[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-2475: Energy barriers and driving forces of tRNA translocation through ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-2475 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
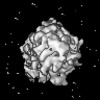
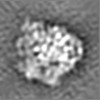
| Title | Energy barriers and driving forces of tRNA translocation through the ribosome | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Substate of E. coli 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal-tRNAfMet complex in intermediate post-translocation state (post3a) | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | Ribosome / translation / translocation / tRNA / molecular dynamics / simulation | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationstringent response / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity ...stringent response / transcription antitermination factor activity, RNA binding / ornithine decarboxylase inhibitor activity / misfolded RNA binding / Group I intron splicing / RNA folding / transcriptional attenuation / endoribonuclease inhibitor activity / positive regulation of ribosome biogenesis / RNA-binding transcription regulator activity / translational termination / negative regulation of cytoplasmic translation / four-way junction DNA binding / DnaA-L2 complex / translation repressor activity / negative regulation of translational initiation / regulation of mRNA stability / negative regulation of DNA-templated DNA replication initiation / mRNA regulatory element binding translation repressor activity / positive regulation of RNA splicing / assembly of large subunit precursor of preribosome / cytosolic ribosome assembly / response to reactive oxygen species / regulation of DNA-templated transcription elongation / ribosome assembly / transcription elongation factor complex / transcription antitermination / DNA endonuclease activity / regulation of cell growth / DNA-templated transcription termination / response to radiation / maintenance of translational fidelity / mRNA 5'-UTR binding / regulation of translation / large ribosomal subunit / ribosome biogenesis / transferase activity / ribosome binding / ribosomal small subunit biogenesis / ribosomal small subunit assembly / ribosomal large subunit assembly / 5S rRNA binding / small ribosomal subunit / small ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic small ribosomal subunit / large ribosomal subunit rRNA binding / cytosolic large ribosomal subunit / cytoplasmic translation / tRNA binding / negative regulation of translation / rRNA binding / structural constituent of ribosome / ribosome / translation / hydrolase activity / response to antibiotic / negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription / mRNA binding / DNA binding / RNA binding / zinc ion binding / membrane / cytoplasm / cytosol Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 20.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bock LV / Blau C / Schroeder GF / Davydov II / Fischer N / Stark H / Rodnina MV / Vaiana AC / Grubmueller H | |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2010 Journal: Nature / Year: 2010Title: Ribosome dynamics and tRNA movement by time-resolved electron cryomicroscopy. Authors: Niels Fischer / Andrey L Konevega / Wolfgang Wintermeyer / Marina V Rodnina / Holger Stark /  Abstract: The translocation step of protein synthesis entails large-scale rearrangements of the ribosome-transfer RNA (tRNA) complex. Here we have followed tRNA movement through the ribosome during ...The translocation step of protein synthesis entails large-scale rearrangements of the ribosome-transfer RNA (tRNA) complex. Here we have followed tRNA movement through the ribosome during translocation by time-resolved single-particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM). Unbiased computational sorting of cryo-EM images yielded 50 distinct three-dimensional reconstructions, showing the tRNAs in classical, hybrid and various novel intermediate states that provide trajectories and kinetic information about tRNA movement through the ribosome. The structures indicate how tRNA movement is coupled with global and local conformational changes of the ribosome, in particular of the head and body of the small ribosomal subunit, and show that dynamic interactions between tRNAs and ribosomal residues confine the path of the tRNAs through the ribosome. The temperature dependence of ribosome dynamics reveals a surprisingly flat energy landscape of conformational variations at physiological temperature. The ribosome functions as a Brownian machine that couples spontaneous conformational changes driven by thermal energy to directed movement. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_2475.map.gz emd_2475.map.gz | 3.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-2475-v30.xml emd-2475-v30.xml emd-2475.xml emd-2475.xml | 11.9 KB 11.9 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  EMD-2475.png EMD-2475.png | 168.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2475 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2475 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2475 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-2475 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  4v78MC  2472C  2473C  2474C  4v6yC  4v6zC  4v70C  4v71C  4v72C  4v73C  4v74C  4v75C  4v76C  4v77C  4v79C  4v7aC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_2475.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 3.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_2475.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 3.3 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Substate of E. coli 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal-tRNAfMet complex in intermediate post-translocation state (post3a) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 3.74 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Substrate of E. coli 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal-tRNAfMet complex in inte...
| Entire | Name: Substrate of E. coli 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal-tRNAfMet complex in intermediate post-translocation state (post3a) |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1000: Substrate of E. coli 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal-tRNAfMet complex in inte...
| Supramolecule | Name: Substrate of E. coli 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal-tRNAfMet complex in intermediate post-translocation state (post3a) type: sample / ID: 1000 / Number unique components: 4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.5 MDa |
-Supramolecule #1: Ribosome
| Supramolecule | Name: Ribosome / type: complex / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: E. coli 70S / Recombinant expression: No / Ribosome-details: ribosome-prokaryote: ALL |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 2.5 MDa |
-Macromolecule #1: fMetVal-tRNAVal
| Macromolecule | Name: fMetVal-tRNAVal / type: rna / ID: 1 / Name.synonym: peptidyl tRNA / Classification: TRANSFER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25 KDa |
-Macromolecule #2: tRNAfMet
| Macromolecule | Name: tRNAfMet / type: rna / ID: 2 / Name.synonym: deacylated tRNA / Classification: TRANSFER / Structure: DOUBLE HELIX / Synthetic?: No |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 25 KDa |
-Macromolecule #3: m022 mRNA
| Macromolecule | Name: m022 mRNA / type: rna / ID: 3 / Name.synonym: mRNA / Details: Coding sequence AUGGUU / Classification: OTHER / Structure: SINGLE STRANDED / Synthetic?: Yes |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.5 Details: 50 mM Tris-HCl, 70 mM NH4Cl, 30 mM KCl, 7 mM MgCl2, 0.6 mM spermine, 0.4 mM spermidine |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 75 % / Chamber temperature: 77 K / Instrument: HOMEMADE PLUNGER Details: Vitrification instrument: Custom-built CEVS. Dew-point temperature (temperature on the grid) adjusted to 18 degrees C Timed resolved state: Samples were vitrified at different time points along the reaction coordinate (1, 2, 5 and 20 minutes after addition of deacylated tRNAfMet to 70S-fMetVal-tRNAVal complexes) Method: Manual blotting for about 2 seconds |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI/PHILIPS CM200FEG |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Average: 77 K |
| Alignment procedure | Legacy - Astigmatism: Objective lens astigmatism was corrected at 200,000 times magnification |
| Date | Jan 2, 2007 |
| Image recording | Category: CCD / Film or detector model: GENERIC TVIPS (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 20 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 160 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Calibrated magnification: 162740 / Illumination mode: SPOT SCAN / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.0 mm / Nominal defocus max: 2.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 0.5 µm / Nominal magnification: 161000 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder: Eucentric / Specimen holder model: GATAN LIQUID NITROGEN |
- Image processing
Image processing
| CTF correction | Details: local |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C1 (asymmetric) / Algorithm: OTHER / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 20.0 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.5 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: IMAGIC, custom, Spider Details: Final maps were calculated from 13 datasets acquired at different time points, computationally sorted into distinct substrates Number images used: 5371 |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller



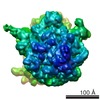
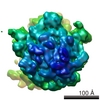
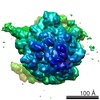
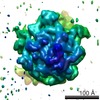
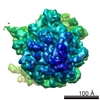
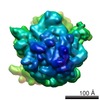






 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)