[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-24415: Structure of the S. cerevisiae P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-24415 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
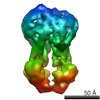
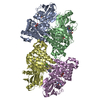
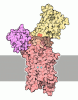
| Title | Structure of the S. cerevisiae P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | Cryo-EM 3D map of S. cerevisiae P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | P4B ATPase lipid flippase / TRANSLOCASE | |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationlysophosphatidylserine flippase activity / trans-Golgi network membrane organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / vacuole organization / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / P-type phospholipid transporter ...lysophosphatidylserine flippase activity / trans-Golgi network membrane organization / Ion transport by P-type ATPases / phosphatidylserine flippase activity / phosphatidylserine floppase activity / ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity / vacuole organization / phosphatidylethanolamine flippase activity / retrograde vesicle-mediated transport, Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum / P-type phospholipid transporter / phospholipid translocation / trans-Golgi network / endocytosis / late endosome / protein transport / endosome / endosome membrane / Golgi membrane / magnesium ion binding / Golgi apparatus / ATP hydrolysis activity / ATP binding / plasma membrane Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 5.64 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Bai L / Jain BK | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021 Journal: Nat Commun / Year: 2021Title: Structural basis of the P4B ATPase lipid flippase activity. Authors: Lin Bai / Bhawik K Jain / Qinglong You / H Diessel Duan / Mehmet Takar / Todd R Graham / Huilin Li /   Abstract: P4 ATPases are lipid flippases that are phylogenetically grouped into P4A, P4B and P4C clades. The P4A ATPases are heterodimers composed of a catalytic α-subunit and accessory β-subunit, and the ...P4 ATPases are lipid flippases that are phylogenetically grouped into P4A, P4B and P4C clades. The P4A ATPases are heterodimers composed of a catalytic α-subunit and accessory β-subunit, and the structures of several heterodimeric flippases have been reported. The S. cerevisiae Neo1 and its orthologs represent the P4B ATPases, which function as monomeric flippases without a β-subunit. It has been unclear whether monomeric flippases retain the architecture and transport mechanism of the dimeric flippases. Here we report the structure of a P4B ATPase, Neo1, in its E1-ATP, E2P-transition, and E2P states. The structure reveals a conserved architecture as well as highly similar functional intermediate states relative to dimeric flippases. Consistently, structure-guided mutagenesis of residues in the proposed substrate translocation path disrupted Neo1's ability to establish membrane asymmetry. These observations indicate that evolutionarily distant P4 ATPases use a structurally conserved mechanism for substrate transport. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_24415.map.gz emd_24415.map.gz | 76.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-24415-v30.xml emd-24415-v30.xml emd-24415.xml emd-24415.xml | 13.8 KB 13.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_24415.png emd_24415.png | 30.3 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-24415.cif.gz emd-24415.cif.gz | 6.4 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24415 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24415 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24415 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-24415 | HTTPS FTP |
-Validation report
| Summary document |  emd_24415_validation.pdf.gz emd_24415_validation.pdf.gz | 437.4 KB | Display |  EMDB validaton report EMDB validaton report |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full document |  emd_24415_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_24415_full_validation.pdf.gz | 437 KB | Display | |
| Data in XML |  emd_24415_validation.xml.gz emd_24415_validation.xml.gz | 6.1 KB | Display | |
| Data in CIF |  emd_24415_validation.cif.gz emd_24415_validation.cif.gz | 7.1 KB | Display | |
| Arichive directory |  https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24415 https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24415 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24415 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-24415 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | 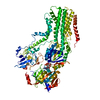 7rd8MC 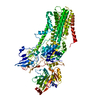 7rd6C 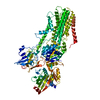 7rd7C C: citing same article ( M: atomic model generated by this map |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_24415.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_24415.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 83.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | Cryo-EM 3D map of S. cerevisiae P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 0.826 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state
| Entire | Name: P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state
| Supramolecule | Name: P4B ATPase lipid flippase in the E1-ATP state / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: #1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase NEO1
| Macromolecule | Name: Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase NEO1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Number of copies: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO / EC number: P-type phospholipid transporter |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 130.363492 KDa |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MPNPPSFKSH KQNLFNSNNN QHANSVDSFD LHLDDSFDAA LDSLQINNNP EPLSKHNTVG DRESFEMRTV DDLDNFSNHS SDSHRKSSN TDTHPLMYDN RLSQDDNFKF TNIASSPPSS SNNIFSKALS YLKVSNTKNW SKFGSPIELS DQHIEREIHP D TTPVYDRN ...String: MPNPPSFKSH KQNLFNSNNN QHANSVDSFD LHLDDSFDAA LDSLQINNNP EPLSKHNTVG DRESFEMRTV DDLDNFSNHS SDSHRKSSN TDTHPLMYDN RLSQDDNFKF TNIASSPPSS SNNIFSKALS YLKVSNTKNW SKFGSPIELS DQHIEREIHP D TTPVYDRN RYVSNELSNA KYNAVTFVPT LLYEQFKFFY NLYFLVVALS QAVPALRIGY LSSYIVPLAF VLTVTMAKEA ID DIQRRRR DRESNNELYH VITRNRSIPS KDLKVGDLIK VHKGDRIPAD LVLLQSSEPS GESFIKTDQL DGETDWKLRV ACP LTQNLS ENDLINRISI TASAPEKSIH KFLGKVTYKD STSNPLSVDN TLWANTVLAS SGFCIACVVY TGRDTRQAMN TTTA KVKTG LLELEINSIS KILCACVFAL SILLVAFAGF HNDDWYIDIL RYLILFSTII PVSLRVNLDL AKSVYAHQIE HDKTI PETI VRTSTIPEDL GRIEYLLSDK TGTLTQNDMQ LKKIHLGTVS YTSETLDIVS DYVQSLVSSK NDSLNNSKVA LSTTRK DMS FRVRDMILTL AICHNVTPTF EDDELTYQAA SPDEIAIVKF TESVGLSLFK RDRHSISLLH EHSGKTLNYE ILQVFPF NS DSKRMGIIVR DEQLDEYWFM QKGADTVMSK IVESNDWLEE ETGNMAREGL RTLVIGRKKL NKKIYEQFQK EYNDASLS M LNRDQQMSQV ITKYLEHDLE LLGLTGVEDK LQKDVKSSIE LLRNAGIKIW MLTGDKVETA RCVSISAKLI SRGQYVHTI TKVTRPEGAF NQLEYLKINR NACLLIDGES LGMFLKHYEQ EFFDVVVHLP TVIACRCTPQ QKADVALVIR KMTGKRVCCI GDGGNDVSM IQCADVGVGI VGKEGKQASL AADFSITQFC HLTELLLWHG RNSYKRSAKL AQFVMHRGLI IAICQAVYSI C SLFEPIAL YQGWLMVGYA TCYTMAPVFS LTLDHDIEES LTKIYPELYK ELTEGKSLSY KTFFVWVLLS LFQGSVIQLF SQ AFTSLLD TDFTRMVAIS FTALVVNELI MVALEIYTWN KTMLVTEIAT LLFYIVSVPF LGDYFDLGYM TTVNYYAGLL VIL LISIFP VWTAKAIYRR LHPPSYAKVQ EFATP UniProtKB: Phospholipid-transporting ATPase NEO1 |
-Macromolecule #2: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID ADENYLATE ESTER
| Macromolecule | Name: PHOSPHOMETHYLPHOSPHONIC ACID ADENYLATE ESTER / type: ligand / ID: 2 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: ACP |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 505.208 Da |
| Chemical component information | 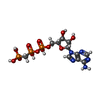 ChemComp-ACP: |
-Macromolecule #3: MAGNESIUM ION
| Macromolecule | Name: MAGNESIUM ION / type: ligand / ID: 3 / Number of copies: 1 / Formula: MG |
|---|---|
| Molecular weight | Theoretical: 24.305 Da |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 60.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: DIFFRACTION |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















