |  | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
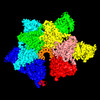
| タイトル | Structure of Lates calcarifer Twinkle helicase with ATP and DNA | |||||||||
 マップデータ マップデータ | ||||||||||
 試料 試料 |
| |||||||||
 キーワード キーワード | Helicase Mitochondrion / REPLICATION-DNA complex | |||||||||
| 機能・相同性 |  機能・相同性情報 機能・相同性情報mitochondrial DNA replication / DNA 5'-3' helicase / single-stranded DNA binding / 5'-3' DNA helicase activity / mitochondrion / ATP binding 類似検索 - 分子機能 | |||||||||
| 生物種 |  Lates calcarifer (あかめ) / synthetic construct (人工物) Lates calcarifer (あかめ) / synthetic construct (人工物) | |||||||||
| 手法 | 単粒子再構成法 / クライオ電子顕微鏡法 / 解像度: 3.51 Å | |||||||||
 データ登録者 データ登録者 | Gao Y / Li Z | |||||||||
| 資金援助 |  米国, 2件 米国, 2件
| |||||||||
 引用 引用 |  ジャーナル: Nucleic Acids Res / 年: 2022 ジャーナル: Nucleic Acids Res / 年: 2022タイトル: Structural and dynamic basis of DNA capture and translocation by mitochondrial Twinkle helicase. 著者: Zhuo Li / Parminder Kaur / Chen-Yu Lo / Neil Chopra / Jamie Smith / Hong Wang / Yang Gao /  要旨: Twinkle is a mitochondrial replicative helicase which can self-load onto and unwind mitochondrial DNA. Nearly 60 mutations on Twinkle have been linked to human mitochondrial diseases. Using cryo- ...Twinkle is a mitochondrial replicative helicase which can self-load onto and unwind mitochondrial DNA. Nearly 60 mutations on Twinkle have been linked to human mitochondrial diseases. Using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and high-speed atomic force microscopy (HS-AFM), we obtained the atomic-resolution structure of a vertebrate Twinkle homolog with DNA and captured in real-time how Twinkle is self-loaded onto DNA. Our data highlight the important role of the non-catalytic N-terminal domain of Twinkle. The N-terminal domain directly contacts the C-terminal helicase domain, and the contact interface is a hotspot for disease-related mutations. Mutations at the interface destabilize Twinkle hexamer and reduce helicase activity. With HS-AFM, we observed that a highly dynamic Twinkle domain, which is likely to be the N-terminal domain, can protrude ∼5 nm to transiently capture nearby DNA and initialize Twinkle loading onto DNA. Moreover, structural analysis and subunit doping experiments suggest that Twinkle hydrolyzes ATP stochastically, which is distinct from related helicases from bacteriophages. | |||||||||
| 履歴 |
|
- 構造の表示
構造の表示
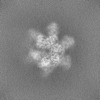
| 添付画像 |
|---|
- ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク
-EMDBアーカイブ
| マップデータ |  emd_27842.map.gz emd_27842.map.gz | 118.2 MB |  EMDBマップデータ形式 EMDBマップデータ形式 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ヘッダ (付随情報) |  emd-27842-v30.xml emd-27842-v30.xml emd-27842.xml emd-27842.xml | 21.5 KB 21.5 KB | 表示 表示 |  EMDBヘッダ EMDBヘッダ |
| 画像 |  emd_27842.png emd_27842.png | 127.1 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-27842.cif.gz emd-27842.cif.gz | 6.7 KB | ||
| その他 |  emd_27842_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27842_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27842_half_map_2.map.gz emd_27842_half_map_2.map.gz | 116.1 MB 116.1 MB | ||
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27842 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27842 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27842 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27842 | HTTPS FTP |
-検証レポート
| 文書・要旨 |  emd_27842_validation.pdf.gz emd_27842_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 |  EMDB検証レポート EMDB検証レポート |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 文書・詳細版 |  emd_27842_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_27842_full_validation.pdf.gz | 1.2 MB | 表示 | |
| XML形式データ |  emd_27842_validation.xml.gz emd_27842_validation.xml.gz | 14.1 KB | 表示 | |
| CIF形式データ |  emd_27842_validation.cif.gz emd_27842_validation.cif.gz | 16.6 KB | 表示 | |
| アーカイブディレクトリ |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27842 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27842 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27842 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-27842 | HTTPS FTP |
-関連構造データ
- リンク
リンク
| EMDBのページ |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| 「今月の分子」の関連する項目 |
- マップ
マップ
| ファイル |  ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_27842.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 125 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_27842.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 125 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
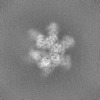
| 投影像・断面図 | 画像のコントロール
画像は Spider により作成 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ボクセルのサイズ | X=Y=Z: 1.07 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 密度 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 対称性 | 空間群: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 詳細 | EMDB XML:
|
-添付データ
-ハーフマップ: #2
| ファイル | emd_27842_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
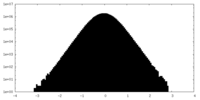
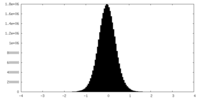
| 密度ヒストグラム |
-ハーフマップ: #1
| ファイル | emd_27842_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 投影像・断面図 |
| ||||||||||||
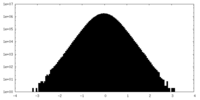
| 密度ヒストグラム |
- 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素
-全体 : Twinkle protein, mitochondrial + DNA
| 全体 | 名称: Twinkle protein, mitochondrial + DNA |
|---|---|
| 要素 |
|
-超分子 #1: Twinkle protein, mitochondrial + DNA
| 超分子 | 名称: Twinkle protein, mitochondrial + DNA / タイプ: complex / ID: 1 / 親要素: 0 / 含まれる分子: #1-#2 |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Lates calcarifer (あかめ) Lates calcarifer (あかめ) |
-分子 #1: Twinkle mtDNA helicase
| 分子 | 名称: Twinkle mtDNA helicase / タイプ: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / コピー数: 6 / 光学異性体: LEVO |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種:  Lates calcarifer (あかめ) Lates calcarifer (あかめ) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 61.29816 KDa |
| 組換発現 | 生物種:  |
| 配列 | 文字列: MQKEEQDFLS PHVMLGYPES LDEQEEGERE LREVQRIWSS AVPFNDLPED EAQLIKTMFQ ITKVSNATLK KFGVRLFKPT KSLVFPWFA GPDSSLKGLK LLSAQNTDTE KVTYNEATVP KISSYYNLFG LTLVGRMDSE VVLTGHELDT LAVSQATGLP S VALPRGVS ...文字列: MQKEEQDFLS PHVMLGYPES LDEQEEGERE LREVQRIWSS AVPFNDLPED EAQLIKTMFQ ITKVSNATLK KFGVRLFKPT KSLVFPWFA GPDSSLKGLK LLSAQNTDTE KVTYNEATVP KISSYYNLFG LTLVGRMDSE VVLTGHELDT LAVSQATGLP S VALPRGVS CLPPMLLPYL EQFKRVTLWL GHDIRSWEAS KIFSRKLGLR RCSLVRPGED RPCPLEALAR GKNLSRIIKT SI PAAHKSI VSFKQLREDV YGELLNTEQV AGVKWTRFPE LNRILKGHRK GELTVFTGPT GSGKTTFISE VALDLCIQGV NTL WGSFQI NNVRLAKIML TQFAMQRLEE NLEQYDFWAD KFEELPLYFM TFHGQQNIKT VLDTMQHAVY LYDINHVIID NLQF MMGQE NLSIDKYAVQ DHIIGAFRKF ATNTSCHVTL IIHPRKEEDD RELQTASIFG SAKASQEADN VLILQEKKLV TCPGR RSLQ VTKNRFDGDV GIFPLDFIKS SLTFSAPIKG KVKLRKVSTK PENEEVGGER GGSEEGRG UniProtKB: Twinkle mtDNA helicase |
-分子 #2: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3')
| 分子 | 名称: DNA (5'-D(P*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*TP*T)-3') / タイプ: dna / ID: 2 / コピー数: 1 / 分類: DNA |
|---|---|
| 由来(天然) | 生物種: synthetic construct (人工物) |
| 分子量 | 理論値: 4.517935 KDa |
| 配列 | 文字列: (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) (DT)(DT)(DT)(DT)(DT) |
-分子 #3: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE
| 分子 | 名称: ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATE / タイプ: ligand / ID: 3 / コピー数: 5 / 式: ATP |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 507.181 Da |
| Chemical component information |  ChemComp-ATP: |
-分子 #4: MAGNESIUM ION
| 分子 | 名称: MAGNESIUM ION / タイプ: ligand / ID: 4 / コピー数: 5 / 式: MG |
|---|---|
| 分子量 | 理論値: 24.305 Da |
-実験情報
-構造解析
| 手法 | クライオ電子顕微鏡法 |
|---|---|
 解析 解析 | 単粒子再構成法 |
| 試料の集合状態 | particle |
- 試料調製
試料調製
| 濃度 | 0.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| 緩衝液 | pH: 8 |
| グリッド | モデル: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / 材質: COPPER / メッシュ: 300 / 前処理 - タイプ: GLOW DISCHARGE / 前処理 - 時間: 60 sec. |
| 凍結 | 凍結剤: ETHANE / チャンバー内湿度: 100 % / チャンバー内温度: 298 K / 装置: FEI VITROBOT MARK I |
| 詳細 | 50 mM Tris (pH 8.0), 150 mM KCl, 3 mM DTT, 1 mM ATP, and 2 mM MgCl2 |
- 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法
| 顕微鏡 | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| 撮影 | フィルム・検出器のモデル: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) 平均電子線量: 49.0 e/Å2 |
| 電子線 | 加速電圧: 300 kV / 電子線源:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| 電子光学系 | 照射モード: FLOOD BEAM / 撮影モード: BRIGHT FIELD / 最大 デフォーカス(公称値): 3.0 µm / 最小 デフォーカス(公称値): 0.6 µm |
| 実験機器 |  モデル: Titan Krios / 画像提供: FEI Company |
+ 画像解析
画像解析
-原子モデル構築 1
| 精密化 | 空間: REAL / プロトコル: AB INITIO MODEL |
|---|---|
| 得られたモデル |  PDB-8e2l: |
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー







 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)