+ Open data
Open data
- Basic information
Basic information
| Entry | 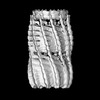 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
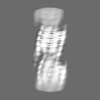
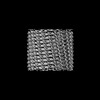
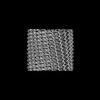
| Title | C11 Vipp1 stacked rings in the presence of EPL | |||||||||
 Map data Map data | ||||||||||
 Sample Sample |
| |||||||||
 Keywords Keywords | membrane tubulation / membrane remodeling / LIPID BINDING PROTEIN | |||||||||
| Function / homology | PspA/IM30 / PspA/IM30 family / plasma membrane / Membrane-associated protein Vipp1 Function and homology information Function and homology information | |||||||||
| Biological species |  | |||||||||
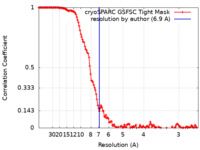
| Method | single particle reconstruction / cryo EM / Resolution: 6.9 Å | |||||||||
 Authors Authors | Junglas B / Sachse B | |||||||||
| Funding support |  Germany, 2 items Germany, 2 items
| |||||||||
 Citation Citation |  Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025 Journal: Nat Struct Mol Biol / Year: 2025Title: Structural basis for Vipp1 membrane binding: from loose coats and carpets to ring and rod assemblies. Authors: Benedikt Junglas / David Kartte / Mirka Kutzner / Nadja Hellmann / Ilona Ritter / Dirk Schneider / Carsten Sachse /  Abstract: Vesicle-inducing protein in plastids 1 (Vipp1) is critical for thylakoid membrane biogenesis and maintenance. Although Vipp1 has recently been identified as a member of the endosomal sorting ...Vesicle-inducing protein in plastids 1 (Vipp1) is critical for thylakoid membrane biogenesis and maintenance. Although Vipp1 has recently been identified as a member of the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport III superfamily, it is still unknown how Vipp1 remodels membranes. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of Synechocystis Vipp1 interacting with membranes: seven structures of helical and stacked-ring assemblies at 5-7-Å resolution engulfing membranes and three carpet structures covering lipid vesicles at ~20-Å resolution using subtomogram averaging. By analyzing ten structures of N-terminally truncated Vipp1, we show that helix α0 is essential for membrane tubulation and forms the membrane-anchoring domain of Vipp1. Lastly, using a conformation-restrained Vipp1 mutant, we reduced the structural plasticity of Vipp1 and determined two structures of Vipp1 at 3.0-Å resolution, resolving the molecular details of membrane-anchoring and intersubunit contacts of helix α0. Our data reveal membrane curvature-dependent structural transitions from carpets to rings and rods, some of which are capable of inducing and/or stabilizing high local membrane curvature triggering membrane fusion. #1:  Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2024 Journal: Biorxiv / Year: 2024Title: Structural basis for Vipp1 membrane binding: From loose coats and carpets to ring and rod assemblies Authors: Junglas B / Kartte D / Kutzner M / Hellmann N / Ritter I / Schneider D / Sachse C | |||||||||
| History |
|
- Structure visualization
Structure visualization
| Supplemental images |
|---|
- Downloads & links
Downloads & links
-EMDB archive
| Map data |  emd_18422.map.gz emd_18422.map.gz | 30 MB |  EMDB map data format EMDB map data format | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Header (meta data) |  emd-18422-v30.xml emd-18422-v30.xml emd-18422.xml emd-18422.xml | 14 KB 14 KB | Display Display |  EMDB header EMDB header |
| FSC (resolution estimation) |  emd_18422_fsc.xml emd_18422_fsc.xml | 13.3 KB | Display |  FSC data file FSC data file |
| Images |  emd_18422.png emd_18422.png | 35.4 KB | ||
| Filedesc metadata |  emd-18422.cif.gz emd-18422.cif.gz | 4.7 KB | ||
| Others |  emd_18422_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18422_half_map_1.map.gz emd_18422_half_map_2.map.gz emd_18422_half_map_2.map.gz | 226.2 MB 226.2 MB | ||
| Archive directory |  http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18422 http://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18422 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18422 ftp://ftp.pdbj.org/pub/emdb/structures/EMD-18422 | HTTPS FTP |
-Related structure data
| Related structure data |  8qfvC  8qhvC  8qhwC  8qhxC  8qhyC  8qhzC  8qi0C  8qi1C  8qi2C  8qi3C  8qi4C  8qi5C  8qi6C  9eomC  9eonC  9eooC  9eopC C: citing same article ( |
|---|---|
| Similar structure data | Similarity search - Function & homology  F&H Search F&H Search |
- Links
Links
| EMDB pages |  EMDB (EBI/PDBe) / EMDB (EBI/PDBe) /  EMDataResource EMDataResource |
|---|
- Map
Map
| File |  Download / File: emd_18422.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) Download / File: emd_18422.map.gz / Format: CCP4 / Size: 244.1 MB / Type: IMAGE STORED AS FLOATING POINT NUMBER (4 BYTES) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & slices | Image control
Images are generated by Spider. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Voxel size | X=Y=Z: 1.3 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
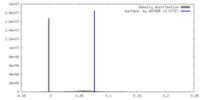
| Density |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symmetry | Space group: 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Details | EMDB XML:
|
-Supplemental data
-Half map: #1
| File | emd_18422_half_map_1.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
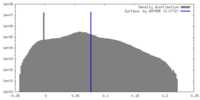
| Density Histograms |
-Half map: #2
| File | emd_18422_half_map_2.map | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Projections & Slices |
| ||||||||||||
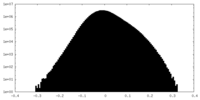
| Density Histograms |
- Sample components
Sample components
-Entire : Vipp1
| Entire | Name: Vipp1 |
|---|---|
| Components |
|
-Supramolecule #1: Vipp1
| Supramolecule | Name: Vipp1 / type: complex / ID: 1 / Parent: 0 / Macromolecule list: all |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
-Macromolecule #1: Vipp1
| Macromolecule | Name: Vipp1 / type: protein_or_peptide / ID: 1 / Details: Vipp1 in the presence of EPL membrane / Enantiomer: LEVO |
|---|---|
| Source (natural) | Organism:  |
| Sequence | String: MGLFDRLGRV VRANLNDLVS KAEDPEKVLE QAVIDMQEDL VQLRQAVART IAEEKRTEQR LNQDTQEAKK WEDRAKLALT NGEENLAREA LARKKSLTDT AAAYQTQLAQ QRTMSENLRR NLAALEAKIS EAKTKKNMLQ ARAKAAKANA ELQQTLGGLG TSSATSAFER ...String: MGLFDRLGRV VRANLNDLVS KAEDPEKVLE QAVIDMQEDL VQLRQAVART IAEEKRTEQR LNQDTQEAKK WEDRAKLALT NGEENLAREA LARKKSLTDT AAAYQTQLAQ QRTMSENLRR NLAALEAKIS EAKTKKNMLQ ARAKAAKANA ELQQTLGGLG TSSATSAFER MENKVLDMEA TSQAAGELAG FGIENQFAQL EASSGVEDEL AALKASMAGG ALPGTSAATP QLEAAPVDSS VPANNASQDD AVIDQELDDL RRRLNNLAAL EVLFQGP UniProtKB: Membrane-associated protein Vipp1 |
-Experimental details
-Structure determination
| Method | cryo EM |
|---|---|
 Processing Processing | single particle reconstruction |
| Aggregation state | particle |
- Sample preparation
Sample preparation
| Buffer | pH: 8 |
|---|---|
| Sugar embedding | Material: vitreous ice |
| Vitrification | Cryogen name: ETHANE |
- Electron microscopy
Electron microscopy
| Microscope | FEI TALOS ARCTICA |
|---|---|
| Image recording | Film or detector model: GATAN K3 BIOQUANTUM (6k x 4k) / Average electron dose: 48.0 e/Å2 |
| Electron beam | Acceleration voltage: 200 kV / Electron source:  FIELD EMISSION GUN FIELD EMISSION GUN |
| Electron optics | Illumination mode: FLOOD BEAM / Imaging mode: BRIGHT FIELD / Nominal defocus max: 3.0 µm / Nominal defocus min: 1.0 µm |
| Experimental equipment |  Model: Talos Arctica / Image courtesy: FEI Company |
 Movie
Movie Controller
Controller










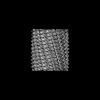
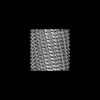
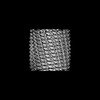

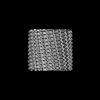












 Z (Sec.)
Z (Sec.) Y (Row.)
Y (Row.) X (Col.)
X (Col.)