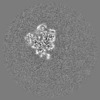
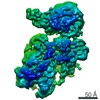
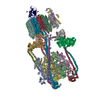
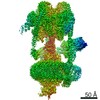
登録情報 データベース : EMDB / ID : EMD-22121タイトル Cryo-EM structure of V-ATPase from bovine brain, state 1 Structure of V-ATPase from bovine brain, state 1 複合体 : Cryo-EM structure of V-ATPase complex from bovine brain, state 1リガンド : x 5種機能・相同性 分子機能 ドメイン・相同性 構成要素
/ / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / / 生物種 Bos taurus (ウシ)手法 / / 解像度 : 3.37 Å Wang R / Li X ジャーナル : Nat Commun / 年 : 2020タイトル : Cryo-EM structures of intact V-ATPase from bovine brain.著者 : Rong Wang / Tao Long / Abdirahman Hassan / Jin Wang / Yingyuan Sun / Xiao-Song Xie / Xiaochun Li / 要旨 : The vacuolar-type H-ATPases (V-ATPase) hydrolyze ATP to pump protons across the plasma or intracellular membrane, secreting acids to the lumen or acidifying intracellular compartments. It has been ... The vacuolar-type H-ATPases (V-ATPase) hydrolyze ATP to pump protons across the plasma or intracellular membrane, secreting acids to the lumen or acidifying intracellular compartments. It has been implicated in tumor metastasis, renal tubular acidosis, and osteoporosis. Here, we report two cryo-EM structures of the intact V-ATPase from bovine brain with all the subunits including the subunit H, which is essential for ATPase activity. Two type-I transmembrane proteins, Ac45 and (pro)renin receptor, along with subunit c", constitute the core of the c-ring. Three different conformations of A/B heterodimers suggest a mechanism for ATP hydrolysis that triggers a rotation of subunits DF, inducing spinning of subunit d with respect to the entire c-ring. Moreover, many lipid molecules have been observed in the Vo domain to mediate the interactions between subunit c, c", (pro)renin receptor, and Ac45. These two structures reveal unique features of mammalian V-ATPase and suggest a mechanism of V1-Vo torque transmission. 履歴 登録 2020年6月7日 - ヘッダ(付随情報) 公開 2020年8月19日 - マップ公開 2020年8月19日 - 更新 2024年10月23日 - 現状 2024年10月23日 処理サイト : RCSB / 状態 : 公開
すべて表示 表示を減らす
 データを開く
データを開く 基本情報
基本情報 マップデータ
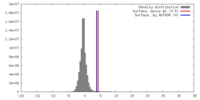
マップデータ 試料
試料 キーワード
キーワード 機能・相同性情報
機能・相同性情報
 データ登録者
データ登録者 引用
引用 ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2020
ジャーナル: Nat Commun / 年: 2020
 構造の表示
構造の表示 ムービービューア
ムービービューア SurfView
SurfView Molmil
Molmil Jmol/JSmol
Jmol/JSmol ダウンロードとリンク
ダウンロードとリンク emd_22121.map.gz
emd_22121.map.gz EMDBマップデータ形式
EMDBマップデータ形式 emd-22121-v30.xml
emd-22121-v30.xml emd-22121.xml
emd-22121.xml EMDBヘッダ
EMDBヘッダ emd_22121.png
emd_22121.png emd-22121.cif.gz
emd-22121.cif.gz http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22121
http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22121 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22121
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-22121 emd_22121_validation.pdf.gz
emd_22121_validation.pdf.gz EMDB検証レポート
EMDB検証レポート emd_22121_full_validation.pdf.gz
emd_22121_full_validation.pdf.gz emd_22121_validation.xml.gz
emd_22121_validation.xml.gz emd_22121_validation.cif.gz
emd_22121_validation.cif.gz https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22121
https://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22121 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22121
ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/validation_reports/EMD-22121 リンク
リンク EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /
EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource
EMDataResource マップ
マップ ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_22121.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 506 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES)
ダウンロード / ファイル: emd_22121.map.gz / 形式: CCP4 / 大きさ: 506 MB / タイプ: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) 試料の構成要素
試料の構成要素 解析
解析 試料調製
試料調製 電子顕微鏡法
電子顕微鏡法 FIELD EMISSION GUN
FIELD EMISSION GUN
 画像解析
画像解析 ムービー
ムービー コントローラー
コントローラー













 X (Sec.)
X (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) Z (Col.)
Z (Col.)