+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-23537 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | DARPin 21.8.HSA-C9.v2 with HSA complex | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species | synthetic construct (others) | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 4.53 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Park YJ / Ivan V / Baker D / Veesler D | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 1 items United States, 1 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021 Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A / Year: 2021Title: Generation of ordered protein assemblies using rigid three-body fusion. Authors: Ivan Vulovic / Qing Yao / Young-Jun Park / Alexis Courbet / Andrew Norris / Florian Busch / Aniruddha Sahasrabuddhe / Hannes Merten / Danny D Sahtoe / George Ueda / Jorge A Fallas / Sara J ...Authors: Ivan Vulovic / Qing Yao / Young-Jun Park / Alexis Courbet / Andrew Norris / Florian Busch / Aniruddha Sahasrabuddhe / Hannes Merten / Danny D Sahtoe / George Ueda / Jorge A Fallas / Sara J Weaver / Yang Hsia / Robert A Langan / Andreas Plückthun / Vicki H Wysocki / David Veesler / Grant J Jensen / David Baker /   Abstract: Protein nanomaterial design is an emerging discipline with applications in medicine and beyond. A long-standing design approach uses genetic fusion to join protein homo-oligomer subunits via α- ...Protein nanomaterial design is an emerging discipline with applications in medicine and beyond. A long-standing design approach uses genetic fusion to join protein homo-oligomer subunits via α-helical linkers to form more complex symmetric assemblies, but this method is hampered by linker flexibility and a dearth of geometric solutions. Here, we describe a general computational method for rigidly fusing homo-oligomer and spacer building blocks to generate user-defined architectures that generates far more geometric solutions than previous approaches. The fusion junctions are then optimized using Rosetta to minimize flexibility. We apply this method to design and test 92 dihedral symmetric protein assemblies using a set of designed homodimers and repeat protein building blocks. Experimental validation by native mass spectrometry, small-angle X-ray scattering, and negative-stain single-particle electron microscopy confirms the assembly states for 11 designs. Most of these assemblies are constructed from designed ankyrin repeat proteins (DARPins), held in place on one end by α-helical fusion and on the other by a designed homodimer interface, and we explored their use for cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure determination by incorporating DARPin variants selected to bind targets of interest. Although the target resolution was limited by preferred orientation effects and small scaffold size, we found that the dual anchoring strategy reduced the flexibility of the target-DARPIN complex with respect to the overall assembly, suggesting that multipoint anchoring of binding domains could contribute to cryo-EM structure determination of small proteins. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
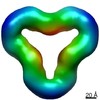
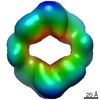
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_23537.map.gz emd_23537.map.gz | 230.1 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-23537-v30.xml emd-23537-v30.xml emd-23537.xml emd-23537.xml | 15.8 KB 15.8 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_23537.png emd_23537.png | 63.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_23537_additional_1.map.gz emd_23537_additional_1.map.gz emd_23537_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23537_half_map_1.map.gz emd_23537_half_map_2.map.gz emd_23537_half_map_2.map.gz | 121.4 MB 226.5 MB 226.5 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23537 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23537 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23537 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-23537 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data | C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|---|
| Related items in Molecule of the Month |
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_23537.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_23537.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.05 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
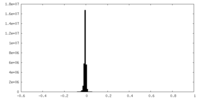
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
-Additional map: #1
| File | emd_23537_additional_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
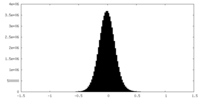
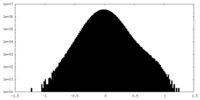
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_23537_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
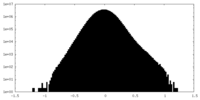
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_23537_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : DARPin D2-21.8.HSA-C9.v2
| Entire | Name: DARPin D2-21.8.HSA-C9.v2 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: DARPin D2-21.8.HSA-C9.v2
| Supramolecule | Name: DARPin D2-21.8.HSA-C9.v2 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: DARPin D2-21.8.HSA-C9.v2
| Macromolecule | Name: DARPin D2-21.8.HSA-C9.v2 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism: synthetic construct (others) |
| Sequence | String: MHHHHHHSEK ARIAVENLEA ALRLNRAAAE MQKSAIKIMR DNSSDEKAFR YLLLTTKVLK MSVELLRASL ELAEKALREE GSDDSAEKVR KEAEEILKES TEILKRAELE TLKAAVRVAA EAAARNATDE EERKRIEEEL KKAEERANRS TNEEEIKKIL EEALARFLLE ...String: MHHHHHHSEK ARIAVENLEA ALRLNRAAAE MQKSAIKIMR DNSSDEKAFR YLLLTTKVLK MSVELLRASL ELAEKALREE GSDDSAEKVR KEAEEILKES TEILKRAELE TLKAAVRVAA EAAARNATDE EERKRIEEEL KKAEERANRS TNEEEIKKIL EEALARFLLE AAWKGAKEAV KLALEAGADV NAADYFGHTP LHLAARNGHA KVVLLLLEQG ADPNADDFAG STPLHLAARA GHAVVVALLL MHGADPNAVD SNGFTPLHLA AQKGHEEVVI LLLAMGADPN AQDKFGKTPF DLAIDNGNEE VVKVLEDH |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 7 |
|---|---|
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K2 SUMMIT (4k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 70.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
- Image processing
Image processing
| Startup model | Type of model: OTHER / Details: cryoSPARC ab initio |
|---|---|
| Final reconstruction | Applied symmetry - Point group: C2 (2 fold cyclic) / Resolution.type: BY AUTHOR / Resolution: 4.53 Å / Resolution method: FSC 0.143 CUT-OFF / Software - Name: cryoSPARC / Number images used: 129230 |
| Initial angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
| Final angle assignment | Type: PROJECTION MATCHING |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller









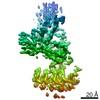
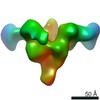




 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)