+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | Database: EMDB / ID: EMD-20948 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title | GPCR-Beta arrestin structure in lipid bilayer | |||||||||
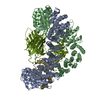
 Map data Map data | GPCR-Beta arrestin in lipid bilayer | |||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
| Biological species |  Homo sapiens (human) / Homo sapiens (human) /  | |||||||||
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 3.6 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Staus DP / Hu H | |||||||||
| Funding support |  United States, 2 items United States, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nature / Year: 2020 Journal: Nature / Year: 2020Title: Structure of the M2 muscarinic receptor-β-arrestin complex in a lipid nanodisc. Authors: Dean P Staus / Hongli Hu / Michael J Robertson / Alissa L W Kleinhenz / Laura M Wingler / William D Capel / Naomi R Latorraca / Robert J Lefkowitz / Georgios Skiniotis /   Abstract: After activation by an agonist, G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) recruit β-arrestin, which desensitizes heterotrimeric G-protein signalling and promotes receptor endocytosis. Additionally, β- ...After activation by an agonist, G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) recruit β-arrestin, which desensitizes heterotrimeric G-protein signalling and promotes receptor endocytosis. Additionally, β-arrestin directly regulates many cell signalling pathways that can induce cellular responses distinct from that of G proteins. In contrast to G proteins, for which there are many high-resolution structures in complex with GPCRs, the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction of β-arrestin with GPCRs are much less understood. Here we present a cryo-electron microscopy structure of β-arrestin 1 (βarr1) in complex with M2 muscarinic receptor (M2R) reconstituted in lipid nanodiscs. The M2R-βarr1 complex displays a multimodal network of flexible interactions, including binding of the N domain of βarr1 to phosphorylated receptor residues and insertion of the finger loop of βarr1 into the M2R seven-transmembrane bundle, which adopts a conformation similar to that in the M2R-heterotrimeric G protein complex. Moreover, the cryo-electron microscopy map reveals that the C-edge of βarr1 engages the lipid bilayer. Through atomistic simulations and biophysical, biochemical and cellular assays, we show that the C-edge is critical for stable complex formation, βarr1 recruitment, receptor internalization, and desensitization of G-protein activation. Taken together, these data suggest that the cooperative interactions of β-arrestin with both the receptor and the phospholipid bilayer contribute to its functional versatility. | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Movie |
 Movie viewer Movie viewer |
|---|---|
| Structure viewer | EM map:  SurfView SurfView Molmil Molmil Jmol/JSmol Jmol/JSmol |
| Supplemental images |
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_20948.map.gz emd_20948.map.gz | 49 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-20948-v30.xml emd-20948-v30.xml emd-20948.xml emd-20948.xml | 12.2 KB 12.2 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| Images |  emd_20948.png emd_20948.png | 62.3 KB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20948 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20948 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20948 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-20948 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_20948.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_20948.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 52.7 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annotation | GPCR-Beta arrestin in lipid bilayer | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.06 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
CCP4 map header:
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
-Supplemental data
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Phosphorylated human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in comp...
| Entire | Name: Phosphorylated human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in complex with rat beta-arrestin1, stabilized by an antibody fragment (Fab30). |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Phosphorylated human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in comp...
| Supramolecule | Name: Phosphorylated human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 in complex with rat beta-arrestin1, stabilized by an antibody fragment (Fab30). type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 |
|---|
-Supramolecule #2: Phosphorylated human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2
| Supramolecule | Name: Phosphorylated human muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M2 type: complex / ID: 2 / Parent: 1 Details: Phosphorylated M2R was generated by ligating a synthetic phosphopeptide derived from the vasopressin-2-receptor (V2Rpp) using the enzyme sortase. |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
-Supramolecule #3: Cysteine-free rat beta-arrestin 1 truncated at amino acid 393
| Supramolecule | Name: Cysteine-free rat beta-arrestin 1 truncated at amino acid 393 type: complex / ID: 3 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Supramolecule #4: Antibody Fragment (Fab30)
| Supramolecule | Name: Antibody Fragment (Fab30) / type: complex / ID: 4 / Parent: 1 |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  Homo sapiens (human) Homo sapiens (human) |
| Recombinant expression | Organism:  |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Concentration | 2 mg/mL |
|---|---|
| Buffer | pH: 7.4 |
| Grid | Details: unspecified |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TITAN KRIOS |
|---|---|
| Image recording | #0 - Image recording ID: 1 / #0 - Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / #0 - Detector mode: COUNTING / #0 - Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 / #1 - Image recording ID: 2 / #1 - Film or detector model: GATAN K2 QUANTUM (4k x 4k) / #1 - Average electron dose: 50.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 300 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | C2 aperture diameter: 50.0 µm / Calibrated magnification: 47169 / Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 2.2 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.2 µm / Nominal magnification: 47169 |
| Sample stage | Specimen holder model: FEI TITAN KRIOS AUTOGRID HOLDER / Cooling holder cryogen: NITROGEN |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Titan Krios / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
+ Image processing
Image processing
-Atomic model buiding 1
| Refinement | Space: REAL / Protocol: FLEXIBLE FIT |
|---|
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller











 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)





















