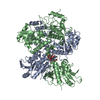
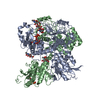
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-26702タイトル Cryo-EM structure of the human Exostosin-1 and Exostosin-2 heterodimer in complex with UDP-GlcA 複合体 : hEXT1/2タンパク質・ペプチド : Exostosin-1タンパク質・ペプチド : Exostosin-2リガンド : URIDINE-5'-DIPHOSPHATE / / / / 機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
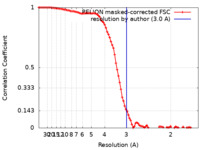
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Homo sapiens (ヒト)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.0 Å Li H 資金援助 Organization Grant number 国 National Institutes of Health/National Cancer Institute (NIH/NCI) CA231466
ジャーナル : Nat Chem Biol / 年 : 2023タイトル : Structural basis for heparan sulfate co-polymerase action by the EXT1-2 complex.著者 : Hua Li / Digantkumar Chapla / Robert A Amos / Annapoorani Ramiah / Kelley W Moremen / Huilin Li / 要旨 : Heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycans are extended (-GlcAβ1,4GlcNAcα1,4-) co-polymers containing decorations of sulfation and epimerization that are linked to cell surface and extracellular matrix ... Heparan sulfate (HS) proteoglycans are extended (-GlcAβ1,4GlcNAcα1,4-) co-polymers containing decorations of sulfation and epimerization that are linked to cell surface and extracellular matrix proteins. In mammals, HS repeat units are extended by an obligate heterocomplex of two exostosin family members, EXT1 and EXT2, where each protein monomer contains distinct GT47 (GT-B fold) and GT64 (GT-A fold) glycosyltransferase domains. In this study, we generated human EXT1-EXT2 (EXT1-2) as a functional heterocomplex and determined its structure in the presence of bound donor and acceptor substrates. Structural data and enzyme activity of catalytic site mutants demonstrate that only two of the four glycosyltransferase domains are major contributors to co-polymer syntheses: the EXT1 GT-B fold β1,4GlcA transferase domain and the EXT2 GT-A fold α1,4GlcNAc transferase domain. The two catalytic sites are over 90 Å apart, indicating that HS is synthesized by a dissociative process that involves a single catalytic site on each monomer. 履歴 登録 2022年4月20日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2022年9月28日 - マップ公開 2022年9月28日 - 更新 2024年11月6日 - 現状 2024年11月6日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報
 マップデータ
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) データ登録者
データ登録者 米国, 1件
米国, 1件  引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Chem Biol / 年: 2023
ジャーナル: Nat Chem Biol / 年: 2023
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_26702.map.gz
emd_26702.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-26702-v30.xml
emd-26702-v30.xml emd-26702.xml
emd-26702.xml EMDBヘッダ
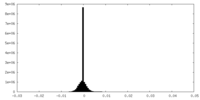
EMDBヘッダ emd_26702_fsc.xml
emd_26702_fsc.xml FSCデータファイル
FSCデータファイル emd_26702.png
emd_26702.png emd-26702.cif.gz
emd-26702.cif.gz emd_26702_half_map_1.map.gz
emd_26702_half_map_1.map.gz emd_26702_half_map_2.map.gz
emd_26702_half_map_2.map.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26702
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26702 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26702
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-26702 emd_26702_validation.pdf.gz
emd_26702_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_26702_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_26702_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_26702_validation.xml.gz
emd_26702_validation.xml.gz emd_26702_validation.cif.gz
emd_26702_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26702
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26702 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26702
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-26702 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_26702.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_26702.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 64 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト) Homo sapiens (ヒト)
Homo sapiens (ヒト)
 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析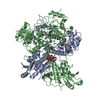
 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー



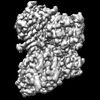









 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)