[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24932: Cryo-EM Structure of dolphin Prestin: Sensor Down II (Expanded II... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24932 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
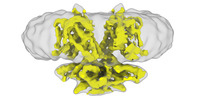
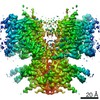
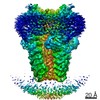
| Title | Cryo-EM Structure of dolphin Prestin: Sensor Down II (Expanded II) state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Outer hair cells / electromotility / mechanotransduction / hearing / deafness / frequency sensation / echolocation / SLC26 / SLC26A5 / MOTOR PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationcochlear outer hair cell electromotile response / secondary active sulfate transmembrane transporter activity / sensory perception of sound / regulation of cell shape / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.7 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bavi N / Clark MD | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2021 Journal: Nature / Year: 2021Title: The conformational cycle of prestin underlies outer-hair cell electromotility. Authors: Navid Bavi / Michael David Clark / Gustavo F Contreras / Rong Shen / Bharat G Reddy / Wieslawa Milewski / Eduardo Perozo /  Abstract: The voltage-dependent motor protein prestin (also known as SLC26A5) is responsible for the electromotive behaviour of outer-hair cells and underlies the cochlear amplifier. Knockout or impairment of ...The voltage-dependent motor protein prestin (also known as SLC26A5) is responsible for the electromotive behaviour of outer-hair cells and underlies the cochlear amplifier. Knockout or impairment of prestin causes severe hearing loss. Despite the key role of prestin in hearing, the mechanism by which mammalian prestin senses voltage and transduces it into cellular-scale movements (electromotility) is poorly understood. Here we determined the structure of dolphin prestin in six distinct states using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. Our structural and functional data suggest that prestin adopts a unique and complex set of states, tunable by the identity of bound anions (Cl or SO). Salicylate, a drug that can cause reversible hearing loss, competes for the anion-binding site of prestin, and inhibits its function by immobilizing prestin in a new conformation. Our data suggest that the bound anion together with its coordinating charged residues and helical dipole act as a dynamic voltage sensor. An analysis of all of the anion-dependent conformations reveals how structural rearrangements in the voltage sensor are coupled to conformational transitions at the protein-membrane interface, suggesting a previously undescribed mechanism of area expansion. Visualization of the electromotility cycle of prestin distinguishes the protein from the closely related SLC26 anion transporters, highlighting the basis for evolutionary specialization of the mammalian cochlear amplifier at a high resolution. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24932.map.gz emd_24932.map.gz | 57.9 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24932-v30.xml emd-24932-v30.xml emd-24932.xml emd-24932.xml | 10.7 KB 10.7 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_24932_fsc.xml emd_24932_fsc.xml | 9.2 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_24932.png emd_24932.png | 61.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24932.cif.gz emd-24932.cif.gz | 5.7 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24932 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24932 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24932 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24932 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7s9cMC  7s8xC  7s9aC  7s9bC  7s9dC  7s9eC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24932.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24932.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 64 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.063 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Dolphin Prestin: Sensor Down II (Expanded II) state
| Entire | Name: Dolphin Prestin: Sensor Down II (Expanded II) state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Dolphin Prestin: Sensor Down II (Expanded II) state
| Supramolecule | Name: Dolphin Prestin: Sensor Down II (Expanded II) state / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Prestin
| Macromolecule | Name: Prestin / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 2 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 80.97375 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Sequence | String: MDHVEETEIL AATQRYYVER PIFSHPVLQE RLHKKDKISE SIGDKLKQAF TCTPKKIRNI IYMFLPITKW LPAYRFKEYV LGDIVSGIS TGVLQLPQGL AFAMLAAVPP VFGLYSSFYP VIMYCFFGTS RHISIGPFAV ISLMIGGVAV RLVPDDIVIP G GVNATNST ...String: MDHVEETEIL AATQRYYVER PIFSHPVLQE RLHKKDKISE SIGDKLKQAF TCTPKKIRNI IYMFLPITKW LPAYRFKEYV LGDIVSGIS TGVLQLPQGL AFAMLAAVPP VFGLYSSFYP VIMYCFFGTS RHISIGPFAV ISLMIGGVAV RLVPDDIVIP G GVNATNST EARDALRVKV AMSVTLLTGI IQFCLGVCRF GFVAIYLTEP LVRGFTTAAA VHVFTSMLKY LFGVKTKRYS GI FSVVYST VAVLQNVKNL NVCSLGVGLM VFGLLLGGKE FNERFKEKLP APIPLEFFAV VMGTGISAGF SLHESYNVDV VGT LPLGLL PPANPDTSLF HLVYVDAIAI AIVGFSVTIS MAKTLANKHG YQVDGNQELI ALGLCNSTGS LFQTFAISCS LSRS LVQEG TGGKTQLAGC LASLMILLVI LATGFLFESL PQAVLSAIVI VNLKGMFMQF SDLPFFWRTS KIELTIWLTT FVSSL FLGL DYGLITAVII ALMTVIYRTQ SPSYIVLGQL PDTDVYIDID AYEEVKEVPG IKIFQINAPI YYANSDLYSS ALKRKT GVN PAFILGARRK AMKKYAKEVG NANMANATVV KVDAEVDAED GTKPEEEEDE IKYPPIVTKS TLPEELQRFM PPGDNVH TI ILDFTQVNFM DSVGVKTLAG IVKEYGDVGI YVYLAGCSAQ VVSDLTQNQF FENPALLDLL FHSIHDAVLG SQVREALA E QEATAAPPQE DSEPNATPEA UniProtKB: Prestin |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | cell |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2.5 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 / Component - Concentration: 125.0 mM / Component - Formula: Na2SO4 / Component - Name: sodium sulfate Details: 125 mM Na2SO4, 5mM Mg(OH)2, 20 Tris-OH, 10-15 mM methanesulfonic acid + 0.02 % GDN |
| Grid | Model: Quantifoil R1.2/1.3 / Support film - Material: CARBON |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Chamber temperature: 295 K / Instrument: FEI VITROBOT MARK IV Details: 4.5 s blot times, blot force 3, and double filter papers on each side of the vitrobot.. |
| Details | Monodisperse peak at around 14 ml using SEC (Superose 6 column) |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 1.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)