登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-27736タイトル RyR1 in presence of IpCa-T26E phosphomimetic and activating ligands RyR1 in presence of IpCa-T26E phosphomimetic and activating ligands 複合体 : RyR1 complex with activating ligands in open state複合体 : Ryanodine receptor 1タンパク質・ペプチド : Ryanodine receptor 1複合体 : Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1B, Calmodulin-1タンパク質・ペプチド : Peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase FKBP1Bタンパク質・ペプチド : Calmodulin-1リガンド : CAFFEINEリガンド : CALCIUM IONリガンド : ADENOSINE-5'-TRIPHOSPHATEリガンド : ZINC ION / / / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
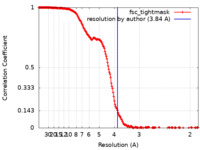
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Oryctolagus cuniculus (ウサギ) / Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.84 Å Haji-Ghassemi O / Van Petegm F 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) PJT-159601 Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) MFE-381863
ジャーナル : Sci Adv / 年 : 2023タイトル : Cryo-EM analysis of scorpion toxin binding to Ryanodine Receptors reveals subconductance that is abolished by PKA phosphorylation.著者 : Omid Haji-Ghassemi / Yu Seby Chen / Kellie Woll / Georgina B Gurrola / Carmen R Valdivia / Wenxuan Cai / Songhua Li / Hector H Valdivia / Filip Van Petegem / 要旨 : Calcins are peptides from scorpion venom with the unique ability to cross cell membranes, gaining access to intracellular targets. Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) are intracellular ion channels that ... Calcins are peptides from scorpion venom with the unique ability to cross cell membranes, gaining access to intracellular targets. Ryanodine Receptors (RyR) are intracellular ion channels that control release of Ca from the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Calcins target RyRs and induce long-lived subconductance states, whereby single-channel currents are decreased. We used cryo-electron microscopy to reveal the binding and structural effects of imperacalcin, showing that it opens the channel pore and causes large asymmetry throughout the cytosolic assembly of the tetrameric RyR. This also creates multiple extended ion conduction pathways beyond the transmembrane region, resulting in subconductance. Phosphorylation of imperacalcin by protein kinase A prevents its binding to RyR through direct steric hindrance, showing how posttranslational modifications made by the host organism can determine the fate of a natural toxin. The structure provides a direct template for developing calcin analogs that result in full channel block, with potential to treat RyR-related disorders. 履歴 登録 2022年7月28日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2023年5月31日 - マップ公開 2023年5月31日 - 更新 2024年11月20日 - 現状 2024年11月20日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報
 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 カナダ, 2件
カナダ, 2件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Sci Adv / 年: 2023
ジャーナル: Sci Adv / 年: 2023


 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_27736.map.gz
emd_27736.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-27736-v30.xml
emd-27736-v30.xml emd-27736.xml
emd-27736.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_27736_fsc.xml
emd_27736_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_27736.png
emd_27736.png emd-27736.cif.gz
emd-27736.cif.gz emd_27736_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_27736_half_map_1.map.gz emd_27736_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_27736_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27736
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27736 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27736
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-27736 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_27736.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 512 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_27736.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 512 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー
































 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)