[English] 日本語
 Yorodumi
Yorodumi- EMDB-23871: Paired helical tau filament extracted from PrP-CAA Patient brain ... -
+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23871 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | Paired helical tau filament extracted from PrP-CAA Patient brain tissue | tau filament | PHF Tau | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | 3 Angstrom resolution of PHF Tau from PrP-CAA | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Function / homology |  Function and homology information Function and homology informationplus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / tubulin complex / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / generation of neurons ...plus-end-directed organelle transport along microtubule / histone-dependent DNA binding / negative regulation of protein localization to mitochondrion / neurofibrillary tangle / microtubule lateral binding / axonal transport / tubulin complex / positive regulation of protein localization to synapse / phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate binding / generation of neurons / rRNA metabolic process / axonal transport of mitochondrion / regulation of mitochondrial fission / axon development / regulation of microtubule-based movement / regulation of chromosome organization / central nervous system neuron development / intracellular distribution of mitochondria / minor groove of adenine-thymine-rich DNA binding / lipoprotein particle binding / microtubule polymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial membrane potential / regulation of microtubule polymerization / dynactin binding / apolipoprotein binding / main axon / protein polymerization / axolemma / Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal proteins / regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization / negative regulation of mitochondrial fission / glial cell projection / neurofibrillary tangle assembly / positive regulation of axon extension / regulation of cellular response to heat / Activation of AMPK downstream of NMDARs / positive regulation of superoxide anion generation / positive regulation of protein localization / cellular response to brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulus / supramolecular fiber organization / regulation of long-term synaptic depression / positive regulation of microtubule polymerization / cytoplasmic microtubule organization / synapse assembly / regulation of calcium-mediated signaling / somatodendritic compartment / axon cytoplasm / astrocyte activation / phosphatidylinositol binding / nuclear periphery / enzyme inhibitor activity / stress granule assembly / protein phosphatase 2A binding / regulation of microtubule cytoskeleton organization / cellular response to reactive oxygen species / microglial cell activation / Hsp90 protein binding / cellular response to nerve growth factor stimulus / protein homooligomerization / synapse organization / PKR-mediated signaling / regulation of synaptic plasticity / regulation of autophagy / SH3 domain binding / response to lead ion / microtubule cytoskeleton organization / memory / neuron projection development / cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein granule / cell-cell signaling / single-stranded DNA binding / protein-folding chaperone binding / cellular response to heat / microtubule cytoskeleton / actin binding / growth cone / cell body / double-stranded DNA binding / microtubule binding / protein-macromolecule adaptor activity / sequence-specific DNA binding / amyloid fibril formation / dendritic spine / microtubule / learning or memory / neuron projection / membrane raft / negative regulation of gene expression / axon / neuronal cell body / DNA damage response / dendrite / protein kinase binding / enzyme binding / mitochondrion / DNA binding / RNA binding / extracellular region / identical protein binding / nucleus Similarity search - Function | |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  Human (human) Human (human) | |||||||||
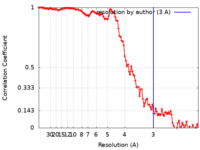
| Method | helical reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.0 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Hoq M | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Acta Neuropathol / Year: 2021 Journal: Acta Neuropathol / Year: 2021Title: Structure of Tau filaments in Prion protein amyloidoses. Authors: Grace I Hallinan / Md Rejaul Hoq / Manali Ghosh / Frank S Vago / Anllely Fernandez / Holly J Garringer / Ruben Vidal / Wen Jiang / Bernardino Ghetti /  Abstract: In human neurodegenerative diseases associated with the intracellular aggregation of Tau protein, the ordered cores of Tau filaments adopt distinct folds. Here, we analyze Tau filaments isolated from ...In human neurodegenerative diseases associated with the intracellular aggregation of Tau protein, the ordered cores of Tau filaments adopt distinct folds. Here, we analyze Tau filaments isolated from the brain of individuals affected by Prion-Protein cerebral amyloid angiopathy (PrP-CAA) with a nonsense mutation in the PRNP gene that leads to early termination of translation of PrP (Q160Ter or Q160X), and Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker (GSS) disease, with a missense mutation in the PRNP gene that leads to an amino acid substitution at residue 198 (F198S) of PrP. The clinical and neuropathologic phenotypes associated with these two mutations in PRNP are different; however, the neuropathologic analyses of these two genetic variants have consistently shown the presence of numerous neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) made of filamentous Tau aggregates in neurons. We report that Tau filaments in PrP-CAA (Q160X) and GSS (F198S) are composed of 3-repeat and 4-repeat Tau isoforms, having a striking similarity to NFTs in Alzheimer disease (AD). In PrP-CAA (Q160X), Tau filaments are made of both paired helical filaments (PHFs) and straight filaments (SFs), while in GSS (F198S), only PHFs were found. Mass spectrometry analyses of Tau filaments extracted from PrP-CAA (Q160X) and GSS (F198S) brains show the presence of post-translational modifications that are comparable to those seen in Tau aggregates from AD. Cryo-EM analysis reveals that the atomic models of the Tau filaments obtained from PrP-CAA (Q160X) and GSS (F198S) are identical to those of the Tau filaments from AD, and are therefore distinct from those of Pick disease, chronic traumatic encephalopathy, and corticobasal degeneration. Our data support the hypothesis that in the presence of extracellular amyloid deposits and regardless of the primary amino acid sequence of the amyloid protein, similar molecular mechanisms are at play in the formation of identical Tau filaments. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23871.map.gz emd_23871.map.gz | 26.2 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23871-v30.xml emd-23871-v30.xml emd-23871.xml emd-23871.xml | 10.2 KB 10.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_23871_fsc.xml emd_23871_fsc.xml | 13.7 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_23871.png emd_23871.png | 102.8 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23871 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23871 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23871 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23871 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  7mkfMC  7mkgC  7mkhC M: atomic model generated by this map C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23871.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23871.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 103 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | 3 Angstrom resolution of PHF Tau from PrP-CAA | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.078 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Paired helical filament (PHF) from PrP-CAA
| Entire | Name: Paired helical filament (PHF) from PrP-CAA |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Paired helical filament (PHF) from PrP-CAA
| Supramolecule | Name: Paired helical filament (PHF) from PrP-CAA / type: organelle_or_cellular_component / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all Details: PHF tau in PrP-CAA, caused by the Q160X truncating mutation in PRNP |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Molecular weight | Experimental: 55 kDa/nm |
-Macromolecule #1: PHF Tau from PrP-CAA Patient
| Macromolecule | Name: PHF Tau from PrP-CAA Patient / type: other / ID: 1 / Classification: other |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Human (human) Human (human) |
| Sequence | String: QX |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | helical reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | filament |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 1 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Sugar embedding | Material: affinity tag |
| Grid | Model: PELCO Ultrathin Carbon with Lacey Carbon / Material: COPPER / Mesh: 400 |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE / Chamber humidity: 100 % / Instrument: GATAN CRYOPLUNGE 3 |
| Details | Filament extracted from frontal cortex of PrP-CAA patient brain |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | TFS KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 (6k x 4k) / Number real images: 2004 / Average electron dose: 1.067 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Cs: 2.7 mm |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Details | Each model was refined using Rosetta |
|---|---|
| Refinement | Space: RECIPROCAL / Overall B value: 24 / Target criteria: Fourier shell correlation |
| Output model |  PDB-7mkf: |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller

















 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)